当前位置:网站首页>填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II [经典层次遍历 | 视为链表 ]
填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II [经典层次遍历 | 视为链表 ]
2022-04-23 14:50:00 【REN_林森】
经典层次遍历 | 视为链表处理
前言
成长需要过程,不是一步登天,需要不断改进的idea。本文通过 LeetCode题–填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II 来思维一步一步向前改进。
除此之外,还能学到经典层次遍历、hash + 递归、链表+dummyNode的利用(把链表next利用起来,将空间复杂度降下来,毕竟next域是花了空间的。)。
一、填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
二、题解
1、层次遍历
//填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
public class Connect {
/* target:每个节点的next指针指向同层右邻节点。 M1—典型的层次遍历+分层 */
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (null == root) return null;
Queue<Node> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.add(root);
int cnt = 1;
Node pre = null;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = que.poll();
if (cur.left != null) que.add(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) que.add(cur.right);
if (pre != null) pre.next = cur;
pre = cur;
if (--cnt == 0) {
pre = null;
cnt = que.size();
}
}
return root;
}
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
}
}
2、错误思维,但部分可参考
//递归方式解决
//bug:思路问题,该版本方法仅提供思路,行不同。
class Connect2 {
/* target:递归将每个节点的next指针指向同层右邻节点。 谁是右邻节点? 1-如果该节点是父节点的左孩子,那么它的右邻节点为其父节点的右孩子|(当父节点的右孩子为null时)父节点的next指针向兄弟节点的左孩子或右孩子(当左孩子为null时)。 2-如果该节点是父节点的右孩子,那么它的右邻节点为其父节点的next指针指向节点的左孩子节点或右孩子节点(当左孩子为空时)。 递归的标志--相同子问题就出来了--上述两种子问题。 M2-递归前序遍历,然后分情况来设置next指针的指向。 递归需要parent指针,当前节点,再配合判断即可完成2种情况的处理。 */
public Node connect(Node root) {
//递归处理next指针。
dfs(null, root);
//直接返回处理后的根节点即可。
return root;
}
/** * 递归处理next指针 * bug:当parent不为null,但其两个孩子都为null的情况,需要不断while寻找下一个同层兄弟。 * * @param parent 父节点 * @param root 当前节点 */
private void dfs(Node parent, Node root) {
//如果传入的当前节点是root,那么next就没什么好设置的了,也不用继续往下递归设置next,毕竟已经null了。
if (root == null) return;
//1-情况1--左孩子情况,需要将next指向父节点的右孩子。(当父节点的右孩子为null时)父节点的next指针向兄弟节点的左孩子或右孩子(当左孩子为null时)。
//当前节点可能是根节点,所以需要避免parent为null的情况,其实也可以把树分为两棵子树进行递归,这样就不会出现parent为null的情况。
if (parent != null && parent.left == root) {
if (parent.right != null || parent.next == null)
root.next = parent.right;
else if (parent.next.left != null)
root.next = parent.next.left;
else {
Node next = parent.next;
while (next != null && next.left == null && next.right == null) next = next.next;
root.next = next == null ? null : next.left != null ? next.left : next.right;
}
}
//2-情况2--右孩子情况,需要将next指向父节点next指针指向兄弟节点的左孩子|右孩子(左孩子为null时)。
