A simple API for working with University of California, Irvine (UCI) Machine Learning (ML) repository
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- About Page of the repository
- Navigating the portal can be challenging and time consuming
- Introducing UCIML Python code base
- Required packages/Dependencies
- How to run it
- Features and functions currently supported
- Example (search and download a particular dataset)
- Example (search for datasets with a particular keyword)
- If want to bypass the simple API and play with the low-level functions
Introduction
UCI machine learning dataset repository is something of a legend in the field of machine learning pedagogy. It is a 'go-to-shop' for beginners and advanced learners alike. This codebase is an attempt to present a simple and intuitive API for UCI ML portal, using which users can easily look up a dataset description, search for a particular dataset they are interested, and even download datasets categorized by size or machine learning task.
About Page of the repository
The UCI Machine Learning Repository is a collection of databases, domain theories, and data generators that are used by the machine learning community for the empirical analysis of machine learning algorithms. The archive was created as an ftp archive in 1987 by David Aha and fellow graduate students at UC Irvine. Since that time, it has been widely used by students, educators, and researchers all over the world as a primary source of machine learning data sets. As an indication of the impact of the archive, it has been cited over 1000 times, making it one of the top 100 most cited "papers" in all of computer science. The current version of the web site was designed in 2007 by Arthur Asuncion and David Newman, and this project is in collaboration with Rexa.info at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. Funding support from the National Science Foundation is gratefully acknowledged.
But navigating the portal can be challenging and time consuming...
UCI ML portal is a wonderful gift to ML practioners. That said, navigating the portal can be bit frustrating and time consuming as there is no simple intuitive API or download link for the dataset you are interested in. You have to hop around multiple pages to go to the raw dataset page that you are looking for. Also, if you are interested in particular type of ML task (regression or classification for example) and want to download all datasets corresponding to that task, there is no simple command to accomplish such.
Introducing UCIML Python code base
This is a MIT-licensed Open-source Python 3.6 codebase which offers functions and methods to allow an user play with the UCI ML datasets in an interactive manner. Download/clone/fork the codebase from my Github page here.
Required packages/Dependencies
Only three widely used Python packages are required to run this code. For easy installation of these supporting packages, setup.bash and setup.bat files are included in my repo. Just execute them in your Linux/Windows shell and you are ready!
How to run it?
Make sure you are connected to Internet:-) Then, just download/clone the Gitgub repo, make sure to have the supporting packages installed.
git clone https://github.com/tirthajyoti/UCI-ML-API.git {your_local_directory}
Then go to the your_local_directory where you have cloned the Git and run the following command at your terminal.
python Main.py
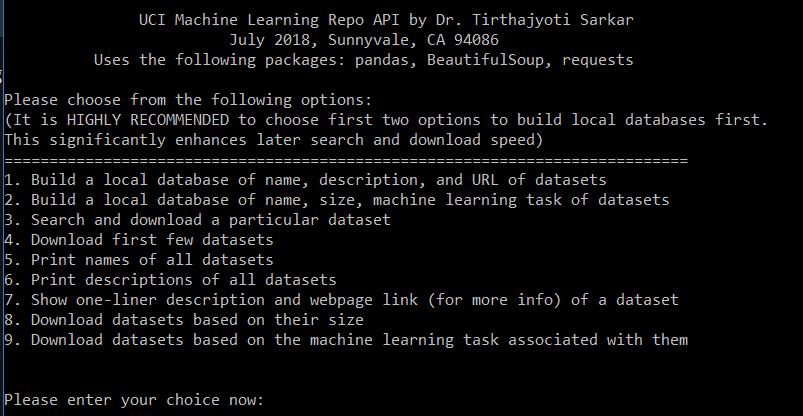
A menu will open up allowing you to perform various tasks. Here is a screenshot of the menu,
Features and functions currently supported
Following features are currently implemented...
