当前位置:网站首页>可视化之路(十)分割画布函数详解
可视化之路(十)分割画布函数详解
2022-04-23 06:17:00 【小猪猪家的大猪猪】
分割画布函数详解
一.前言
在使用matplotlib库进行数据可视化的过程中,我们都离不开一个重要载体–画布(Figure)。一个Figure对象是所有绘图元素的顶层容器,想要实现画布的合理使用,分区使用必不可少。
首先理解一下子区这个概念,子区顾名思义就是将大画布(FIgure)划分成若干个子画布,这些子画布构成绘图区域,其本质是在纵横交错的行列网格中添加坐标轴系统。接下来主要介绍一下3个相关函数,下文中的所有实例代码均在Ipython上实现,且相关库导入以及中文修改语句已经省略,文中所提及的方法二字和函数等价。
二.subplots函数
这个函数最为简单直接,调用plt.subplots()会直接创建一个1行1列的网格布局子区间,同时创建一个Figure对象。
2.1函数定义
subplots(nrows=1,
ncols=1,
*,
sharex=False,
sharey=False,
squeeze=True,
subplot_kw=None,
gridspec_kw=None,
fig_kw)
参数说明:
参数1:nrows:整数型,指定子图网格的行数
参数2:ncols:整数型,指定子图网格的列数
参数3:sharex:布尔型或字符型,指定是否共享x轴,可选{‘none’,‘all’,‘row’,‘col’}
none:等同于False,指定所有子图不共享
all:指定x轴或y轴将在所有子图之间共享
row:指定每行子图将共享一个x轴或y轴
col:指定每列子图将共享一个x轴或y轴
参数4:sharey:布尔型或字符型,指定是否共享y轴,可选{‘none’,‘all’,‘row’,‘col’}
none:等同于False,指定所有子图不共享
all:指定x轴或y轴将在所有子图之间共享
row:指定每行子图将共享一个x轴或y轴
col:指定每列子图将共享一个x轴或y轴
参数5:squeeze:布尔型,指定是否进行压缩
参数6:subplot_kw:字典型,传递给add_subplot方法,指定创建每个子图的调用的关键字参数
参数7:gridspec_kw:字典型,传递给GridSpec类,指定子图放置的网格的关键字参数
参数8:**fig_kw:字典型,传递给 pyplot.figure方法
返回值1:FIgure实例
返回值2:Axes实例或者Axes实例数组,该数组和网格有相同的形状
参数详解:
- fig_kw的参数传递给pyplot.figure方法的意思是该参数的所有内容会直接传递给plt.figure方法。subplot_kw、subplot_kw同理。
- 对参数squeeze,如果为True且仅构造一个子图,则返回的单个Axes对象将作为标量返回。对于Nx1或1xM子图,返回的对象是包含Axes对象的numpy数组。对于N×M个,副区与N> 1和M> 1返回为2D阵列。如果为False,则完全不进行压缩:返回的Axes对象始终是包含Axes实例的2D数组,即使最终它是1x1。具体示例见下文。
2.2函数讲解
这个函数的优势是一步到位,创建Figure对象的同时创建指定行列的网格布局,在代码量上减少了很多。下文是该函数的内部实现:
fig = figure(fig_kw) #创建Figure对象
axs = fig.subplots(nrows=nrows, #指定行
ncols=ncols, #指定列
sharex=sharex, #指定是否共享X轴
sharey=sharey, #指定是否共享y轴
squeeze=squeeze, #指定是否进行返回值压缩
subplot_kw=subplot_kw,
gridspec_kw=gridspec_kw)
return fig, axs #返回Figure对象和坐标轴系统
可以看到调用plt.figure函数并传递参数fig_kw并创建一个Figure对象,这就是上文中说传递给plt.figure函数的意思。接着调用Figure.subplots方法创建网格布局和坐标轴系统。下文是fig.subplots的核心代码:
if self.get_constrained_layout():
gs = GridSpec(nrows, ncols, figure=self, gridspec_kw) #创建GridSpec类实例
else:
# this should turn constrained_layout off if we don't want it
gs = GridSpec(nrows, ncols, figure=None, gridspec_kw)
self._gridspecs.append(gs)
