当前位置:网站首页>Keywords static, extern + global and local variables
Keywords static, extern + global and local variables
2022-04-23 20:47:00 【Computer white】

Catalog
One 、 A brief introduction to global and local variables
Two 、 keyword + Detailed explanation of global and local variables
1. keyword static+ Modify local variables
2. keyword extern+ Modify global variable
Preface
C All variables in a language have their own scope .C Variables in language , There are two types of... By scope , Local variables and global variables . Before learning global and local variables , First of all, we need to understand the keywords static and extern( Next I will introduce in detail )
Once in the program, it's like a sea , Since then, long hair is a passer-by ......
One 、 A brief introduction to global and local variables
null , stay {} The variables defined inside are local variables , stay {} All variables defined outside are global variables
#include <stdio.h>
int b = 10; //b Defined as a global variable
int main()
{
int i = 0;//i Defined as a global variable
return 0;
}
Two 、 keyword + Detailed explanation of global and local variables
stay C In language , Keywords are C Language gives us , You can't create !!!
static Is used to modify variables and functions :
1. Modify local variables - Called static local variables
2. Modify global variable - Called static global variables
3. Modify function - Called static function
1. keyword static+ Modify local variables
The following code example :
// Code 1( Without any modification )
#include <stdio.h>
void test()
{
static int i=0;
i++;
printf("%d ", i);
}
int main()
{
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
{
test();
}
return 0;
}
Code example after running ( Yes no static Modify and contrast ):


From the above we can see that , When the code has no static When decorating , The result of running is different ...
The first code diagram runs parsing ( nothing static When decorating ): We all know that code execution is compiled and executed from top to bottom , Compile to for loop , That is, enter the custom function test(),test() Is an independent piece of program code , When a piece of program code is executed , Our data will be destroyed , Not in storage , This led to the second visit test() when ,i The value of is still equal to 0; So the running structure of the program will have a loop , Always for 1.
The first code diagram runs parsing ( Yes static When decorating ): When there is static When decorating ,static Modifying a local variable will change the life cycle of the variable ,test() in i The value of is out of order test() This program code will not be destroyed ,i The value of will gradually increase , Static variables are out of scope and still exist , Until the end of the program , The life cycle is over
2. keyword extern+ Modify global variable
The following code example :
// Code 1
//test1.c( Create another source file )
int g_val = 2018;
//test.c
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", g_val);
return 0;
}
// Code 2
//test1.c( Create another source file )
static int g_val = 2018;
//test.c
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", g_val);
return 0;
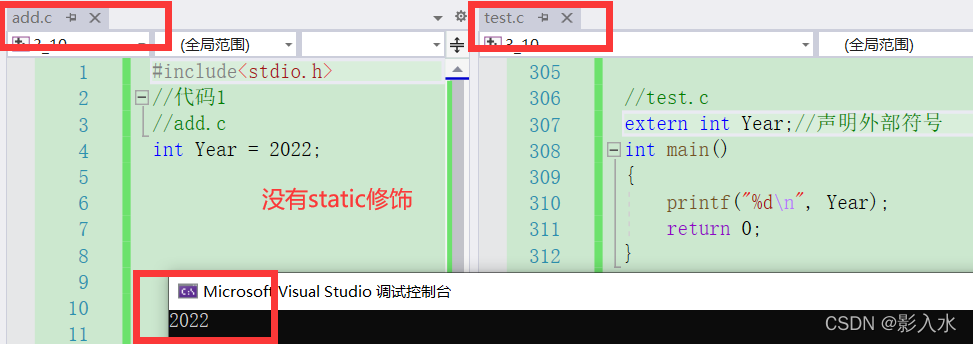
}Code example after running ( nothing static modification ):
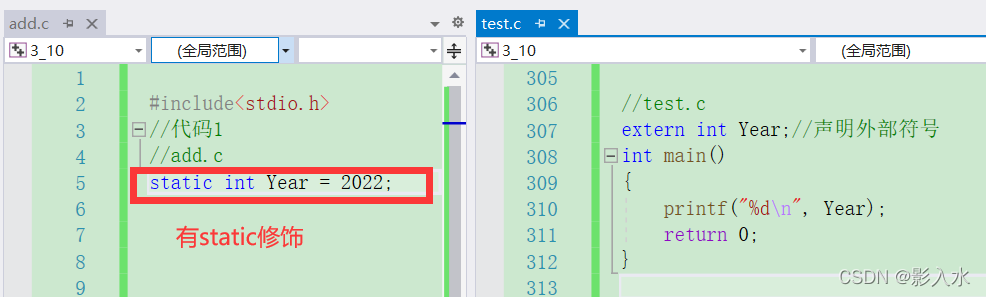
Code example after running ( Yes static modification ):
 From the above we can see that , When the code has no static When decorating , The result of running is different ...
From the above we can see that , When the code has no static When decorating , The result of running is different ...
The first code diagram runs parsing ( nothing static When decorating ): From the above, we can know that a global variable has external link properties , Can be used under different source files , You need keywords when using extern Statement can be used only
The second code diagram runs parsing ( Yes static When decorating ): A global variable is originally defined by an external link attribute , By static After modification , It becomes an internal link property , Can only be used in their own source file , Cannot be used in other files , In use, the scope becomes smaller , So there will be unresolved external symbols .
extern yes C Language keywords , Is used to declare external symbols .
If a project consists of multiple source files , If you want to refer to an external variable defined in another source file in one source file , You need to use... In the source file of the referenced variable extern Keyword declaration variables .
3.static Modify function
// Code 1
//add.c
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x+y;
}
//test.c
extern int Add(int x,int y);// Declare external symbols
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", Add(2, 3));
return 0;
}
// Code 2
//add.c
static int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
//test.c
extern int Add(int x,int y);// Declare external symbols
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", Add(2, 3));
return 0;
}
static The principle and of modifying function static Decorating global variables has the same effect , But draw the ladle according to the gourd , There's no show here. Parents can try it .
summary
Global static variables
advantage : Both object methods and class methods can access and modify global static variables , And external classes cannot call static variables , After definition, it will only point to the fixed pointer address , For all objects , Save a space .
shortcoming : The life cycle of existence is long , From definition to the end of the program .
Local static variable
advantage : After definition, only one value will exist , Each call uses the value of the memory address of the same object , Not recreated , Save a space , Can only be used in this local code block .
shortcoming : The life cycle of existence is long , From definition to the end of the program , Can only be used in this local code block .
版权声明
本文为[Computer white]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204210546128284.html
边栏推荐
- BMP JPEG picture to vector image contourtrace
- UKFslam
- Mysql database common sense storage engine
- go interface
- Is qiniu school useful and is the recommended securities account safe
- Cmake project under vs2019: calculating binocular parallax using elas method
- How to configure SSH public key in code cloud
- 又一款数据分析神器:Polars 真的很强大
- Parsing methods of JSON data in C - jar and jobobject: error reading jar from jsonreader Current JsonReader item
- Another data analysis artifact: Polaris is really powerful
猜你喜欢

