当前位置:网站首页>基于VGG卷积神经网络的图像识别代码实现
基于VGG卷积神经网络的图像识别代码实现
2022-04-23 05:50:00 【Stephen_Tao】
VGG模型介绍
VGG(Oxford Visual Geometry Group)模型是2014年ILSVRC竞赛的第二名,,由Karen Simonyan和Andrew Zisserman实现。VGG是卷积神经网络模型,是在AlexNet的基础上做的改进。

TensorFLow的keras库中集成有VGG16、VGG19模型,可以打印模型的结构,下面以VGG16为例进行模型结构说明:
from tensorflow.python.keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16
model = VGG16()
print(model.summary())
VGG模型打印结果
Model: "vgg16"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 224, 224, 3)] 0
_________________________________________________________________
block1_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 1792
_________________________________________________________________
block1_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 36928
_________________________________________________________________
block1_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 112, 112, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block2_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128) 73856
_________________________________________________________________
block2_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128) 147584
_________________________________________________________________
block2_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 56, 56, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block3_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 295168
_________________________________________________________________
block3_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080
_________________________________________________________________
block3_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080
_________________________________________________________________
block3_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 28, 28, 256) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block4_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 1180160
_________________________________________________________________
block4_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block4_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block4_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block5_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block5_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block5_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block5_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 7, 7, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
flatten (Flatten) (None, 25088) 0
_________________________________________________________________
fc1 (Dense) (None, 4096) 102764544
_________________________________________________________________
fc2 (Dense) (None, 4096) 16781312
_________________________________________________________________
predictions (Dense) (None, 1000) 4097000
=================================================================
Total params: 138,357,544
Trainable params: 138,357,544
Non-trainable params: 0
基于VGG实现图像识别
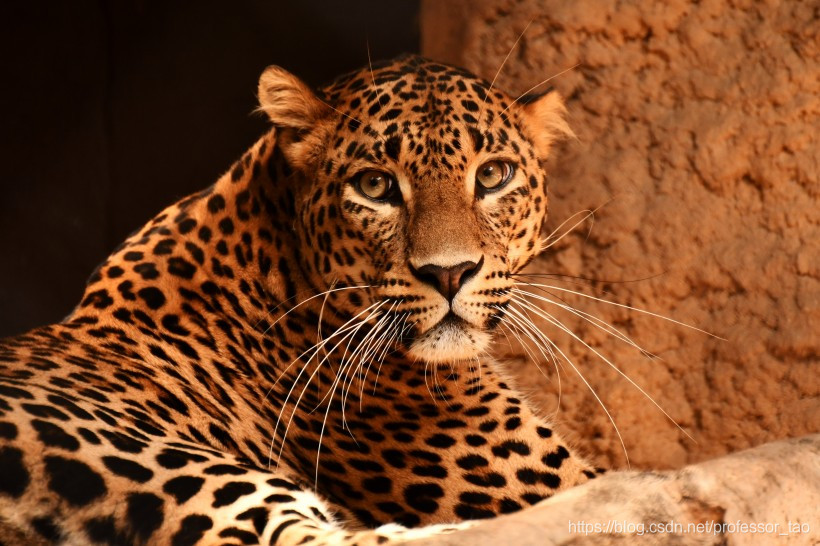
本文从网络上找了两张动物的图片,一种是哈士奇,一直是美洲豹,通过VGG模型对图像进行
类的识别。
哈士奇:

美洲豹:

代码实现
由于VGG模型是集成好的,所以只需要调用相应的API就能实现图像识别任务。
哈士奇识别
from tensorflow.python.keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16,decode_predictions,preprocess_input
from tensorflow.python.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img,img_to_array
model = VGG16()
# 将输入图片变为(224,224)的固定大小
image = load_img("./dog.jpeg",target_size=(224,224))
# 将图片转换为3维数组
image = img_to_array(image)
# 图片变成4维,满足VGG模型的输入要求
image = image.reshape(1,image.shape[0],image.shape[1],image.shape[2])
# 对输入图片进行数据预处理
image = preprocess_input(image)
# 对图片的类别进行预测
y_predict = model.predict(image)
# 对预测结果进行解码
label = decode_predictions(y_predict)
res = label[0][0]
print("预测的类别为:%s,概率为:(%.2f%%)",(res[1],res[2]*100))
运行结果
预测的类别为:Siberian_husky,概率为:(51.18%)
美洲豹识别
from tensorflow.python.keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16,decode_predictions,preprocess_input
from tensorflow.python.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img,img_to_array
model = VGG16()
# 将输入图片变为(224,224)的固定大小
image = load_img("./leopard.jpg",target_size=(224,224))
# 将图片转换为3维数组
image = img_to_array(image)
# 图片变成4维,满足VGG模型的输入要求
image = image.reshape(1,image.shape[0],image.shape[1],image.shape[2])
# 对输入图片进行数据预处理
image = preprocess_input(image)
# 对图片的类别进行预测
y_predict = model.predict(image)
# 对预测结果进行解码
label = decode_predictions(y_predict)
res = label[0][0]
print("预测的类别为:%s,概率为:(%.2f%%)",(res[1],res[2]*100))
运行结果
预测的类别为:leopard,概率为:(62.83%)
总结
本文介绍了VGG模型,并基于TensorFlow.Keras中集成的API搭建了VGG模型。通过两张动物图片验证了模型在图像识别任务中的准确性。
版权声明
本文为[Stephen_Tao]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://blog.csdn.net/professor_tao/article/details/119538510
边栏推荐
- [opencv] use filestorage to read and write eigenvectors
- C [document operation] PDF files and pictures are converted to each other
- Rust 中的指针:Box、Rc、Cell、RefCell
- 【UDS统一诊断服务】四、诊断典型服务(4)— 在线编程功能单元(0x34-0x38)
- 生成验证码
- Vscode custom comments
- Rust:在线程池中共享变量
- [UDS unified diagnosis service] i. diagnosis overview (3) - ISO 15765 architecture
- Rust: Tcp 服务器与客户端的一个简单例子
- 进程管理命令
猜你喜欢
Opencv uses genericindex for KNN search

MySQL groups are sorted by a field, and the first value is taken

【UDS统一诊断服务】一、诊断概述(2)— 主要诊断协议(K线和CAN)

Cross domain issues - allow origin header contains multiple values but only one is allowed
![[UDS unified diagnosis service] i. diagnosis overview (3) - ISO 15765 architecture](/img/ef/173281ffb354b9abe1b730b89469cc.png)
[UDS unified diagnosis service] i. diagnosis overview (3) - ISO 15765 architecture

A solution to replace not in in SQL

文件查看命令和用户管理命令

Graduation project, curriculum link, student achievement evaluation system
利用文件保存数据(c语言)
Robocode教程7——雷达锁定
随机推荐
Uniapp encapsulates request
for()循环参数调用顺序
大学概率论与数理统计知识点详细整理
【UDS统一诊断服务】四、诊断典型服务(1)— 诊断和通信管理功能单元
【无标题】
生成验证码
C语言实用小技巧合集(持续更新)
【UDS统一诊断服务】四、诊断典型服务(6)— 输入输出控制单元(0x2F)
P1018 maximum product solution
共用数据的保护
文件查看命令和用户管理命令
Completely clean up MySQL win
[UDS unified diagnosis service] i. diagnosis overview (2) - main diagnosis protocols (K-line and can)
Rust 中的指针:Box、Rc、Cell、RefCell
gcc ,g++,gdb的安装
Make your own small program
Feign请求日志统一打印
Cross domain issues - allow origin header contains multiple values but only one is allowed
Rust:单元测试(cargo test )的时候显示 println 的输出信息
Initialization of classes and objects (constructors and destructors)