# Create array to hold all axes.
axarr = np.empty((nrows, ncols), dtype=object) #创建一个空矩阵,类型是对象
#循环创建坐标轴系统,下标0开始
for row in range(nrows):
for col in range(ncols):
shared_with = {
"none": None, "all": axarr[0, 0],"row": axarr[row, 0], "col": axarr[0, col]} #sharex和sharey的检查字典
subplot_kw["sharex"] = shared_with[sharex] #字典取值
subplot_kw["sharey"] = shared_with[sharey] #字典取值
axarr[row, col] = self.add_subplot(gs[row, col], subplot_kw) #创建坐标轴系统
# turn off redundant tick labeling
#设置共享X轴
if sharex in ["col", "all"]:
# turn off all but the bottom row
for ax in axarr[:-1, :].flat:
ax.xaxis.set_tick_params(which='both', labelbottom=False, labeltop=False)
ax.xaxis.offsetText.set_visible(False)
#设置共享Y轴
if sharey in ["row", "all"]:
# turn off all but the first column
for ax in axarr[:, 1:].flat:
ax.yaxis.set_tick_params(which='both', labelleft=False, labelright=False)
ax.yaxis.offsetText.set_visible(False)
if squeeze:
return axarr.item() if axarr.size == 1 else axarr.squeeze() #调用squeeze方法压删除一维
else:
return axarr #返回一个二维矩阵
首先创建GridSpec类实例,该类用于指定网格的几何形状。然后循环创建坐标轴系统,并添加到一个空矩阵中,此时squeeze参数并产生作用,返回值是一个指定形状的二维矩阵,接下来两个if-for代码块用来设置sharex和sharey参数响应。最后对squeeze参数进行检测,假设为True则依据行列数返回一个纯实例还是二维矩阵,假设为False则无论如何都返回一个二维矩阵。
2.3函数示例
2.3.1squeeze参数示例
首先创建一个1行1列的网格布局,squeeze参数为False,看看其返回值:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(squeeze=False)
ax.shape, ax
其结果如下:
((1, 1), array([[<AxesSubplot:>]], dtype=object))
证明返回的是一个二位数组,而不是一个对象,接下来将squeeze参数改为True:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(squeeze=True)
ax
其结果如下:
<AxesSubplot:>
返回值是单纯的一个对象。但是假设我们设定多行或者多列会怎么样呢?
fig, ax2 = plt.subplots(2, 2, squeeze=True)
ax2.shape, ax2
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(2, 2, squeeze=False)
ax1.shape, ax1
其结果如下:
((2, 2),
array([[<AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>],
[<AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>]], dtype=object))
((2, 2),
array([[<AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>],
[<AxesSubplot:>, <AxesSubplot:>]], dtype=object))
证明在多行多列的情况下,squeeze是没有影响的。
2.3.2综合示例
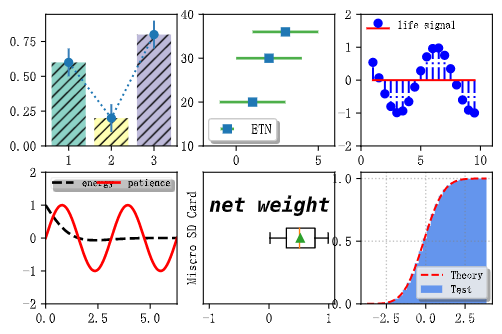
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 3)
colors_list = ['#8dd3c7', '#ffffb3', '#bebada']
ax[0, 0].bar([1, 2, 3], [0.6, 0.2, 0.8], color=colors_list, width=0.8, hatch='///', align='center')
ax[0, 0].errorbar([1, 2, 3], [0.6, 0.2, 0.8], yerr=0.1, capsize=0, ecolor='#377eb8', fmt='o:')
ax[0, 1].errorbar([1, 2, 3], [20, 30, 36], xerr=2, ecolor='#4daf4a', elinewidth=2, fmt='s', label='ETN')
ax[0, 1].legend(loc=3, fancybox=True, shadow=True, fontsize=10, borderaxespad=0.4)
ax[0, 1].set_ylim(10, 40)
ax[0, 1].set_xlim(-2, 6)
x3 = np.arange(1, 10, 0.5)
y3 = np.cos(x3)
ax[0, 2].stem(x3, y3, basefmt='r-', linefmt='b-.', markerfmt='bo', label='life signal')
