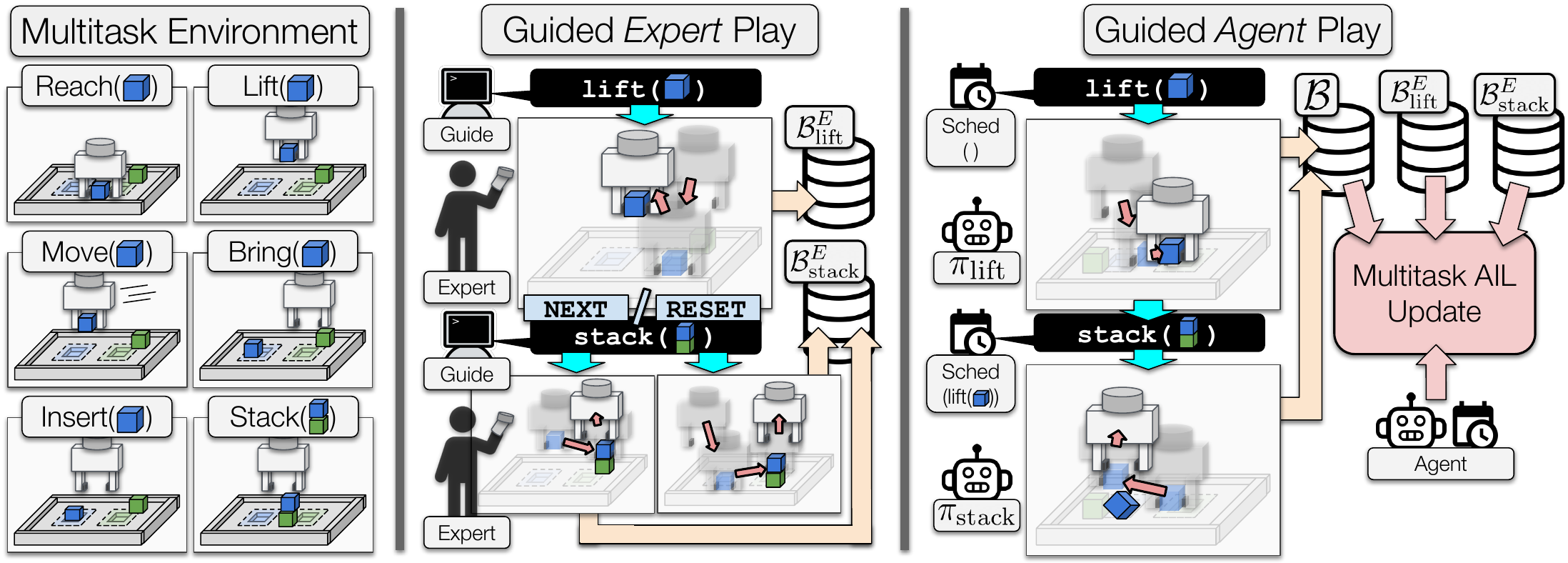
Learning from Guided Play: A Scheduled Hierarchical Approach for Improving Exploration in Adversarial Imitation Learning
Trevor Ablett*, Bryan Chan*, Jonathan Kelly (*equal contribution)
Poster at Neurips 2021 Deep Reinforcement Learning Workshop
Adversarial Imitation Learning (AIL) is a technique for learning from demonstrations that helps remedy the distribution shift problem that occurs with Behavioural Cloning. Empirically, we found that for manipulation tasks, off-policy AIL can suffer from inefficient or stagnated learning. In this work, we resolve this by enforcing exploration of a set of easy-to-define auxiliary tasks, in addition to a main task.
This repository contains the source code for reproducing our results.
Setup
We recommend the readers set up a virtual environment (e.g. virtualenv, conda, pyenv, etc.). Please also ensure to use Python 3.7 as we have not tested in any other Python versions. In the following, we assume the working directory is the directory containing this README:
.
