当前位置:网站首页>【NLP】HMM隐马尔可夫+维特比分词
【NLP】HMM隐马尔可夫+维特比分词
2022-04-23 14:26:00 【myaijarvis】
【参考:NLP-HMM隐马尔可夫+维特比分词,代码+数据+讲解_哔哩哔哩_bilibili】 PPT浅显易懂,非常不错
【参考:shouxieai/nlp-hmm-word-cut: nlp-hmm-word-cut】
如何通俗地讲解 viterbi 算法? - 路生的回答 - 知乎
如何通俗地讲解 viterbi 算法? - JustCoder的回答 - 知乎
PPT
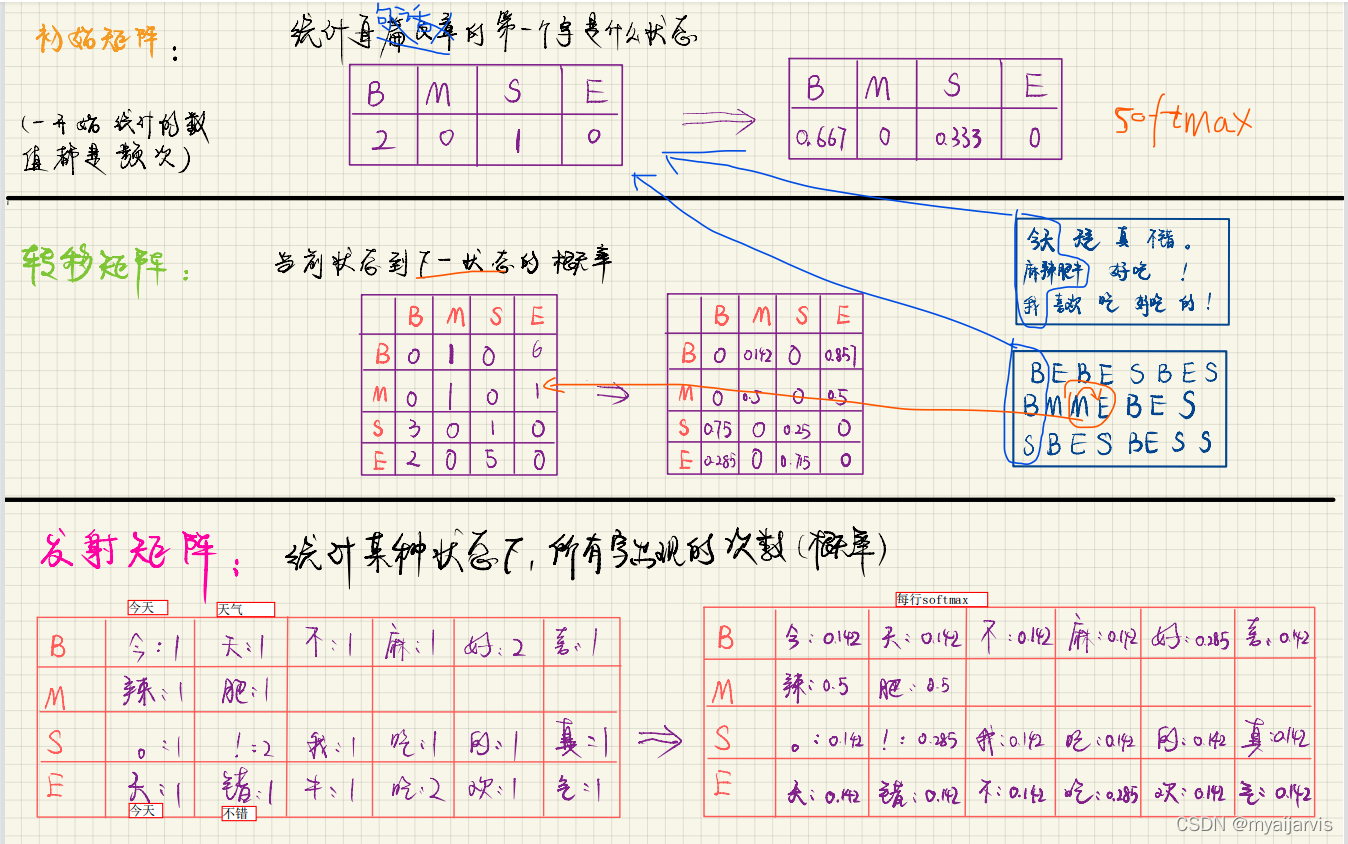
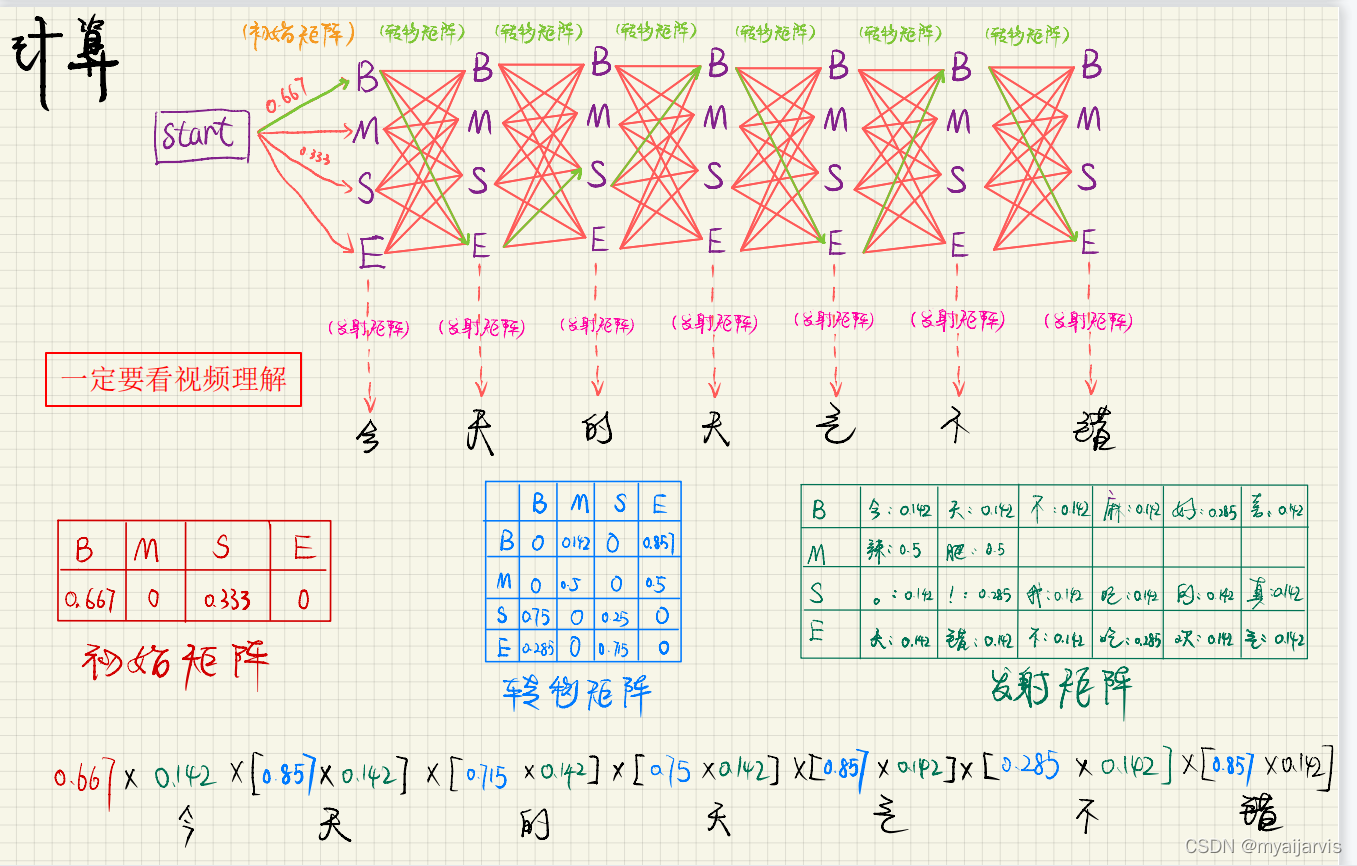
代码
import pickle
from tqdm import tqdm
import numpy as np
import os
def make_label(text_str): # 从单词到label的转换, 如: 今天 ----> BE 麻辣肥牛: ---> BMME 的 ---> S
text_len = len(text_str)
if text_len == 1:
return "S"
return "B" + "M" * (text_len - 2) + "E" # 除了开头是 B, 结尾是 E,中间都是M
# 将原始的语料库转换为 对应的状态文件 如: 今天要上学 -> BE S BE
def text_to_state(file="all_train_text.txt"): # 将原始的语料库转换为 对应的状态文件
# all_train_text 里面已经用空格分好词了
if os.path.exists("all_train_state.txt"): # 如果存在该文件, 就直接退出
return
all_data = open(file, "r", encoding="utf-8").read().split("\n") # 打开文件并按行切分到 all_data 中 , all_data 是一个list
with open("all_train_state.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f: # 打开写入的文件
for d_index, data in tqdm(enumerate(all_data)): # 逐行 遍历 , tqdm 是进度条提示 , data 是一篇文章(一行), 有可能为空
if data: # 如果 data 不为空
state_ = ""
for w in data.split(" "): # 当前 文章按照空格切分, w是文章中的一个词语
if w: # 如果 w 不为空
state_ = state_ + make_label(w) + " " # 制作单个词语的label
if d_index != len(all_data) - 1: # 最后一行不要加 "\n" 其他行都加 "\n"
state_ = state_.strip() + "\n" # 每一行都去掉 最后的空格
f.write(state_) # 写入文件, state_ 是一个字符串
# 定义 HMM类, 其实最关键的就是三大矩阵
class HMM:
def __init__(self, file_text="all_train_text.txt", file_state="all_train_state.txt"):
