当前位置:网站首页>Interesting talk about network protocol
Interesting talk about network protocol
2022-04-23 13:59:00 【Pistachio 2021】
Geek time - Easy to learn , Efficient learning - Geek state
Catalog
One 、 Why learn network protocols
1、 Why learn network protocols
Four 、 From the physical layer to MAC layer
5、 ... and 、 Switches and VLAN
One 、 Why learn network protocols
The three elements of the agreement : grammar 、 semantics 、 The order
1、 Why learn network protocols
Only through network protocol , To make a large number of machines cooperate with each other 、 Accomplish one thing together .
【 Take online ordering as an example 】
Enter an e-commerce website in the browser , The browser will go through DNS Or more precisely HTTPDNS Find specific IP.
After finding the target address , The browser starts to package its requests . For ordinary browsing requests , Often use HTTP agreement , But for shopping requests , Encrypted transmission is often required , So I will use HTTPS agreement .
DNS、HTTP、HTTPS Where we are, we become application layer , After application layer encapsulation , The browser will give the package of the application layer to the next layer to complete , adopt socket Programming to achieve . Is the next layer Transport layer . The transport layer has two protocols , One is connectionless protocol UDP, One is connection oriented TCP( Connection oriented is ,TCP It will ensure that the package can reach the destination , If not , Send it all the time , Until you can ). For payment , Often use TCP agreement .
TCP There are two ports in the protocol , One is the port on which the browser listens , One is the server monitoring port of e-commerce . Operating systems often judge by ports , Which process should it get the package for .
After the completion of transport layer encapsulation , The browser will deliver the package to the operating system The network layer . The protocol of the network layer is IP agreement . stay IP There will be something in the agreement IP Address , That is, the browser's machine IP Address and destination IP Address .
When the operating system starts , Will be DHCP Protocol configuration IP Address , And the default gateway IP Address 192.168.1.1, Get the goal IP After the address , The operating system passes through ARP The protocol found the default gateway MAC Address , therefore , take IP Give the bag to the next floor , That is to say MAC layer , The network card will send the packet again , Get it to the gateway .
The communication protocol between gateway and gateway becomes routing protocol , Commonly used OSPF and BGP.
Thanks to the communication between gateways , Network packets can get the information of the next gateway from one gateway MAC Address , Until the target server is found .
Remove the target server MAC head , To the operating system The network layer , Find out IP It's right , Just take it off IP head .IP What will be written on the head is TCP agreement , Then give it to Transport layer , namely TCP layer .
In this layer , For the package received , There is a reply package indicating that you have received ( just TCP A description of the layer , Not the result of the order request ).
If after a while , The sender did not receive a reply , Sending end TCP The layer will resend the packet ( Resend means TCP End retry , It's not that the browser requests the order again , Unless it is TCP Something went wrong. , If the connection is broken ).
The network packet arrived safely TCP After the layer ,TCP There is a target port number in the header , Through port number , You can find the port number that the e-commerce website is monitoring .
The process of e-commerce website has been HTTP Requested content , Will pass RPC call ( Remote procedure call ) To tell the relevant process what to do .
After the relevant processes are handled , Just reply to one HTTPS My bag , Inform the results of the order , The packet eventually enters the sender browser , Show payment success .
2、 Network protocol to learn
application layer :DHCP HTTP HTTPS RTMP P2P DNS GTP RPC
Transport layer :UDP TCP
The network layer :ICMP IP OSPF BGP IPSec GRE
The link layer :ARP VLAN STP
The physical layer : Network jumpers
Two 、ip addr
IP Address It is the communication address of a network card in the network world
MAC Address Is the physical address of a network card , Its unique design is for networking , When different network cards are put in a network , No need to worry about conflict .MAC The communication range of the address is limited to a subnet .
IP The address is designed to underestimate the future development of the network ,32 Bit addresses are far from enough ( Hence the IPv6(128 position ))
It's not enough 32 position IP The address is also divided into 5 class , among B The maximum number of hosts that a class address can contain is 6w+, General enterprises can't reach this scale , Idle addresses create waste , and C The maximum number of hosts that a class address can contain is too small , Only 254 individual . Thus, a compromise method is produced, which is called untyped inter domain routing .
No type of inter domain routing (CIDR): take 32 position IP The address is split in two , The front is the network number , Followed by the host number . Such as :10.100.122.2/24, Express 32 In a , front 24 Bit is the network number , after 8 Bit is the host number .