ax[0, 2].legend(loc=2, fancybox=True, shadow=True, frameon=False, fontsize=8, borderaxespad=0.6, borderpad=0.0)
ax[0, 2].set_ylim(-2, 2)
ax[0, 2].set_xlim(0, 11)
x4 = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 500)
x4_1 = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 1000)
y4 = np.cos(x4)*np.exp(-x4)
y4_1 = np.sin(2*x4_1)
line1, line2 = ax[1, 0].plot(x4, y4, 'k--', x4_1, y4_1, 'r-', lw=2)
ax[1, 0].legend((line1, line2), ('energy', 'patience'), loc=2, fancybox=True, shadow=True, framealpha=0.3,mode='expand', fontsize=8, ncol=2, columnspacing=2, borderpad=0.1, markerscale=0.1)
ax[1, 0].set_ylim(-2, 2)
ax[1, 0].set_xlim(0, 2*np.pi)
x5 = np.random.rand(100)
ax[1, 1].boxplot(x5, vert=False, showmeans=True, meanprops=dict(color='black'))
ax[1, 1].set_yticks([])
ax[1, 1].set_xlim(-1.1, 1.1)
ax[1, 1].set_ylabel('Miscro SD Card')
ax[1, 1].text(-1.0, 1.2, 'net weight', fontsize=15, style='italic', weight='black', family='monospace')
mu = 0.0
sigma = 1.0
x6 = np.random.randn(10000)
n, bins, patches = ax[1, 2].hist(x6, bins=30, histtype='stepfilled', cumulative=True, color='cornflowerblue',
label='Test', density=True)
y = ((1 / (np.sqrt(2 * np.pi) * sigma)) * np.exp(-0.5 * (1 / sigma * (bins-mu)) 2))
y = y.cumsum()
y /= y[-1]
ax[1, 2].plot(bins, y, 'r--', lw=1.5, label='Theory')
ax[1, 2].set_ylim([0.0, 1.1])
ax[1, 2].grid(ls=':', lw=1, color='grey', alpha=0.5)
ax[1, 2].legend(fontsize=8, shadow=True, fancybox=True, framealpha=0.8)
ax[1, 2].autoscale()
plt.show()
其结果如下:
三.plt.subplot函数
该函数是一个对Figure.add_subplot方法的包装,他的作用在于将轴添加到现有Figure对象,或者检索现有轴,其核心语句就是fig = gcf()获取当前Figure对象。
3.1函数定义
subplot有多种形式,其部分示例如下:
subplot(nrows, ncols, index, kwargs)
subplot(pos, kwargs)
subplot(kwargs)
subplot(ax)
参数说明:
参数1:* args:指定描述子图的方法
(nrows,ncols,index):指定行数、列数和当前激活子图索引,索引从左上角的1开始并向右增加。索引也可以是两元素元组指定(start, end) ,即绘制一个跨区子图
三位整数:百位、十位、个位分别指定行数、列数和索引,只有当子图数不超过9个的时候才可使使用。
参数2:projection:指定轴投影,{None,“ aitoff”,“ hammer”,“ lambert”,“ mollweide”,“ polar”,“ rectalinear”,str}
参数3:polar:布尔型,指定是否使用projection=‘polar’,即使用极坐标系
参数4:sharex:指定是否共享X轴
参数5:sharey:指定是否共享Y轴
参数6:label:指定轴标签
返回值:基于所指定的投影方式返回轴基类
参数详解:
- polar这个参数尽量不要用,所有的投影参数最好都使用projection参数来传递。
- 使用此函数的时候索引下标都是从1开始。而不是0,切记!!!
3.2函数讲解
以下是subplot函数的内部实现:
fig = gcf() #调用plt.gcf获得当前Figure对象
# First, search for an existing subplot with a matching spec.
key = SubplotSpec._from_subplot_args(fig, args)
#检索撇配现有坐标轴系统
for ax in fig.axes:
# if we found an axes at the position sort out if we can re-use it
if hasattr(ax, 'get_subplotspec') and ax.get_subplotspec() == key:
# if the user passed no kwargs, re-use
if kwargs == {
}:
break
# if the axes class and kwargs are identical, reuse
elif ax._projection_init == fig._process_projection_requirements(
*args, **kwargs):
break
else:
# we have exhausted the known Axes and none match, make a new one!
ax = fig.add_subplot(*args, **kwargs) #如果没有匹配则依据参数创建相应的子图
fig.sca(ax) #将当前轴设置为ax,将当前Figure设置为ax的parent
因为该函数具备检索现有轴的能力,所以先调用gcf方法获取当前Figure对象,在对该对象的坐标轴系统进行检索匹配,假设有则设为ax,没有的话调用add_subplots方法创建一个新的坐标轴系统,最后使用sca方法将ax设为当前坐标轴系统并返回,从而完成了将轴添加到现有Figure对象,或者检索现有轴这个功能。
3.3函数示例
3.3.1projection参数实例
首先介绍四种地球投影方式,分别是Aitoff、Hammer、Lambert、Mollweide。Aitoff映射程序如下:
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(projection="aitoff")
plt.title("Aitoff")
plt.grid(True)
Aitoff画图结果如下:

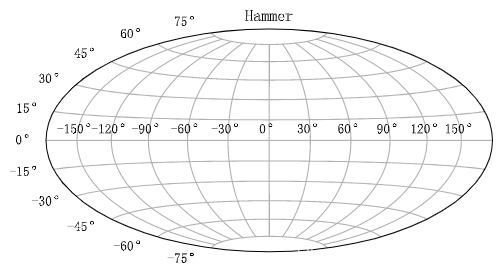
Hammer映射程序如下:
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(projection="hammer")
plt.title("Hammer")
plt.grid(True)
Hammer画图结果如下:
Lambert映射程序如下:
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(projection="lambert")
plt.title("Lambert")
plt.grid(True)
Lambert画图结果如下:

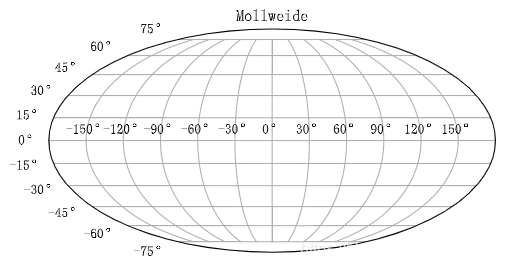
Mollweide映射程序如下:
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(projection="mollweide")
plt.title("Mollweide")
plt.grid(True)
Mollweide画图结果如下:
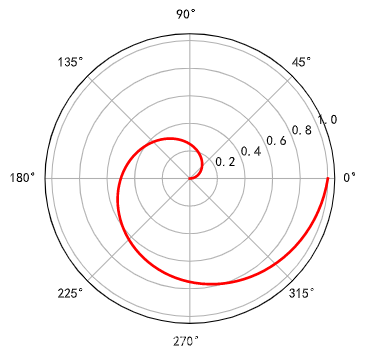
最后介绍一种最常用的映射即polar映射,也就是极坐标系,polar映射映射程序如下:
radi = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
theta = 2*np.pi*radi
ax = plt.subplot(111, polar=True)
ax.plot(theta, radi, color='r', lw=2)
plt.show()
polar画图结果如下:
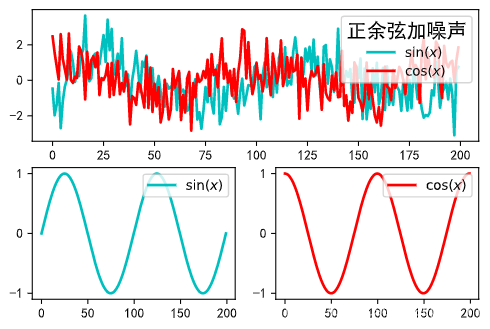
3.3.2综合示例
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, (1, 2))
ax.plot(y+np.random.randn(200), ls='-', lw=2, color='c', label=r'$\sin(x)$')
ax.plot(y1+np.random.randn(200), ls='-', lw=2, color='r', label=r'$\cos(x)$')
ax.legend(title='正余弦加噪声', title_fontsize=15, loc='upper right')
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
ax.plot(y, ls='-', lw=2, color='c', label=r'$\sin(x)$')
ax.legend(loc='upper right')
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
ax.plot(y1, ls='-', lw=2, color='r', label=r'$\cos(x)$')
ax.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.show()
其画图结果如下:
四.add_subplots函数
这个方法是Figure类的类方法也是上面两个函数的最重要的内部实现函数。
4.1函数定义
add_subplot(nrows, ncols, index, **kwargs)
add_subplot(pos, **kwargs)
add_subplot(ax)
add_subplot()
add_subplots函数的参数同plt.subplot方法的参数几乎一致,再次就不在赘述了,可以看上文的plt.subplot函数的介绍。
4.2函数讲解
该方法最大的特点就是作为类方法,其使用必须要有相应的实例,而不是像其他两个函数一样都是用gcf()方法调用当前Figure对象,这就是说我们可以在多个Figure对象上进行操作,精确创建不同对象上的分图。
4.3函数示例
4.3.1综合示例
程序展示了如何精确的创建两个Figure对象上的分图,示例程序如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
fig1 = plt.figure(num=1)