├── lfgp_data/
├── liegroups/
├── manipulator-learning/
├── rl_sandbox/
├── README.md
└── requirements.txt
To install, simply clone and install with pip, which will automatically install all dependencies:
git clone [email protected]:utiasSTARS/lfgp.git && cd lfgp
pip install rl_sandbox
Environments
In this paper, we evaluated our method in the four environments listed below:
bring_0 # bring blue block to blue zone
stack_0 # stack blue block onto green block
insert_0 # insert blue block into blue zone slot
unstack_stack_env_only_0 # remove green block from blue block, and stack blue block onto green block
Trained Models and Expert Data
The expert and trained lfgp models can be found at this google drive link. The zip file is 570MB. All of our generated expert data is included, but we only include single seeds of each trained model to reduce the size.
The Data Directory
This subsection provides the desired directory structure that we will be assuming for the remaining README. The unzipped lfgp_data directory follows the structure:
.
├── lfgp_data/
│ ├── expert_data/
│ │ ├── unstack_stack_env_only_0-expert_data/
│ │ │ ├── reset/
│ │ │ │ ├── 54000_steps/
│ │ │ │ └── 9000_steps/
│ │ │ └── play/
│ │ │ └── 9000_steps/
│ │ ├── stack_0-expert_data/
│ │ │ └── (same as unstack_stack_env_only_0-expert_data)/
│ │ ├── insert_0-expert_data/
│ │ │ └── (same as unstack_stack_env_only_0-expert_data)/
│ │ └── bring_0-expert_data/
│ │ └── (same as unstack_stack_env_only_0-expert_data)/
│ └── trained_models/
│ ├── experts/
│ │ ├── unstack_stack_env_only_0/
│ │ ├── stack_0/
│ │ ├── insert_0/
│ │ └── bring_0/
│ ├── unstack_stack_env_only_0/
│ │ ├── multitask_bc/
│ │ ├── lfgp_ns/
│ │ ├── lfgp/
│ │ ├── dac/
│ │ ├── bc_less_data/
│ │ └── bc/
│ ├── stack_0/
│ │ └── (same as unstack_stack_env_only_0)
│ ├── insert_0/
│ │ └── (same as unstack_stack_env_only_0)
│ └── bring_0/
│ └── (same as unstack_stack_env_only_0)
├── liegroups/
├── manipulator-learning/
├── rl_sandbox/
├── README.md
└── requirements.txt
Create Expert and Generate Expert Demonstrations
Readers can generate their own experts and expert demonstrations by executing the scripts in the rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/lfgp/experts directory. More specifically, create_expert.py and create_expert_data.py respectively train the expert and generate the expert demonstrations. We note that training the expert is time consuming and may take up to multiple days.
To create an expert, you can run the following command:
# Create a stack expert using SAC-X with seed 0. --gpu_buffer would store the replay buffer on the GPU.
# For more details, please use --help command for more options.
python rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/lfgp/experts/create_expert.py \
--seed=0 \
--main_task=stack_0 \
--device=cuda \
--gpu_buffer
A results directory will be generated. A tensorboard, an experiment setting, a training progress file, model checkpoints, and a buffer checkpoint will be created.
To generate play-based and reset-based expert data using a trained model, you can run the following commands:
# Generate play-based stack expert data with seed 1. The program halts when one of --num_episodes or --num_steps is satisfied.
# For more details, please use --help command for more options
python rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/lfgp/experts/create_expert_data.py \
--model_path=data/stack_0/expert/state_dict.pt \
--config_path=data/stack_0/expert/sacx_experiment_setting.pkl \
--save_path=./test_expert_data \
--num_episodes=10 \
--num_steps=1000 \
--seed=1 \
--render
# Generate reset-based stack expert data with seed 1. Note that --num_episodes will need to be scaled by number of tasks (i.e. num_episodes * num_tasks).
python rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/lfgp/experts/create_expert_data.py \
--model_path=data/stack_0/expert/state_dict.pt \
--config_path=data/stack_0/expert/sacx_experiment_setting.pkl \
--save_path=./test_expert_data \
--num_episodes=10 \
--num_steps=1000 \
--seed=1 \
--render \
--reset_between_intentions
The generated expert data will be stored under --save_path, in separate files int_0.gz, ..., int_{num_tasks - 1}.gz.