CIDR Can be used to judge a IP Is the address a local address .
With CIDR There is a broadcast address ,10.100.122.255, If you send this address , all 10.100.122 All the machines in the network can receive . The other is the subnet mask ,255.255.255.0.
Mask the subnet with IP address AND Calculation , You can get the network number .
D Class is a multicast address , Use this type of address , All machines in the group can receive information
linux in perform ip addr The returned information :

scope: about eth0 For this network card , global, It means that this network card can be used externally , Can receive packets from all over the world . about lo Speaking of , yes host, It shows that this network card can only be used for local communication .
lo : The full name is loopback, Also known as loopback interface , Often assigned to 127.0.0.1 This address . This address is used for local communication , Directly return after kernel processing , Not in any network .
< BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP > : yes net_device flags, Status identification of network devices .
UP Indicates that the network card is in the startup state ;
BROADCAST This network card has a broadcast address , You can send broadcast packets ;
MULTICAST Indicates that the network card can send multicast packets ;
LOWER_UP Express L1 It's started , That is to say, the network cable is plugged in .
MTU1500 : Refers to the maximum transmission unit MTU by 1500, It's the default for Ethernet .
MTU It's on the second floor MAC The concept of layers .MAC Layer has a MAC The head of the , Ethernet connection MAC The headband and the text together , It is not allowed to exceed 1500 Bytes .
qdisc :queueing discipline Queuing rules . If the kernel needs to send packets through a network interface , You need to follow the configuration for this interface qdics Put packets in the queue . The simplest qdisc yes prifo , It doesn't do anything with packets , Packets are queued first in, first out .prifo_first The queue consists of three bands (band), Packets are grouped by service type (Type of Service,TOS) Assigned to different bands , The three bands have different priorities , Band internal FIFO .
3、 ... and 、DHCP And PXE
1、DHCP
DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol .
Operation mode :
When a new configuration is added to a machine DHCP Sever When it comes to the Internet , First of all DHCP Discover, That is to use IP Address 0.0.0.0 Send a broadcast packet , Purpose IP The address is 255.255.255.255. The broadcast package encapsulates UDP,UDP Encapsulates the BOOTP.DHCP yes BOOTP Enhanced Edition , But if you grab the bag , Most likely, the name is still BOOTP agreement .
In this broadcast package , The new machine Boot request.
DHCP Sever It will be assigned a IP Address , This process is called DHCP Offer. meanwhile ,DHCP Sever Will keep this IP Address , No longer assign... To other machines . here ,DHCP Sever Also use the broadcast address as the destination address , because , Current request allocation IP Your new machine doesn't have its own IP, besides , The server also sends the subnet mask 、 gateway 、 and IP Information such as the service life of the address .
If there are many times DHCP Sever, This new machine will receive multiple DHCP Offer, It will choose one of them as its own IP Address , Usually the first one to arrive , And send a message to the network DHCP Request Broadcast packet , Contains the client's MAC Address 、 Accepted IP Address 、 Provide IP Address of the DHCP Server address, etc. , And tell everyone DHCP Sever Which server will it accept IP Address , At the same time, request the rest DHCP Sever Withdraw what they offer IP.
Customer opportunities are in IP The service life has passed 50% When , Direct to IP Address of the DHCP Sever send out DHCP request Message packet . Received a response from the server DHCP ACK After package , According to the new service life provided in the package and other updated TCP/IP Parameters , Update your own configuration , such ,IP The service life is updated .
2、PXE
Network administrators can not only automatically assign IP, You can also install the operating system
This process is similar to the process of operating system startup .
【 attach : Operating system startup process 】 First , start-up BIOS,BIOS It's a very small system , Can only do a very small thing , Is to read the hard disk MBR Boot sector , take GRUB Start it up , And then give power to GRUB,GRUB Loading kernel 、 Loaded as root system file initramfs file , And then give power to the core , Finally, the kernel starts , Initialize the entire operating system .
The process of installing the operating system , It can only be plugged into the boot BIOS Before , Because before the system was installed , Not even the boot sector . thus , This process is called Pre boot execution environment (Pre-boot Execution Environment), abbreviation PXE.
PXE The protocol is divided into client and server , Because there is no operating system yet , You can only put the client in BIOS Inside , When the computer starts ,BIOS take PXE The client calls into memory , You can connect to the server to do some operations .