- Building a local database of name, description, and URL of datasets by crawling the entire portal
- Building a local database of name, size, machine learning task of datasets by crawling the entire portal
- Search and download a particular dataset
- Download first few datasets
- Print names of all datasets
- Print short descriptions of all datasets
- Search for one-liner description and webpage link (for more info) of a dataset
- Download datasets based on their size
- Download datasets based on the machine learning task associated with them
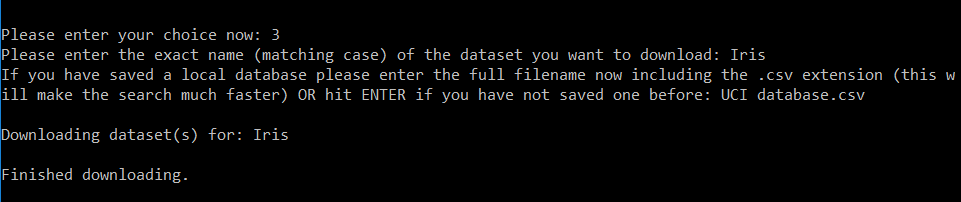
Example (search and download a particular dataset)
For example if you want to download the famous dataset Iris, just choose the option 3 from the menu, enter the name of the local database stored (to make the search faster) and voila! You will have the Iris dataset downloaded and stored in a folder called 'Iris' in your directory!
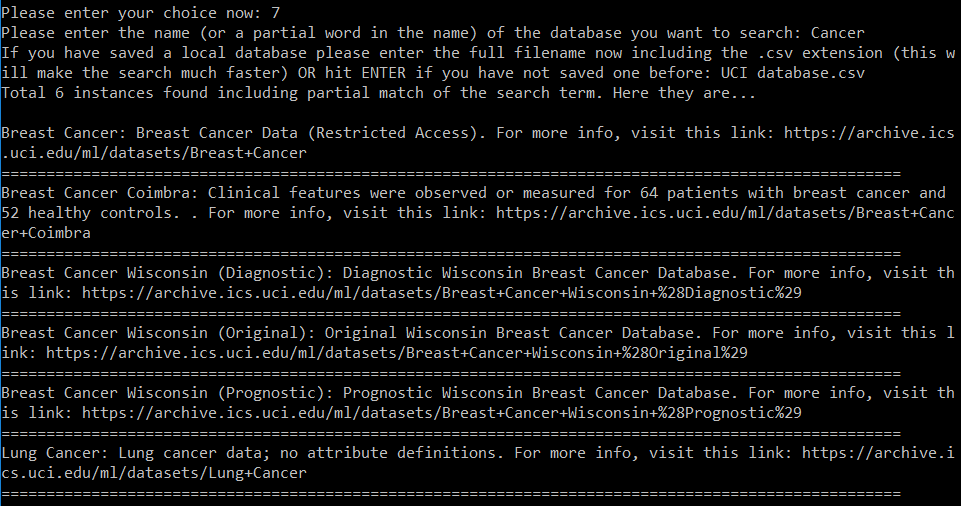
Example (search for datasets with a particular keyword)
If you search using a keyword by choosing option 7, then you will get back short one-liner abstracts about all the datasets whose name match your search string (even partially). You will also get the associated web page link for each of these results, so that you can go and explore them more if you want. Below screenshot shows an example of searching with the term Cancer.
If want to bypass the simple API and play with the low-level functions
In case you want to bypass the simple user API and play with the low-level functions, you are welcome to do so. Here is the rundown on them. First, import the necessary packages,
from UCI_ML_Functions import *
import pandas as pd
read_dataset_table(): Reads the table of datasets from the url: "https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets.html" and process it further to clean and categorize.
clean_dataset_table(): Accepts the raw dataset table (a DataFrame object) and returns a cleaned up version removing entries with unknown number of samples and attributes. Also rationalizes the 'Default task' category column indicating the main machine learning task associated with the datasets.
build_local_table(filename=None,msg_flag=True): Reads through the UCI ML portal and builds a local table with information such as name, size, ML task, data type.
filename: Optional filename that can be chosen by the user. If not chosen, a default name ('UCI table.csv') will be selected by the program.msg_flag: Controls verbosity.