self.all_states = open(file_state, "r", encoding="utf-8").read().split("\n")[:200] # 按行获取所有的状态
self.all_texts = open(file_text, "r", encoding="utf-8").read().split("\n")[:200] # 按行获取所有的文本
self.states_to_index = {
"B": 0, "M": 1, "S": 2, "E": 3} # 给每个状态定义一个索引, 以后可以根据状态获取索引
self.index_to_states = ["B", "M", "S", "E"] # 根据索引获取对应状态
self.len_states = len(self.states_to_index) # 状态长度 : 这里是4
# 最重要的就是下面三个矩阵
self.init_matrix = np.zeros((self.len_states)) # 初始矩阵 : 1 * 4 , 对应的是 BMSE
self.transfer_matrix = np.zeros((self.len_states, self.len_states)) # 转移状态矩阵: 4 * 4 ,
# 发射矩阵, 使用的 2级 字典嵌套
# # 注意这里初始化了一个 total 键 , 存储当前状态出现的总次数, 为了后面的归一化使用
self.emit_matrix = {
"B": {
"total": 0}, "M": {
"total": 0}, "S": {
"total": 0}, "E": {
"total": 0}}
# 计算 初始矩阵
def cal_init_matrix(self, state):
self.init_matrix[self.states_to_index[state[0]]] += 1 # BMSE 四种状态, 对应状态出现 1次 就 +1
# 计算转移矩阵
def cal_transfer_matrix(self, states):
sta_join = "".join(states) # 状态转移 从当前状态转移到后一状态, 即 从 sta1 每一元素转移到 sta2 中
sta1 = sta_join[:-1]
sta2 = sta_join[1:]
for s1, s2 in zip(sta1, sta2): # 同时遍历 s1 , s2
self.transfer_matrix[self.states_to_index[s1], self.states_to_index[s2]] += 1
# 计算发射矩阵
def cal_emit_matrix(self, words, states):
for word, state in zip("".join(words), "".join(states)): # 先把words 和 states 拼接起来再遍历, 因为中间有空格
self.emit_matrix[state][word] = self.emit_matrix[state].get(word, 0) + 1
self.emit_matrix[state]["total"] += 1 # 注意这里多添加了一个 total 键 , 存储当前状态出现的总次数, 为了后面的归一化使用
# 将矩阵归一化
def normalize(self):