PXE After the client starts up , Will send a HDCP request , Give Way DHCP Sever Assign it a IP Address . If you want to use PXE, except IP Address , You also need to configure next-sever, Point to PXE The address of the server , In addition, you need to configure the initial startup file filename. such ,PXE The client knows PXE Where's the server , You can also know how to get from PXE Download a file from the server , To initialize the operating system .
Knowing this ,PXE The client can start downloading , Download with TFTP agreement , So in PXE Server , Often you need another TFTP The server , take PXE The files to be downloaded by the client are passed to it .
PXE After the client receives the file , Start file execution . This document will indicate PXE client , towards TFTP The server requests the configuration information of the computer pxelinux.cfg.TFTP The server will give PXE Client a configuration file , It says where the kernel is 、initramfs Where is the .PXE The client will request these files .
Last , start-up Linux kernel .
Four 、 From the physical layer to MAC layer
1、 The physical layer
When there is no router , How to configure LAN for two computers (LAN) Well ?
You can use a computer to connect to the computer's network cable ( Previous cross wiring , Crystal head 1-3、2-6 Cross connection method to make a cross line . The first of the crystal heads 1、2 And the 3、6 foot , Take up... Separately 、 The function of signaling ,1-3、2-6 Swap places . Now the network card has adaptive direct connection ) Plug one end of the network cable into the network card of a computer , Plug one end into the network card of another computer , The signal sent by one end can be realized at the physical level , The other end can receive the function .
Of course , Except that the cables have to cross , Also configure the of these two computers IP Address 、 Subnet mask and default gateway . If you want two computers to be able to communicate , These three must be configured as a network .
that , How to connect the three networks together ? Except for the switch , There's another one called Hub Things that are , That's the hub . This device has multiple ports , You can connect multiple computers . however , It's different from a switch , The hub has no brain , It works entirely in the physical layer , It will send every byte it receives , Copy to other ports .
this , It is the connectivity scheme of the first physical layer .
2、 Data link layer
Hub It adopts the mode of broadcasting , Several problems need to be solved :
- Who did the bag go to ?
- Will multiple machines contract out at the same time cause confusion ? Is there a priority rule
- How to solve the problem of sending errors ?
These problems are the data link layer , That is to say MAC Layer to be solved .
MAC The full name is Medium Access Control, Media access control , The control is when sending data to the media , Who starts first , Who's behind , Prevent confusion . The solution is the second problem , The rule in the problem is called multiple access .
Solution : Channel division 、 Take turns 、 Random access protocol
Solve the first problem , You need a physical address , It's called link layer address , Also called MAC Address .
For Ethernet , The beginning of the second floor , It's the goal MAC Address and source address .

Then there's the type . Most of the types are IP Data packets , then IP It contains TCP、UDP as well as HTTP etc. , It's all about the inner packaging .
Had a target MAC Address , Packets broadcast over the link ,MAC Only with your network card can you know that this bag is for it .
MAC Put your bag away with your network card , Then open the IP package , Find out IP The address is your own , And on again TCP package , Discover that the port is itself , That is to say nginx Monitoring 80, The request is then submitted to nginx.
nginx Return to a web page . Then send the web page to the machine that needs to send back the request . Then the hierarchical encapsulation , The last to MAC layer . The source of coming MAC Address , When you return, it becomes the destination address , Return to the requested machine .
For Ethernet , The last side of the second floor is CRC, That is to say Cyclic redundancy detection . adopt XOR The XOR algorithm , To calculate whether the whole packet has an error in the sending process , It mainly solves the third problem .
There's another problem , If the source machine does not know the target machine's MAC Address , What to do ?
This requires ARP agreement , It is known that IP Address , seek MAC Address agreement .
In a LAN , Send a broadcast packet query .
To avoid using it every time ARP request , The machine will do it locally ARP cache . Of course , The machine will go online and offline IP It could change , therefore ARP Of MAC The address cache will expire after a period of time .