fig2 = plt.figure(num=2)
x = np.linspace(-2*np.pi, 2*np.pi, 200)
y = np.sin(x)
y1 = np.cos(x)
ax = fig1.add_subplot(2, 2, (1, 2))
ax.plot(y+np.random.randn(200), ls='-', lw=2, color='c', label=r'$\sin(x)$')
ax.plot(y1+np.random.randn(200), ls='-', lw=2, color='r', label=r'$\cos(x)$')
ax.legend(title='正余弦加噪声', title_fontsize=15, loc='upper right')
ax = fig1.add_subplot(2, 2, 3)
ax.plot(y, ls='-', lw=2, color='c', label=r'$\sin(x)$')
ax.legend(loc='upper right')
ax = fig1.add_subplot(2, 2, 4)
ax.plot(y1, ls='-', lw=2, color='r', label=r'$\cos(x)$')
ax.legend(loc='upper right')
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 500)
y = np.sin(x)*np.exp(-x)
ax = fig2.add_subplot(1, 2, 1, title='子图1')
ax.plot(x, y, 'k--', lw=2)
ax.set_title('折线图')
ax = fig2.add_subplot(1, 2, 2, title='子图2')
ax.scatter(x, y, s=10, c='skyblue', marker='o')
ax.set_title('散点图')
fig2.subplots_adjust(top=0.8)
plt.show()
其画图结果如下:

五.总结
个人认为最常用肯定是add_subplot方法和plt.subplots方法,一般情况下创建子区不会使用plt.subplot方法,他的用处在于检索而不是创建。假设需要精确控制创建子区的Figure对象,则使用add_subplot方法进行创建,通常学习或者简单绘图的话则考虑直接使用plt.subplots方法。
六.参考
版权声明
本文为[小猪猪家的大猪猪]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://blog.csdn.net/pcx171/article/details/116447977
边栏推荐
- pytorch:关于GradReverseLayer实现的一个坑
- DMR system solution of Kaiyuan MINGTING hotel of Fengqiao University
- 华为云MVP邮件
- SDC intelligent communication patrol management system of Nanfang investment building
- GIS实战应用案例100篇(五十二)-ArcGIS中用栅格裁剪栅格,如何保持行列数量一致并且对齐?
- Warning "force fallback to CPU execution for node: gather_191" in onnxruntime GPU 1.7
- “泉”力以赴·同“州”共济|北峰人一直在行动
- 不需要破解markdown编辑工具Typora
- CMSIS CM3源码注解
- 启动mqbroker.cmd失败解决方法
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
无盲区、长续航|公专融合对讲机如何提升酒店服务效率?
SPI NAND FLASH小结
基于51单片机的体脂检测系统设计(51+oled+hx711+us100)
枫桥学院开元名庭酒店DMR系统解决方案
go语言:在函数间传递切片
Emergency communication system for flood control and disaster relief
美摄科技推出桌面端专业视频编辑解决方案——美映PC版
Typora语法详解(一)
“泉”力以赴·同“州”共济|北峰人一直在行动
The simplest and complete example of libwebsockets
机器视觉系列(02)---TensorFlow2.3 + win10 + GPU安装
Systrace 解析
公专融合对讲机是如何实现多模式通信下的协同工作?
DMR system solution of Kaiyuan MINGTING hotel of Fengqiao University
Int8 quantification and inference of onnx model using TRT
Pep517 error during pycuda installation
Solution of self Networking Wireless Communication intercom system in Beifeng oil and gas field
北峰油气田自组网无线通信对讲系统解决方案
AUTOSAR从入门到精通100讲(八十三)-BootLoader自我刷新
Résolution du système