self.init_matrix = self.init_matrix / np.sum(self.init_matrix)
self.transfer_matrix = self.transfer_matrix / np.sum(self.transfer_matrix, axis=1, keepdims=True) # 每一行
# 这里*1000 是为了不让概率太小,也可以不要这个
self.emit_matrix = {
state: {
word: t / word_times["total"] * 1000 for word, t in word_times.items() if word != "total"} for
state, word_times in self.emit_matrix.items()}
# 训练开始, 其实就是3个矩阵的求解过程
def train(self):
if os.path.exists("three_matrix.pkl"): # 如果已经存在参数了 就不训练了
self.init_matrix, self.transfer_matrix, self.emit_matrix = pickle.load(open("three_matrix.pkl", "rb"))
return
for words, states in tqdm(zip(self.all_texts, self.all_states)): # 按行读取文件, 调用3个矩阵的求解函数
words = words.split(" ") # 在文件中 都是按照空格切分的
states = states.split(" ")
self.cal_init_matrix(states[0]) # 计算三大矩阵
self.cal_transfer_matrix(states)
self.cal_emit_matrix(words, states)
self.normalize() # 矩阵求完之后进行归一化
pickle.dump([self.init_matrix, self.transfer_matrix, self.emit_matrix], open("three_matrix.pkl", "wb")) # 保存参数
# 这个实现有点难度
def viterbi_t(text, hmm):
states = hmm.index_to_states
emit_p = hmm.emit_matrix
trans_p = hmm.transfer_matrix
start_p = hmm.init_matrix
V = [{
}]
path = {
}
for y in states:
V[0][y] = start_p[hmm.states_to_index[y]] * emit_p[y].get(text[0], 0)
path[y] = [y]
for t in range(1, len(text)):
V.append({
})
newpath = {
}
# 检验训练的发射概率矩阵中是否有该字
neverSeen = text[t] not in emit_p['S'].keys() and \
text[t] not in emit_p['M'].keys() and \
text[t] not in emit_p['E'].keys() and \
text[t] not in emit_p['B'].keys()
for y in states:
emitP = emit_p[y].get(text[t], 0) if not neverSeen else 1.0 # 设置未知字单独成词
# 每四条路径里挑一条概率最大的
temp = []
for y0 in states:
if V[t - 1][y0] >= 0: # 纠错 这里是>=
temp.append((V[t - 1][y0] * trans_p[hmm.states_to_index[y0], hmm.states_to_index[y]] * emitP, y0))
(prob, state) = max(temp)
# (prob, state) = max([(V[t - 1][y0] * trans_p[hmm.states_to_index[y0],hmm.states_to_index[y]] * emitP, y0) for y0 in states if V[t - 1][y0] >= 0])
V[t][y] = prob
newpath[y] = path[state] + [y]
path = newpath
(prob, state) = max([(V[len(text) - 1][y], y) for y in states]) # 求最大概念的路径
result = "" # 拼接结果
for t, s in zip(text, path[state]):
result += t
if s == "S" or s == "E": # 如果是 S 或者 E 就在后面添加空格
result += " "
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
text_to_state()
# text = "虽然一路上队伍里肃静无声"
text = "一个人无论学什么专业,总得懂一些文学知识,有一点艺术素养,这对于丰富自己的思想和生活,提高自己的审美能力很有好处"
# text = "北京市北京大学" # 涉及专业词汇就不太行了,因为训练文本里面缺少相关的语料
# debug 对照的ppt看流程更易懂
hmm = HMM()
hmm.train()
result = viterbi_t(text, hmm)
print(result)
一个 人 无 论学 什么 专业 , 总得 懂 一些 文学 知识 , 有 一点 艺术 素养 , 这 对于 丰富 自己 的 思想 和 生活 , 提高 自己 的 审美 能力 很 有 好处
版权声明
本文为[myaijarvis]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://blog.csdn.net/Jruo911/article/details/124352226
边栏推荐
- Docker (V) MySQL installation
- QT actual combat: Yunxi calendar
- LM317的直流可调稳压电源Multisim仿真设计(附仿真+论文+参考资料)
- 本以为能躺着进华为,结果陆续收到京东/滴滴/爱奇艺offer的我迷茫了
- Ali developed three sides, and the interviewer's set of combined punches made me confused on the spot
- 51单片机的花卉、农田自动浇水灌溉系统开发,Proteus仿真,原理图和C代码
- C语言知识点精细详解——数据类型和变量【1】——进位计数制
- Web page, adaptive, proportional scaling