Write table of MySQL Foundation (create table)

Devaxpress report replay: complete the drawing of conventional two-dimensional report + histogram + pie chart
MySQL basic collection

2022dasctf APR x fat epidemic prevention challenge crypto easy_ real
GSI-ECM工程建设管理数字化平台
vulnhub DC:1渗透笔记
Imitation Baidu map realizes the three buttons to switch the map mode by automatically shrinking the bottom

Unity solves Z-fighting

Come in and teach you how to solve the problem of port occupation
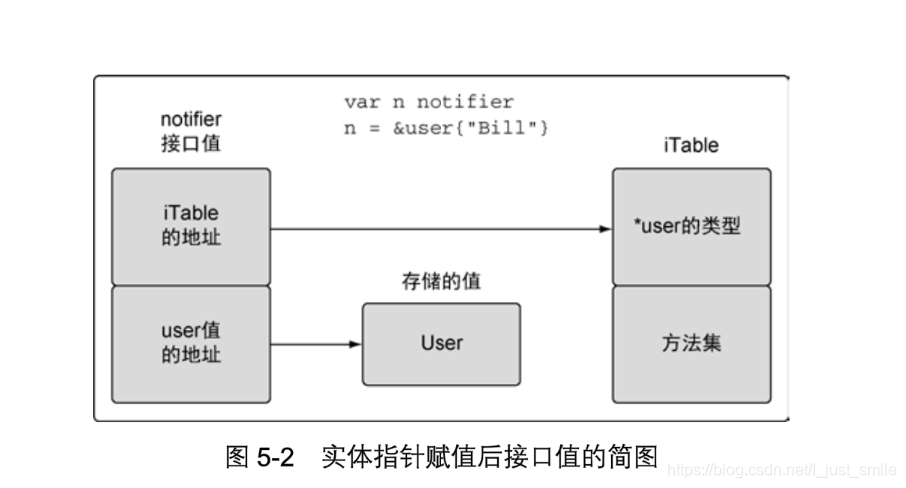
go interface
随机推荐
On the three paradigms of database design
The problem of 1 pixel border on the mobile terminal
深入探究ASP.NET Core读取Request.Body的正确方式
Elastic box model
MySQL数据库常识之储存引擎
Selenium 显示等待WebDriverWait
Resolve the eslint warning -- ignore the warning that there is no space between the method name and ()
MySQL 存储过程和函数
Unity animation creates sequence frame code and generates animationclip
Imitation Baidu map realizes the three buttons to switch the map mode by automatically shrinking the bottom
MySQL基础合集
go defer
缓存淘汰算法初步认识(LRU和LFU)
Devaxpress report replay: complete the drawing of conventional two-dimensional report + histogram + pie chart
LeetCode 1351、统计有序矩阵中的负数
MySQL进阶之常用函数
Learn to C language fourth day
Leetcode 232, queue with stack
启牛学堂有用吗,推荐的证券账户是否安全
Syntax Error: TypeError: this. getOptions is not a function