【 attach :RARP agreement 】 A machine without a hard disk is a diskless workstation , Cannot persist IP Address with local , But there are network cards , So it can be used RARP Agreement to get IP Address .RARP It can also be applied to the machine that the LAN administrator wants to specify IP( Bind to the machine , immutable ), I don't want every machine to set static IP The situation of , Can pass in RARP Configuration on the server MAC and IP For the ARP surface ,, But get the of each machine MAC The address is also very troublesome . Now use BOOTTP and DHCP There are more .
by Hub Networking mode , Once the number of machines increases , There will be problems . because Hub It's broadcast , Whether an interface needs , be-all Bit Will be sent back , Then let the host determine whether it needs , Doing so will cause a lot of waste , And prone to conflict .
What kind of machine can remember a computer's MAC Address , If the target machine MAC Not from this computer , Just don't forward it ? Obviously, it can bring MAC Take your head off , Check the target MAC Address , Then the layer-2 device switch forwarded according to the policy !
How does the switch know the computer of each port MAC The address? ? Through the study !
a MAC1 The computer sends a bag to MAC2 The computer , When the packet first arrived at the switch , I don't know MAC2 Which port is your computer at , The packet can only be forwarded to all ports except the one from which it came , meanwhile , Exchange opportunities and remember MAC1 Mouth from , The destination address of the package in the future is MAC1 when , Send it directly to this port .
When the switch works for a period of time , There's a whole network structure , This is the time , There's basically no need to broadcast . Of course , Of every machine IP The address will change , The mouth where you are will change , thus , Forwarding table —— That is, the learning result of the switch , There is also an expiration time .
5、 ... and 、 Switches and VLAN
Multiple switches are connected together , Formed topology . When the topology is too complex , The network cable goes around , There will inevitably be some accidents , The most common one is Loop problem ( Two switches connect two LANs at the same time ).
When a loop occurs , Two packages go around , The road will be blocked , How to break the loop ?
In data structure , There's a way Minimum spanning tree . We often refer to rings as graphs , Break the ring in the graph , It becomes a tree . In a computer network , The algorithm of spanning tree is called STP(Spanning Tree Protocol).
STP Some concepts in the protocol :
Root Bridge: Root switch .
Designated Bridges: Specify switch . Other switches go to the Dagen switch through the designated switch .
Bridge Protocol Data Units(BPDU): Bridge protocol data unit . Only the root switch can send , Other switches can only convey the instructions of the root switch .
Priority Vector: Priority vector . A group of ID number :Root Bridge ID,Root Path Cost( Distance from the root router ),Bridge ID,Port ID. The smaller the value. , The higher the priority .
Too many switches will face isolation problems , Can pass VLAN Form a virtual lan . Use VLAN, A switch will be connected to machines belonging to multiple LANs . Just add one on the head of the original second floor TAG,TAG Store one in the 12 Bit VLAN ID, You can distinguish which LAN the machine belongs to .
If we buy a switch that supports VLAN Of , When this switch takes down the head of the second floor , You can identify this VLAN ID, such , Only the same VLAN My bag , Will forward to each other . such , Broadcasting problems and security problems can be solved .
You can set the... To which each port of the switch belongs VLAN.
Support VLAN Switchboard , There is a kind of oral call Trunk mouth , It can be forwarded to any VLAN The mouth of , Switches can be connected to each other through this port .
6、 ... and 、ICMP And ping
ICMP Full name Internet Control Message Protocol, Internet control message protocol
When a network packet is transmitted in a complex network environment , There are always problems . When there is a problem , There's a message coming out , Report the situation , Before you can adjust the transmission strategy .
ICMP The message itself is very simple , It's encapsulated in IP The inside of the bag . Because the source address and destination address must be required when transmitting instructions .
ICMP There are many types of messages , Different types have different codes . The most common type is active request 8, The response to the active request is 0
1、 Query message type
frequently-used ping It's a query message , It's an active request , And actively get a response ICMP agreement .ping The package sent also conforms to ICMP Form of agreement , It just adds its own format at the back .
Yes ping The active request of , Carry out network packet capturing , be called ICMP ECHO REQUEST, Empathy , Unsolicited response , be called ICMP ECHO REPLY, Compared with the original ICMP, There are two more fields: identifier and serial number . In the option data ,ping It also stores the time value of sending the request , To calculate the round-trip time , Explain the distance .
ping: Use of query message type
ping When executing an order , The source host will first build a ICMP Request packet ,ICMP The packet contains multiple fields , The two most important , One is the type field , For request packets, the field is 8; The other is the sequence number , Mainly used to distinguish continuous ping When sending out multiple packets . Every packet sent , The sequence number will be added automatically 1. In order to be able to calculate the round trip time RTT, It will insert the sending time in the data part of the message .
then , from ICMP The protocol will send this packet with the address 192.168.1.2 Give it to IP layer .IP The layers will be 192.168.1.2 As the destination address , This machine IP Address as source address , Plus some other control information , Construct a IP Data packets .