- XX project structure notes
- 单相交交变频器的Matlab Simulink建模设计,附Matlab仿真、PPT和论文等资料
猜你喜欢

OpenFaaS实战之四:模板操作(template)

Ali developed three sides, and the interviewer's set of combined punches made me confused on the spot
setcontext getcontext makecontext swapcontext
单片机的函数信号发生器,输出4种波形,频率可调,原理图,仿真和C程序
555 timer + 74 series chip to build eight way responder, 30s countdown, proteus simulation, etc
51单片机的花卉、农田自动浇水灌溉系统开发,Proteus仿真,原理图和C代码
Nacos作为配置中心(四) 使用Demo
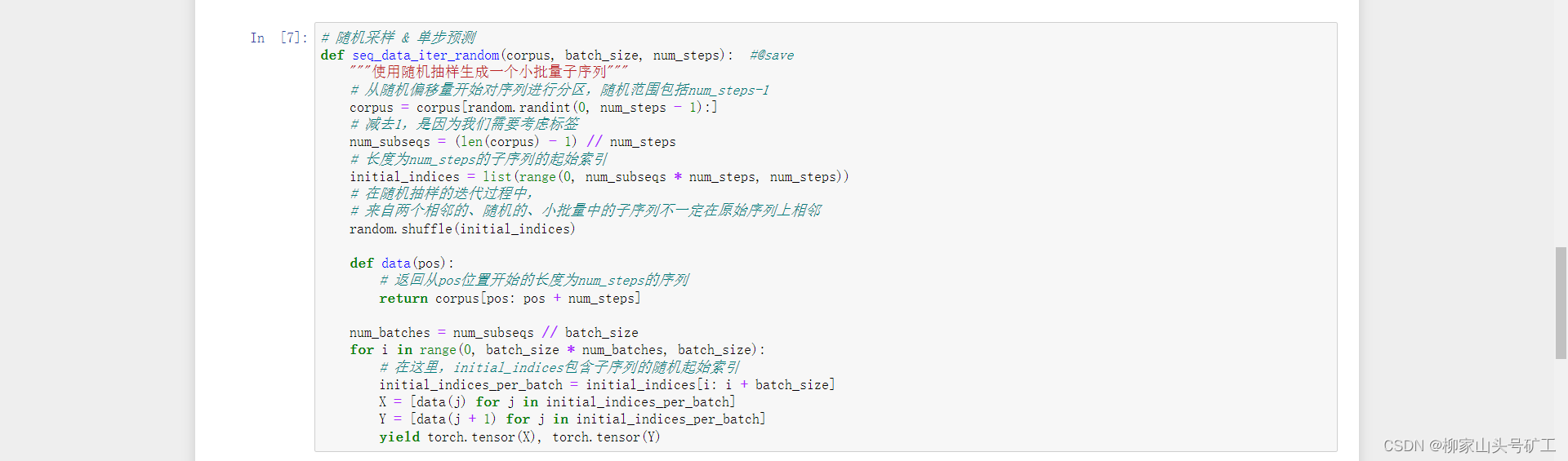
8.3 语言模型与数据集
交通灯系统51单片机设计(附Proteus仿真、C程序、原理图及PCB、论文等全套资料)
SHT11传感器的温度湿度监控报警系统单片机Proteus设计(附仿真+论文+程序等)
随机推荐
ArrayList collection basic usage
Logical volume creation and expansion
Redis cluster 原理
Qt实战:云曦聊天室篇
基础正则表达式
循环队列的基本操作(实验)
外包干了四年,废了...
I thought I could lie down and enter Huawei, but I was confused when I received JD / didi / iqiyi offers one after another
Unity_代码方式添加绑定按钮点击事件
Processing MKDIR: unable to create directory 'AAA': read only file system
TLC5615 based multi-channel adjustable CNC DC regulated power supply, 51 single chip microcomputer, including proteus simulation and C code
Redis源码分析之HSET流程与ziplist
LotusDB 设计与实现—1 基本概念
电子秤称重系统设计,HX711压力传感器,51单片机(Proteus仿真、C程序、原理图、论文等全套资料)
直流可调稳压电源的Proteus仿真设计(附仿真+论文等资料)
555定时器+74系列芯片搭建八路抢答器,30s倒计时,附Proteus仿真等
Four ways of SSH restricting login
Basic regular expression
Mq-2 and DS18B20 fire temperature smoke alarm system design, 51 single chip microcomputer, with simulation, C code, schematic diagram, PCB, etc
asp.net使用MailMessage发送邮件的方法