当前位置:网站首页>PyMySQL
PyMySQL
2022-04-23 14:02:00 【沉觞流年】
PyMySQL是从Python连接到MySQL数据库服务器的接口。 它实现了Python数据库API v2.0,并包含一个纯Python的MySQL客户端库
安装PyMySQL
pip install PyMySQL
若下载速度慢,可使用国内镜像源
pip install PyMySQL -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
安装成功后,测试是否能连接上数据库
import pymysql
# 创建链接,连接数据库(服务器地址、端口号、用户名、密码、数据库名称、编码格式)
conn = pymysql.connect(host="192.168.134.1",
port=3306,
user='root',
passwd='123456',
db='testdb',
charset='utf8')
# 使用cursor()方法获取一个游标(查询数据返回为元组格式)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 执行sql语句中查询版本信息的方法
sql = '''SELECT VERSION(); '''
cursor.execute(sql)
# 查询所有数据,返回数据为元组格式
data = cursor.fetchall()
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭链接
conn.close()
print("数据库版本为:{}".format(data))
打印结果
数据库版本为:(('10.3.27-MariaDB-0+deb10u1',),)
【注意】:sql语句结尾最好带上;
创建数据库表
import pymysql
# 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host="192.168.134.1",
port=3306,
user='root',
passwd='123456',
db='testdb',
charset='utf8')
# 创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 若表存在则删除
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS users")
# 准备建表的语句
sql = """CREATE TABLE users( id int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, phonenum int(20) NOT NULL, nickname char(20) DEFAULT NULL, sex char(1) DEFAULT NULL, birth_year int(4) DEFAULT NULL, birth_month int(2) DEFAULT NULL, birth_day int(2) DEFAULT NULL, avatar char(10) DEFAULT NULL, location char(10) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;"""
#执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
插入操作
将记录创建到数据库表中时,需要执行INSERT操作。
import pymysql
# 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host="192.168.134.1",
port=3306,
user='root',
passwd='123456',
db='testdb',
charset='utf8')
# 创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 准备sql语句
sql = """INSERT INTO users(phonenum,nickname, sex, birth_year,birth_month,birth_day,avatar,location) VALUES (13766665555,'bobo',1,1998,5,27,'00','gz')"""
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
except:
# 若出现错误,则回滚
conn.rollback()
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
查询操作
在建立数据库连接后,就可以对此数据库进行查询了。 可以使用fetchone()方法获取单条记录或fetchall()方法从数据库表中获取多个值。
-
fetchone()获取查询结果集的下一行。 结果集是当前使用游标对象来查询表时返回的对象。 -
fetchmany(n)获取查询结果集的下n行。 结果集是当前使用游标对象来查询表时返回的对象。 -
fetchall()获取结果集中的所有行。 如果已经从结果集中提取了一些行,则从结果集中检索剩余的行。
users 表内容
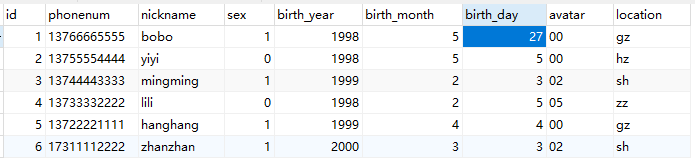
游标在初始位置,可通过fetchall() 获取结果集中的所有行
import pymysql
# 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host="192.168.134.1",
port=3306,
user='root',
passwd='123456',
db='testdb',
charset='utf8')
# 创建游标(查询数据返回为元组格式)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 1. 执行SQL,进行查询操作
sql1= '''SELECT * FROM users WHERE sex =1 ; '''
effect_row1 = cursor.execute(sql1)
# 2. 展示查询的所有数据,返回数据为元组格式
result1 = cursor.fetchall()
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
print(result1)
# 打印结果
''' ( (1, '13766665555', 'bobo', 1, 1998, 5, 27, '00', 'gz'), (3, '13744443333', 'mingming', 1, 1999, 2, 3, '02', 'sh'), (5, '13722221111', 'hanghang', 1, 1999, 4, 4, '00', 'gz'), (6, '17311112222', 'zhanzhan', 1, 2000, 3, 3, '02', 'sh') ) '''
游标在初始位置,可通过fetchone() 获取查询结果集的第一行
(对于数据库中的数据,查询出来后为了方便进行处理,可转化为字典格式,通过key-value的方式获取需要的数据)
import pymysql
# 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host="192.168.134.1",
port=3306,
user='root',
passwd='123456',
db='testdb',
charset='utf8')