//注:需要判断兄弟节点是否不存在,指向了null。
if (parent != null && parent.right == root && parent.next != null) {
if (parent.next.left != null) root.next = parent.next.left;
else {
Node next = parent.next;
while (next != null && next.left == null && next.right == null) next = next.next;
root.next = next == null ? null : next.left != null ? next.left : next.right;
}
}
//开始递归设置next。
dfs(root, root.left);
dfs(root, root.right);
}
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
}
}
3、根据2的错误思维中有用思维进行改进(hash记录每层tail节点 + 递归)
//方法二改进:记录每一层的pre节点,遇到一个节点,将该层的pre节点取出,如果pre==null,则不管,否则pre.next = cur node。最后更新pre为当前节点。
//M3--hash配合level层记录当层链表的tailNode + 设置链表的next + 更新链表的tail指向,即更新pre指向。
class Connect3 {
//方法二改进:记录每一层的pre节点,遇到一个节点,将该层的pre节点取出,如果pre==null,则不管,否则pre.next = cur node。最后更新pre为当前节点。
//M3--hash配合level层记录当层链表的tailNode + 设置链表的next + 更新链表的tail指向,即更新pre指向。
public Node connect(Node root) {
//递归处理next指针。
dfs(root, 1);
//直接返回处理后的根节点即可。
return root;
}
Map<Integer, Node> hash = new HashMap<>();
/** * 配合hashMap递归处理每一层链表的连接。 * * @param root * @param level */
private void dfs(Node root, int level) {
//如果传入的当前节点是root,那么next就没什么好设置的了,也不用继续往下递归设置next,毕竟已经null了。
if (root == null) return;
//设置该层链表的新tail
Node tail = hash.get(level);
if (null != tail) tail.next = root;
//更新tail
hash.put(level, root);
//开始递归设置每层链表next
dfs(root.left, level + 1);
dfs(root.right, level + 1);
}
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
}
}
4、利用next域将空间复杂度降到O(1)(同样采用错误方法2中的有用思维–视为链表)
/* 受方法三启示,其实就是把每层当着链表处理即可。 注:看到别人说,next类似B+树的next指针,当数据库搜索范围时,只需要logN确定起节点,然后next取后面范围内的节点。 注:就是人人都有next,这样利用好next,则知道上一层的所有节点,从而避免了用队列知道上一层的所有节点。 总; next指针好处: 1-通过next能拿到当前所有节点,从而拿到下一层有序节点,是队列+Node(left,right)的替代品,即Queue+Node(left,right) == Node(left,right,next)。 有点像链表的归并空间复杂度为O(1)一样。 2-通过next 配合 搜索树O(logN)查找起节点,从而快速确定范围,应用场景--SQL的range查询。而不是从root开始重新查找。 */
class Connect4 {
/* M4-根据上层链表节点的left和right来建立下层列表,每层设置dummyNode统一操作。 当当前列表为空链表时,结束处理! */
public Node connect(Node root) {
Node dummyPre = new Node();
dummyPre.next = root;
Node dummyCur = new Node();
Node p1 = dummyPre, p2 = dummyCur;
while (p1.next != null) {
Node pre = p1.next;
if (pre.left != null) {
p2.next = pre.left;
p2 = p2.next;
}
if (pre.right != null) {
p2.next = pre.right;
p2 = p2.next;
}
p1 = p1.next;
if (p1.next == null) {
p1 = dummyCur;
dummyCur = new Node();
p2 = dummyCur;
}
}
//直接返回处理后的根节点即可。
return root;
}