Next , Need to add MAC head . If in this section ARP Find... In the mapping table IP Address 192.168.1.2 The corresponding MAC Address , You can use it directly ; without , You need to send ARP Protocol query MAC Address , get MAC After the address , Building a data frame from the data link layer , The destination address is IP From the floor MAC Address , The source address is native MAC Address ; And add some control information , According to the media access rules of Ethernet , Send them out .
host B After receiving this data frame , Check its purpose first MAC Address , And with the native MAC Address contrast , Accept if it meets the requirements , If not, discard . After receiving, check that the data frame will IP Packets are extracted from frames , Give it to this machine IP layer . Again ,IP After layer inspection , Extract useful information and give it to ICMP agreement .
host B Will build a ICMP Answer pack , The type field of the response packet is 0, The sequence number is the sequence number in the received request packet , And then send it to the host A.
Within the prescribed time , If the source host does not receive ICMP The answer pack , The target host is not reachable ; If you receive ICMP Answer pack , It means that the target host can reach . here , The source host will check , Subtract the time when the packet was originally sent from the source host from the current time , Namely ICMP Packet time delay .
If you cross network segments , It also involves the forwarding of the gateway 、 Router forwarding, etc .
If you are within your control , When you encounter the problem of network failure , In addition to direct ping Target IP Outside the address , There should also be a clear network topology . It is necessary to clearly know which devices a network packet needs to pass from the source address to the destination address , And then one by one ping An intermediate device or machine . If possible , At these key points , adopt tcpdump -i eth0 icmp, Check to see if the package has reached a certain point , Where did the reply packet arrive , It's easier to infer the location of the error .
If it's no longer under our control , Many intermediate devices are prohibited ping Of , however ping It doesn't mean that the network is blocked , Use... At this time telnet, Test whether the network is unblocked through other protocols .
2、 Error message type :
Reports initiated by abnormal conditions correspond to ICMP Error message type of
3 The end is unreachable . The network unreachable code is 0, The host is not reachable 1, The agreement is not reachable 2, Port unreachable 3, It needs to be segmented, but no segmentation is set 4
4 Source inhibition . That is, let the source station slow down the transmission speed .
11 Overtime . Beyond the lifetime of the network packet .
5 Redirect , Let's send it to another router next time
The structure of error message is relatively complex , Except for the front, it's still IP,ICMP Before 8 The byte doesn't change , Then follow the wrong IP Bag IP The head and IP Text Before 8 Bytes .
No error message is generated :
- For carrying ICMP Datagram of error message , No longer produce ICMP Error message . If the host A Sent a ICMP Send the data message to the host B, An error occurred when the data passed through one of the routers during transmission , Because the router has received a ICMP The data packet , So there won't be another ICMP Error message .
- For segmented datagrams , If it's not the first slice , It doesn't produce ICMP Error message . For hosts A Sent a piece of data , If the fragment data received by the routing device or host is not the first fragment data , Will not produce ICMP Error message .
- For datagrams with multicast addresses , Do not produce ICMP Error message . If one ip If the address is a broadcast address , Will not produce ICMP Error message .
- For special addresses, such as (127.0.0.0 or 0.0.0.0) Datagram , Do not produce ICMP Error message .
Traceroute: Use of error message types
Traceroute Will use ICMP The rules , Deliberately creating scenarios that can make mistakes .
Traceroute The first function of is to deliberately set up special TTL(Time To Live Survival time value , This field specifies IP The maximum number of network segments that a packet is allowed to pass through before it is discarded by the router ), To track the routers that pass by on their way to their destinations .Traceroute The parameter of the is pointing to a purpose IP Address , It will send one UDP Data packets of , Willingly TTL Set to 1, such , When you encounter the first router, you will return a ICMP package , That is to say Network error packets , The type is time out .