# 创建游标(查询数据返回为字典格式)
cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 1. 执行SQL,进行查询操作
sql1= '''SELECT * FROM users WHERE sex =1 ; '''
effect_row1 = cursor.execute(sql1)
# 2. 仅展示查询数据的第一条
result1 = cursor.fetchone()
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
print(result1)
# 打印结果
''' {'id': 1, 'phonenum': '13766665555', 'nickname': 'bobo', 'sex': 1, 'birth_year': 1998, 'birth_month': 5, 'birth_day': 27, 'avatar': '00', 'location': 'gz'} '''
通过fetchone() 获取数据时,游标在初始位置,所以fetchone() 获取的数据是查询集中的第一条数据;
通过fetchmany(2) 获取数据时,游标在初始位置的下一行,所以fetchmany(2) 获取的数据是查询集中的第二条和第三条数据;
通过fetchall() 获取数据时,游标也发生了移动,此时测试集中仅剩一条数据,所以fetchall() 获取的数据是查询集中的最后一条数据(第四条);
import pymysql
# 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host="192.168.134.1",
port=3306,
user='root',
passwd='123456',
db='testdb',
charset='utf8')
# 创建游标(查询数据返回为元组格式)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 1. 执行SQL
sql1= '''SELECT * FROM users WHERE sex =1 ; '''
effect_row1 = cursor.execute(sql1)
# 2. 返回数据
result1 = cursor.fetchone()
result2 = cursor.fetchmany(2)
result3 = cursor.fetchall()
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
print(result1)
print(result2)
print(result3)
# 打印结果
''' result1 (1, '13766665555', 'bobo', 1, 1998, 5, 27, '00', 'gz') result2 ( (3, '13744443333', 'mingming', 1, 1999, 2, 3, '02', 'sh'), (5, '13722221111', 'hanghang', 1, 1999, 4, 4, '00', 'gz') ) result3 ( (6, '17311112222', 'zhanzhan', 1, 2000, 3, 3, '02', 'sh'), ) '''
【拓展】 :执行sql语句时,sql里面的参数,可能需要动态传参,
比如 select * from users where phonenum ='13766665555';里面的手机号码,需要从excel文件中动态获取然后进行查询,这里可以有两种方式。
- 一是采用
format函数:
sql = "select * from users where phonenum ={};".format(phone)
但是一般情况下不推荐使用format函数,因为format函数里的内容可以比较长,内容比较多,可能造成sql注入等一系列安全问题,比如插入执行了一条删除语句,可能就会造成表的删除
- 二是通过
%s占位符
按住Ctrl,点击cursor.execute(sql1)中的execute()函数,跳转到源码
def execute(self, query, args=None):
"""Execute a query :param str query: Query to execute. :param args: parameters used with query. (optional) :type args: tuple, list or dict :return: Number of affected rows :rtype: int If args is a list or tuple, %s can be used as a placeholder in the query. If args is a dict, %(name)s can be used as a placeholder in the query. """
while self.nextset():
pass
query = self.mogrify(query, args)
result = self._query(query)
self._executed = query
return result
这里解释了, execute() 函数是可以传递参数的,这个参数可以是列表、元组、字典
sql = "select * FROM users WHERE birth_year < %s and birth_month > %s "
cursor.execute(sql=sql,args=[2000,4])
这种方式会更加安全
封装查询
对于数据库中的数据,查询操作是最常用的操作,在接口自动化测试项目中,经常会要查询数据库中的数据,这里简单封装一下查询操作
这里介绍两种封装方式
第一种:数据库配置不需要改动,则将数据库信息填写到初始化配置中
import pymysql
from pymysql.cursors import DictCursor
class MysqlUtil:
def __init__(self,return_dict=False):
# 配置数据库
self.coon = pymysql.connect(
host="192.168.174.132",
port=3306,
user='bobo',
passwd='hh123456',
db='swiper',
charset='utf8'
)
# self.cursor = self.coon.cursor(DictCursor)
if return_dict:
self.cursor = self.coon.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 指定每行数据以字典的形式返回
else:
self.cursor = self.coon.cursor() # 指定每行数据以元祖的形式返回
def close(self):
self.cursor.close() # 关闭查询
self.coon.close() # 关闭连接
# 查询一条数据
def fetch_one(self, sql):
# 执行SQL
self.cursor.execute(sql)
# 获取结果
result = self.cursor.fetchone() # 返回元祖()/ 返回字典 {}
return result # 返回结果
# 查询多条数据
def fetch_all(self, sql):
# 执行SQL
self.cursor.execute(sql)
# 获取结果
results = self.cursor.fetchall() # 返回列表 [(),()...] / [{},{}...]