Training the Models with Imitation Learning
In the following, we assume the expert data is generated following the previous section and is stored under test_expert_data. The training scripts run_*.py are stored in rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/lfgp directory. There are five run scripts, each corresponding to a variant of the compared methods (except for behavioural cloning less data, since the change is only in the expert data). The runs will be saved in the same results directory mentioned previously. Note that the default hyperparameters specified in the scripts are listed on the appendix.
Behavioural Cloning (BC)
There are two scripts for single-task and multitask BC: run_bc.py and run_multitask_bc.py. You can run the following commands:
# Train single-task BC agent to stack with using reset-based data.
# NOTE: intention 2 is the main intention (i.e. stack intention). The main intention is indexed at 2 for all environments.
python rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/lfgp/run_bc.py \
--seed=0 \
--expert_path=test_expert_data/int_2.gz \
--main_task=stack_0 \
--render \
--device=cuda
# Train multitask BC agent to stack with using reset-based data.
python rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/lfgp/run_multitask_bc.py \
--seed=0 \
--expert_paths=test_expert_data/int_0.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_1.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_2.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_3.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_4.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_5.gz
--main_task=stack_0 \
--render \
--device=cuda
Adversarial Imitation learning (AIL)
There are three scripts for Discriminator-Actor-Critic (DAC), Learning from Guided Play (LfGP), and LfGP-NS (No Schedule): run_dac.py, run_lfgp.py, run_lfgp_ns.py. You can run the following commands:
# Train DAC agent to stack with using reset-based data.
python rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/lfgp/run_dac.py \
--seed=0 \
--expert_path=test_expert_data/int_2.gz \
--main_task=stack_0 \
--render \
--device=cuda
# Train LfGP agent to stack with using reset-based data.
python rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/lfgp/run_lfgp.py \
--seed=0 \
--expert_paths=test_expert_data/int_0.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_1.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_2.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_3.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_4.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_5.gz
--main_task=stack_0 \
--device=cuda \
--render
# Train LfGP-NS agent to stack with using reset-based data.
python rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/lfgp/run_lfgp_ns.py \
--seed=0 \
--expert_paths=test_expert_data/int_0.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_1.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_2.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_3.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_4.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_5.gz,\
test_expert_data/int_6.gz \
--main_task=stack_0 \
--device=cuda \
--render
Evaluating the Models
The readers may load up trained agents and evaluate them using the evaluate.py script under the rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/eval_tools directory. Currently, only the lfgp agent is supplied due to the space restrictions mentioned above.
# For single-task agents - DAC, BC
# To run single-task agent (e.g. BC)
python rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/eval_tools/evaluate.py \
--seed=1 \
--model_path=data/stack_0/il_agents/bc/state_dict.pt \
--config_path=data/stack_0/il_agents/bc/bc_experiment_setting.pkl \
--num_episodes=5 \
--intention=0 \
--render \
--device=cuda
# For multitask agents - SAC-X, LfGP, LfGP-NS, Multitask BC
# To run all intentions for multitask agents (e.g. SAC-X)
python rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/eval_tools/evaluate.py \
--seed=1 \
--model_path=data/stack_0/expert/state_dict.pt \
--config_path=data/stack_0/expert/sacx_experiment_setting.pkl \
--num_episodes=5 \
--intention=-1 \
--render \
--device=cuda
# To run only the main intention for multitask agents (e.g. LfGP)
python rl_sandbox/rl_sandbox/examples/eval_tools/evaluate.py \
--seed=1 \
--model_path=data/stack_0/il_agents/lfgp/state_dict.pt \
--config_path=data/stack_0/il_agents/lfgp/lfgp_experiment_setting.pkl \
--num_episodes=5 \
--intention=2 \
--render \
--device=cuda