build_dataset_list(): Scrapes through the UCI ML datasets page and builds a list of all datasets.
build_dataset_dictionary(): Scrapes through the UCI ML datasets page and builds a dictionary of all datasets with names and description. Also stores the unique identifier corresponding to the dataset. This identifier string is needed by the downloader function to download the data file. Generic name won't work.
build_full_dataframe(): Builds a DataFrame with all information together including the url link for downloading the data.
build_local_database(filename=None,msg_flag=True): Reads through the UCI ML portal and builds a local database with information such as: name, abstract, data page URL.
filename: Optional filename that can be chosen by the user. If not chosen, a default name ('UCI database.csv') will be selected by the program.msg_flag: Controls verbosity.
return_abstract(name,local_database=None,msg_flag=False): Returns one-liner description (and webpage link for further information) of a particular dataset by searching the given name.
local_database: Name of the database (CSV file) stored locally i.e. in the same directory, which contains information about all the datasets on UCI ML repo.msg_flag: Controls verbosity.
describe_all_dataset(msg_flag=False): Calls the build_dataset_dictionary function and prints description of all datasets from that.
print_all_datasets_names(msg_flag=False): Calls the build_dataset_dictionary function and prints names of all datasets from that.
extract_url_dataset(dataset,msg_flag=False): Given a dataset identifier this function extracts the URL for the page where the actual raw data resides.
download_dataset_url(url,directory,msg_flag=False,download_flag=True): Download all the files from the links in the given url.
msg_flag: Controls verbosity.download_flag: Default is True. If set to False, only creates the directories but does not initiate download (for testing purpose).
download_datasets(num=10,local_database=None,msg_flag=True,download_flag=True): Downloads datasets and puts them in a local directory named after the dataset. By default downloads first 10 datasets only. User can choose the number of dataets to be downloaded.
msg_flag: Controls verbosity.download_flag: Default is True. If set to False, only creates the directories but does not initiate download (for testing purpose).
download_dataset_name(name,local_database=None,msg_flag=True,download_flag=True): Downloads a particular dataset by searching the given name.
local_database: Name of the database (CSV file) stored locally i.e. in the same directory, which contains information about all the datasets on UCI ML repo.msg_flag: Controls verbosity.download_flag: Default is True. If set to False, only creates the directories but does not initiate download (for testing purpose).
download_datasets_size(size='Small',local_database=None,local_table=None,msg_flag=False,download_flag=True): Downloads all datasets which satisfy the 'size' criteria.
size: Size of the dataset which user wants to download. Could be any of the following: 'Small', 'Medium', 'Large','Extra Large'.local_database: Name of the database (CSV file) stored locally i.e. in the same directory, which contains name and URL information about all the datasets on UCI ML repo.local_table: Name of the database (CSV file) stored locally i.e. in the same directory, which contains features information about all the datasets on UCI ML repo i.e. number of samples, type of machine learning task to be performed with the dataset.msg_flag: Controls verbosity.download_flag: Default is True. If set to False, only creates the directories but does not initiate download (for testing purpose).
download_datasets_task(task='Classification',local_database=None,local_table=None,msg_flag=False,download_flag=True): Downloads all datasets which match the ML task criteria as eneterd by the user.
task: Machine learning task for which user wants to download the datasets. Could be any of the following:
'Classification', 'Recommender Systems', 'Regression', 'Other/Unknown', 'Clustering', 'Causal Discovery'.
local_database: Name of the database (CSV file) stored locally i.e. in the same directory, which contains name and URL information about all the datasets on UCI ML repo.local_table: Name of the database (CSV file) stored locally i.e. in the same directory, which contains features information about all the datasets on UCI ML repo i.e. number of samples, type of machine learning task to be performed with the dataset.msg_flag: Controls verbosity.download_flag: Default is True. If set to False, only creates the directories but does not initiate download (for testing purpose).
So, give it a try and put a star to my Github repo if you like it.
Feedbacks and suggestions for improvements are most welcome at [email protected]