【 attach : About Traceeoute Hair UDP, Error return ICMP Why : Under normal circumstances , Protocol stack goes to UDP, Will return normally UDP, But the host unreachable is the network layer ( Not yet arrived UDP, Transport layer ), I'll only come back ICMP( The network layer ), Message fragmentation is the same 】
Next , take TTL Set to 2、3…… So again and again , Know to reach the target host . such ,Traceroute I got all the routers IP. Of course , Some routers will not return this ICMP, This is also Traceroute A public address , The reason why you can't see the intermediate route .
How do I know UDP Did you get to the destination host ?Traceroute The program will send a copy of UDP The packet is sent to the destination host , But it will choose an impossible value as UDP Port number ( Greater than 30000), When the packet arrives , Will make the destination host's UDP The module generates a copy of “ Port unreachable ” error ICMP message . If the data doesn't arrive , It could be overtime .
Traceroute Another function is to deliberately set no segmentation , To determine the path of MTU. The first thing to do is to send packets , And set up “ Not in pieces ” sign . The length of the first packet sent is just the same as the exit MTU equal . If there is a narrow gap in the middle, it will get stuck , Will send ICMP Network error packets , The type is “ Sharding is required but the non sharding bit is set ”. Every time I received ICMP“ Inseparable ” When there is an error, the length of the packet is reduced , Until we reach the target host .
版权声明
本文为[Pistachio 2021]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231358276998.html