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
}
}
总结
1)层次遍历 :Queue + cnt计数
2)二叉树本身就是递归结构,递归遍历是它的基础,所以可递归+hash记录每层tail节点解题。
3)利用链表的next域,要让它占了一份空间,发挥减少两份空间的使用。
4)next好处,
1-通过next能拿到当前所有节点,从而拿到下一层有序节点,是队列+Node(left,right)的替代品,即Queue+Node(left,right) == Node(left,right,next)。
有点像链表的归并空间复杂度为O(1)一样。
2-通过next 配合 搜索树O(logN)查找起节点,从而快速确定范围,应用场景–SQL的range查询。而不是从root开始重新查找。
参考文献
版权声明
本文为[REN_林森]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43164662/article/details/124361160
边栏推荐
- SVN详细使用教程
- Swift: entry of program, swift calls OC@_ silgen_ Name, OC calls swift, dynamic, string, substring
- How do I open the win10 startup folder?
- LeetCode 练习——396. 旋转函数
- Using MATLAB programming to realize the steepest descent method to solve unconstrained optimization problems
- OC 转 Swift 条件编译、标记、宏、 Log、 版本检测、过期提示
- 详解TCP的三次握手
- Want to be an architect? Tamping the foundation is the most important
- QT actual combat: Yunxi chat room
- ASEMI超快恢复二极管与肖特基二极管可以互换吗
猜你喜欢
OC to swift conditional compilation, marking, macro, log, version detection, expiration prompt

LeetCode162-寻找峰值-二分-数组

Is asemi ultrafast recovery diode interchangeable with Schottky diode
DVWA之暴力破解(Brute Force)Low-->high
UML项目实例——抖音的UML图描述
Branch statement of process control
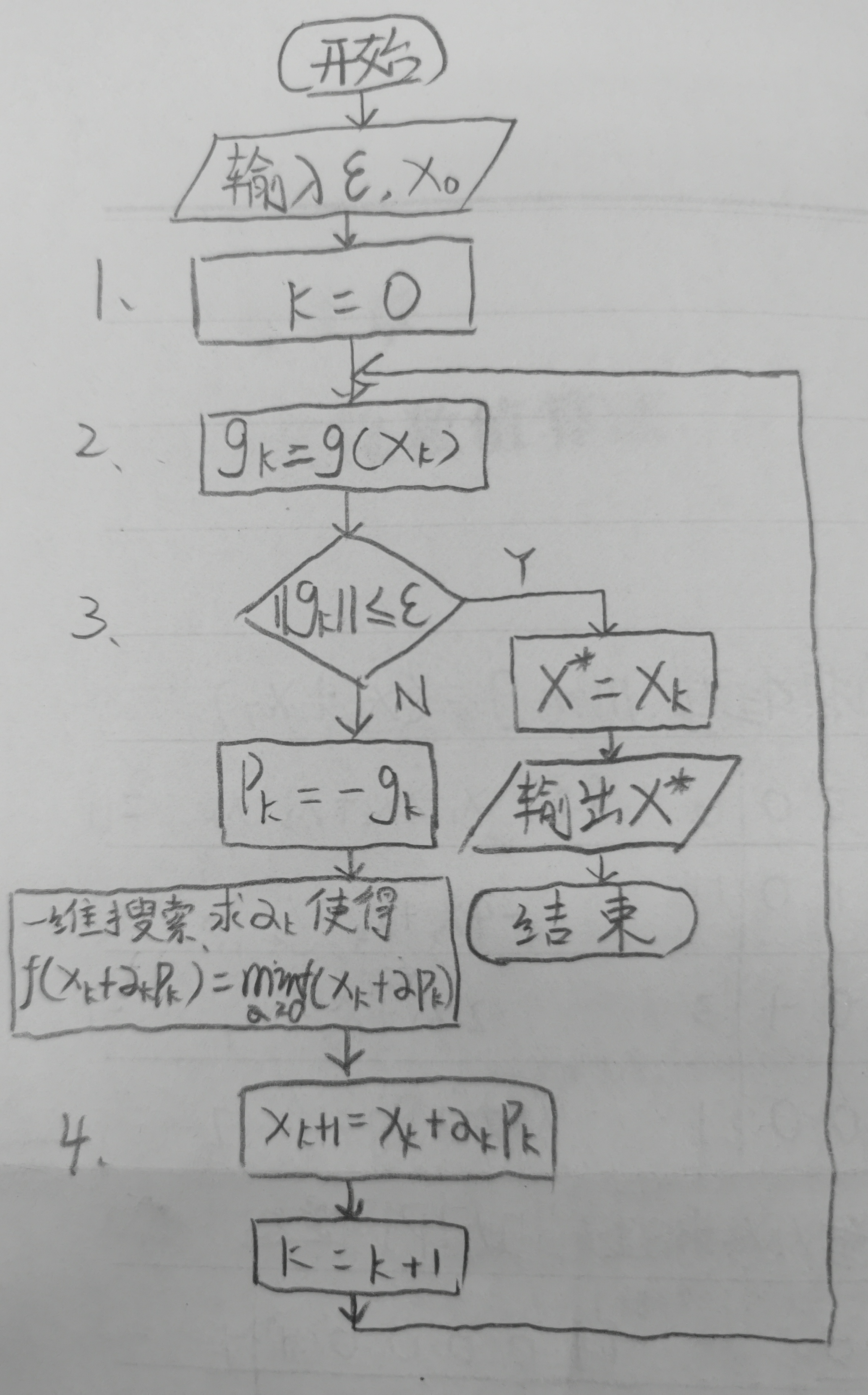
Using MATLAB programming to realize the steepest descent method to solve unconstrained optimization problems
ASEMI三相整流桥和单相整流桥的详细对比
GIS数据处理-cesium中模型位置设置
A good tool: aardio
随机推荐
Set up an AI team in the game world and start the super parametric multi-agent "chaos fight"
Arduino for esp8266串口功能简介
ArrayList collection basic usage
2-GO variable operation
Swift:Entry of program、Swift调用OC、@_silgen_name 、 OC 调用Swift、dynamic、String、Substring
剑指 Offer II 019. 最多删除一个字符得到回文(简单)
2-Go变量操作
Raised exception class eaccexviolation with 'access violation at address 45efd5 in module error
Comment eolink facilite le télétravail
Do (local scope), initializer, memory conflict, swift pointer, inout, unsafepointer, unsafebitcast, success
封面和标题中的关键词怎么写?做自媒体为什么视频没有播放量
面试官:说一下类加载的过程以及类加载的机制(双亲委派机制)
外包幹了四年,廢了...
Contraction mapping theorem
MDS55-16-ASEMI整流模块MDS55-16
外包干了四年,废了...
你还不知道责任链模式的使用场景吗?
L'externalisation a duré quatre ans.
Provided by Chengdu control panel design_ It's detailed_ Introduction to the definition, compilation and quotation of single chip microcomputer program header file
Leetcode162 - find peak - dichotomy - array