return results
if __name__ == '__main__':
mysql = MysqlUtil(return_dict=True)
sql = "select * from users where phonenum ='13766665555';"
result = mysql.fetch_one(sql)
print(result["birth_day"])
# 注意一定要关闭
mysql.close()
# 打印结果 27
第二种:出于安全考虑,将数据库信息写到配置文件中,类的复用性更高,且sql更安全
import pymysql
from pymysql.cursors import DictCursor
class DBHandler:
# init中的数据后续换成由config文件中读取
def __init__(self,host="192.168.174.132",
user='bobo',
passwd='hh123456',
db='swiper',
charset='utf8',
cursorclass=DictCursor,
**kw
):
# 创建连接
self.con = pymysql.connect(host=host,user=user,passwd=passwd,db=db,charset=charset,cursorclass=cursorclass,**kw)
# 创建游标(查询数据返回为字典格式)
self.cursor = self.con.cursor()
def query(self,sql,args=None,query_one=True):
'''查询语句,默认只查询一条'''
self.cursor.execute(sql,args)
# 获取结果
if query_one :
return self.cursor.fetchone()
else:
return self.cursor.fetchall()
def close(self):
self.cursor.close() # 关闭查询
self.con.close() # 关闭连接
if __name__ == '__main__':
sql = "select * FROM users WHERE birth_year < %s and birth_month>%s "
db = DBHandler()
res =db.query(sql=sql,args=[2000,4],one=False)
print(res)
# 结果
[
{
'id': 1, 'phonenum': '13766665555', 'nickname': 'bobo', 'sex': 1, 'birth_year': 1998, 'birth_month': 5, 'birth_day': 27, 'avatar': '00', 'location': 'gz'},
{
'id': 2, 'phonenum': '13755554444', 'nickname': 'yiyi', 'sex': 0, 'birth_year': 1999, 'birth_month': 5, 'birth_day': 5, 'avatar': '00', 'location': 'hz'}
]
更新操作
UPDATE 语句可对任何数据库中的数据进行更新操作,它可用于更新数据库中已有的一个或多个记录。
import pymysql
# 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host="192.168.134.1",
port=3306,
user='root',
passwd='123456',
db='testdb',
charset='utf8')
# 创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 准备sql语句(将sex=0的人的出生年份+1)
sql = "UPDATE users SET birth_year = birth_year + 1 WHERE SEX = '%c'" % ('0')
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
except:
# 若出现错误,则回滚
conn.rollback()
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
删除操作
当要从数据库中删除一些记录时,那么可以执行DELETE操作。
import pymysql
# 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host="192.168.134.1",
port=3306,
user='root',
passwd='123456',
db='testdb',
charset='utf8')