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
![MySQL [read / write lock + table lock + row lock + mvcc]](/img/a9/ace85899a01a7d4fd80b2e631e44d6.png)
MySQL [read / write lock + table lock + row lock + mvcc]
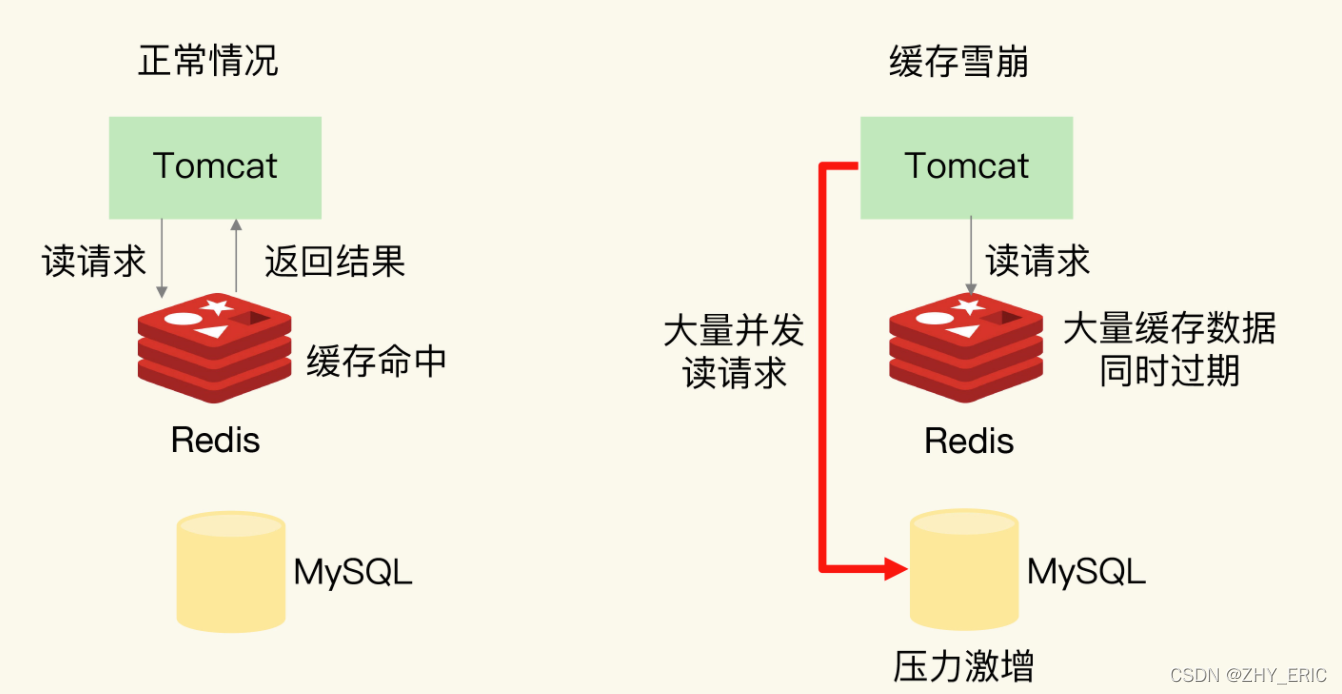
How does redis solve the problems of cache avalanche, cache breakdown and cache penetration
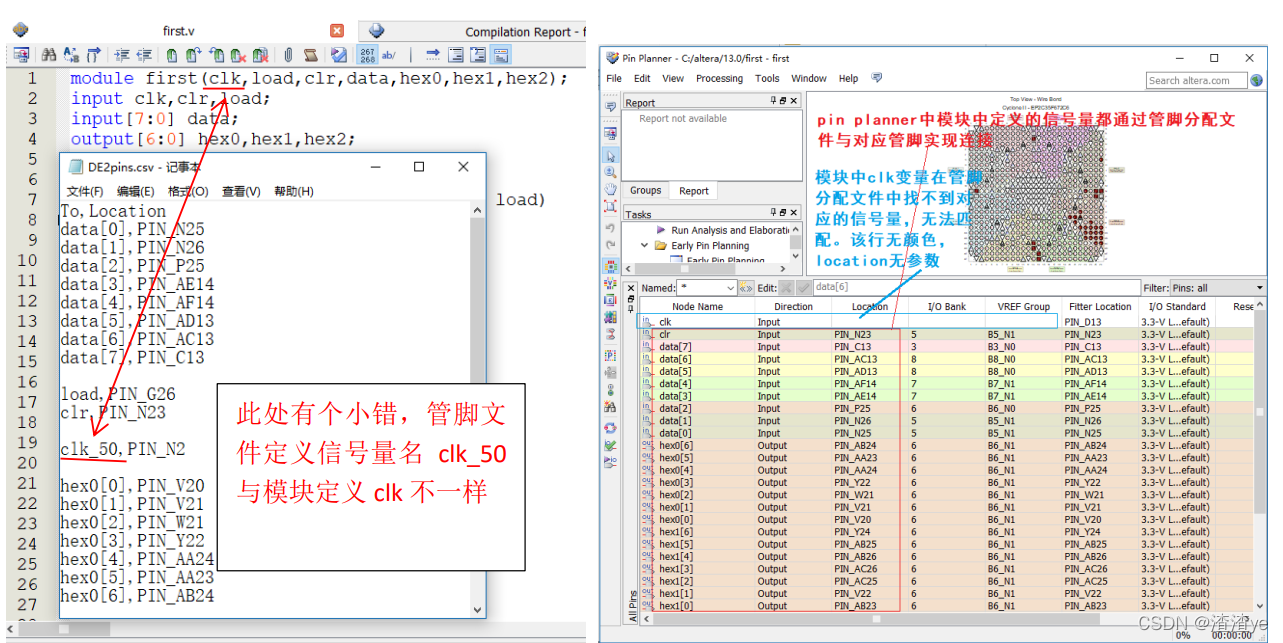
Quartus Prime硬件实验开发(DE2-115板)实验一CPU指令运算器设计

Express middleware ③ (custom Middleware)

Express②(路由)
Wechat applet
![MySQL [SQL performance analysis + SQL tuning]](/img/71/2ca1a5799a2c7a822158d8b73bd539.png)
MySQL [SQL performance analysis + SQL tuning]
The art of automation

Leetcode | 38 appearance array
Port occupied 1
随机推荐
Tensorflow Download
Analysis of unused index columns caused by implicit conversion of timestamp
JS 力扣刷题 102. 二叉树的层序遍历
解决方案架构师的小锦囊 - 架构图的 5 种类型
Oracle RAC database instance startup exception analysis IPC send timeout
【项目】小帽外卖(八)
Get the attribute value difference between two different objects with reflection and annotation
33 million IOPs, 39 microsecond delay, carbon footprint certification, who is serious?
OSS cloud storage management practice (polite experience)
Postman reference summary
村上春树 --《当我谈跑步时,我谈些什么》句子摘录
RAC environment alert log error drop transient type: systp2jw0acnaurdgu1sbqmbryw = = troubleshooting
YARN线上动态资源调优
Neuron and neural network
19c environment ora-01035 login error handling
Android篇:2019初中级Android开发社招面试解答(中
AttributeError: ‘dict‘ object has no attribute ‘iteritems‘
神经元与神经网络
Spark入门基本操作
What is the difference between blue-green publishing, rolling publishing and gray publishing?