# 创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 准备sql语句(将birth_year 在2000年后的人删除)
sql = "DELETE FROM users WHERE birth_year > '%d'" % (2000)
try:
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
except:
# 若出现错误,则回滚
conn.rollback()
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
封装PyMySQL
dbconf.yaml
db_product:
dbname: test
host: test.com
port: 3306
user: Admin
pwd: 123456
db_test:
dbname: testdb
host: 192.168.132.1
port: 3306
user: bobo
pwd: 123456
通过读取 yaml 文件中的配置信息,连接数据库,进行数据库操作
DBHandler.py
import pymysql
from pymysql.cursors import DictCursor
class MysqlUtil:
def __init__(self,dbconf):
self.dbconf = dbconf
self.conn = self.get_conn() # 连接对象
self.cursor = self.get_cursor() # 游标对象
def get_conn(self):
""" 获取连接对象 """
conn = pymysql.connect(host=self.dbconf['host'],
port=self.dbconf['port'],
user=self.dbconf['user'],
passwd=self.dbconf['pwd'],
db=self.dbconf['dbname'],
charset='utf8')
return conn
def get_cursor(self):
"""获取游标对象"""
# cursor = None
cursor = self.conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
return cursor
def query(self, sql, args=None, one=True):
'''查询语句,默认只查询一条'''
self.cursor.execute(sql, args)
# 获取结果
if one:
return self.cursor.fetchone()
else:
return self.cursor.fetchall()
def commit_data(self, sql):
""" 提交数据(更新、插入、删除操作) """
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
def close(self):
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close()
YamlHandler.py
import yaml
# 读取yaml文件
class ReadYaml:
def __init__(self, path, param=None):
self.path = path # 文件路径
self.param = param # 不传默认获取所有数据
# 获取yaml文件中的数据
def get_data(self, encoding='utf-8'):
with open(self.path, encoding=encoding) as f:
data = yaml.load(f.read(), Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
if self.param == None:
return data # 返回所有数据
else:
return data.get(self.param) # 获取键为param的值
测试执行文件
test.py
from DBHandler import MysqlUtil
from YamlHandler import ReadYaml
import os
if __name__ == '__main__':
dir_path = os.path.split(os.path.abspath(__file__))[0]
yaml_path = os.path.join(dir_path,'test.yaml')
db_conf = ReadYaml(yaml_path,'db_test').get_data()
db = MysqlUtil(db_conf)
sql = "select * FROM users WHERE birth_year < %s and birth_month>%s "
res = db.query(sql=sql, args=[2000, 4], one=False)
print(res)
db.close()
版权声明
本文为[沉觞流年]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44614026/article/details/123387913
边栏推荐
- 室内外地图切换(室内基于ibeacons三点定位)
- Un modèle universel pour la construction d'un modèle d'apprentissage scikit
- 浅谈基于openssl的多级证书,Multi-level CA的签发和管理,以及双向认证
- 生产环境——
- linux安装mysql后修改密码
- Quartus prime hardware experimental development (de2-115 board) experiment II function adjustable comprehensive timer design
- Introduction to spark basic operation
- Quartus Prime硬件实验开发(DE2-115板)实验二功能可调综合计时器设计
- 微信小程序进行蓝牙初始化、搜索附近蓝牙设备及连接指定蓝牙(一)
- Programming travel function
猜你喜欢
Quartus prime hardware experimental development (de2-115 board) experiment II function adjustable comprehensive timer design

Android interview theme collection
What is the difference between blue-green publishing, rolling publishing and gray publishing?
Quartus prime hardware experimental development (de2-115 board) experiment 1 CPU instruction calculator design
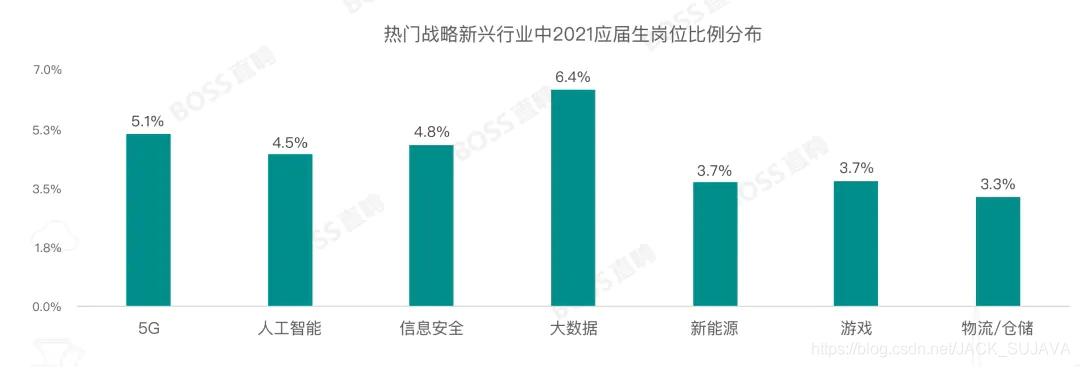
Autumn recruitment in 2021, salary ranking No
Qt Designer怎样加入资源文件
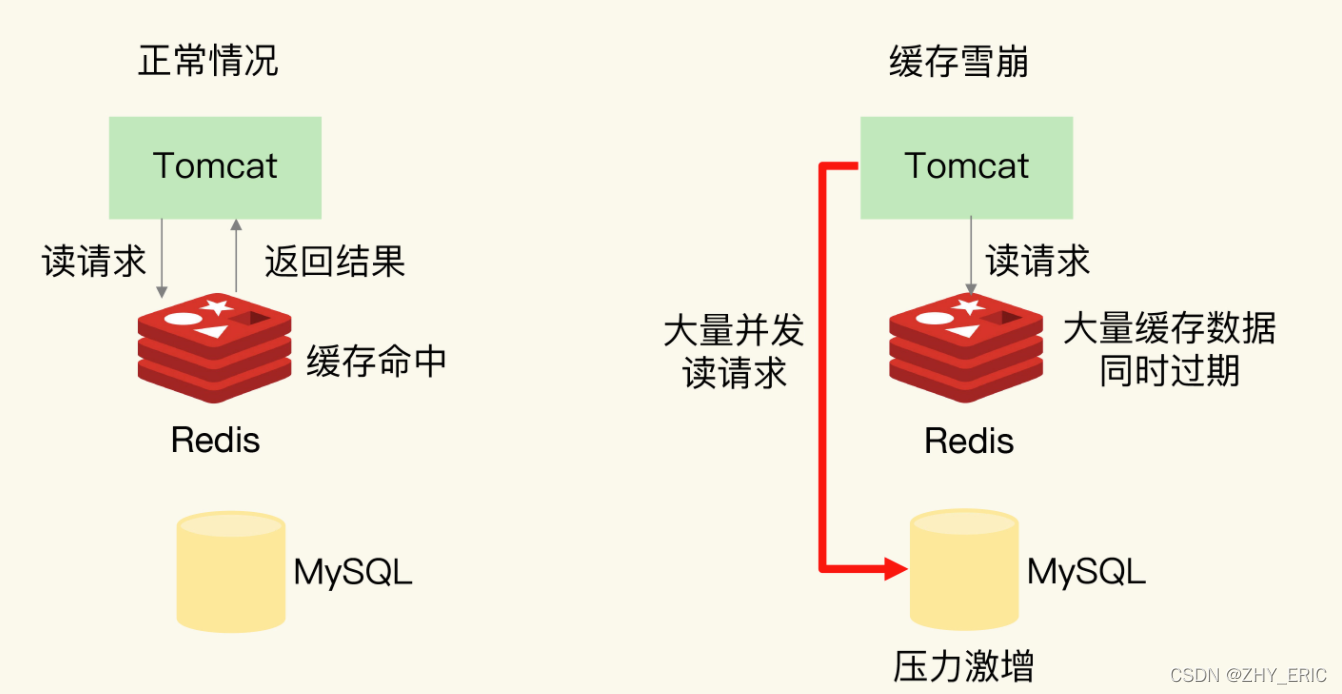
How does redis solve the problems of cache avalanche, cache breakdown and cache penetration
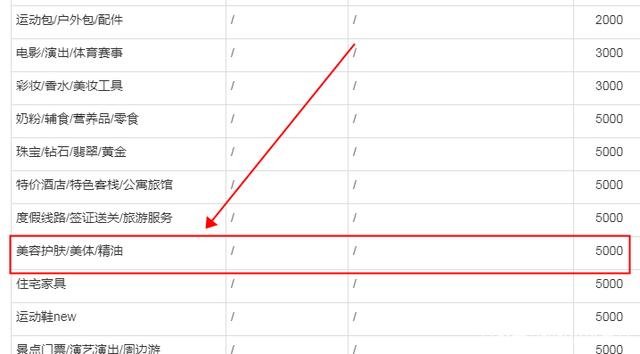
淘宝发布宝贝提示“您的消保保证金额度不足,已启动到期保障”
记录一个奇怪的bug:缓存组件跳转之后出现组件复制
Program compilation and debugging learning record
随机推荐
基于微信小程序的wifi模块使用
Logging模块
基于ibeacons三点定位(微信小程序)
联想产品经理林林:天津当地网络运营商网络故障 ZUI系统后台服务器暂时无法正常工作
SQL数据库
基于ibeacons签到系统
Record a strange bug: component copy after cache component jump
Taobao released the baby prompt "your consumer protection deposit is insufficient, and the expiration protection has been started"
微信小程序与低功耗蓝牙通信-接受硬件端发送来的数据(四)
理解虚基类、虚函数与纯虚函数的概念(转)
AtCoder Beginner Contest 248C Dice Sum (生成函数)
elmo(BiLSTM-CRF+elmo)(Conll-2003 命名实体识别NER)
FBS(fman build system)打包
The art of automation
Android interview theme collection
VsCode-Go
Quartus prime hardware experimental development (de2-115 board) experiment II function adjustable comprehensive timer design
室内外地图切换(室内基于ibeacons三点定位)
3300万IOPS、39微秒延迟、碳足迹认证,谁在认真搞事情?
nodejs通过require读取本地json文件出现Unexpected token / in JSON at position