当前位置:网站首页>Extended Chinese Remainder Theorem
Extended Chinese Remainder Theorem
2022-08-10 22:04:00 【aWty_】
exCRT
CRT
关于 C R T CRT CRT,The main idea is this,for a system of equations:
{ x ≡ a 1 ( m o d m 1 ) x ≡ a 1 ( m o d m 2 ) ⋮ x ≡ a n ( m o d m n ) \begin{cases} x \equiv a_1 \pmod {m_1} \\ x \equiv a_1 \pmod {m_2} \\ \vdots \\ x \equiv a_n \pmod {m_n} \end{cases} ⎩⎨⎧x≡a1(modm1)x≡a1(modm2)⋮x≡an(modmn)
Let's say we make:
m = ∏ i = 1 n m i , M i = m m i m = \prod_{i = 1}^n m_i, M_i = \frac m {m_i} m=i=1∏nmi,Mi=mim
然后求出 M i M_i Mi 在模 m i m_i mi 意义下的乘法逆元 t i t_i ti,So we got the answer:
a n s = ∑ i = 1 n a i M i t i ans = \sum_{i = 1}^n a_i M_i t_i ans=i=1∑naiMiti
in the calculation step here,Obviously, when calculating the inverse element, it requires gcd ( M i , m i ) = 1 \gcd(M_i, m_i) = 1 gcd(Mi,mi)=1,then the requirement { m i } \{ m_i \} { mi} l两两互质.
exCRT
总体思路
Extending the Chinese remainder theorem is to solve m i m_i mi Methods of Solving Equations When Pairs Are Not Coprime.
But we can find out after a little thought,要想在 C R T CRT CRT On the basis of small changes to achieve e x C R T exCRT exCRT impossible,因为如果 gcd ( M i , m i ) ≠ 1 \gcd(M_i, m_i) \neq 1 gcd(Mi,mi)=1 If so, then the inverse element does not even exist.,So we need to jump out C R T CRT CRT framework to think about how to scale.
We consider combining the two equations,if it can be merged quickly,So we only need to continue to be merged to directly solve the rest,The only one,简单的,显然的,The linear congruence equation will solve the problem.
合并
Consider the merger of two equations:
{ x ≡ a 1 ( m o d m 1 ) x ≡ a 2 ( m o d m 2 ) \begin{cases} x \equiv a_1 \pmod {m_1} \\ x \equiv a_2 \pmod {m_2} \end{cases} { x≡a1(modm1)x≡a2(modm2)
So we can get according to the nature of the congruence:
x = k 1 m 1 + a 1 = k 2 m 2 + a 2 x = k_1m_1 + a_1 = k_2 m_2 + a_2 x=k1m1+a1=k2m2+a2
移一下项:
k 1 m 1 − k 2 m 2 = a 2 − a 1 k_1m_1 - k_2m_2 = a_2 - a_1 k1m1−k2m2=a2−a1
The form of this formula may not be so intuitive,所以我们令 a = m 1 , b = m 2 , c = a 2 − a 1 , x = k 1 , y = − k 2 a = m_1, b = m_2, c = a_2 - a_1, x = k_1, y = -k_2 a=m1,b=m2,c=a2−a1,x=k1,y=−k2,Did this formula suddenly become like this?:
a x + b y = c ax + by = c ax+by=c
This is a classical indefinite equation solving problem.,Then according to Pei Shu's theorem,我们就能知道:
- 如果 gcd ( m 1 , m 2 ) ∣ ( r 2 − r 1 ) \gcd(m_1, m_2) \mid (r_2 - r_1) gcd(m1,m2)∣(r2−r1),Then the equation can be directly used e x g c d exgcd exgcd find a set of special solutions for her
- 否则,方程无解
那么我们求出 x = k 1 m 1 + a 1 x = k_1m_1 + a_1 x=k1m1+a1 之后就得到了一个 x x x The special solution at the same time satisfy the two equations.We give this special solution a new variable name X X X.
So we can happy new equations:
x ≡ X ( m o d l c m ( m 1 , m 2 ) ) x \equiv X \pmod {lcm(m_1, m_2)} x≡X(modlcm(m1,m2))
This construction should be very obvious,因为 x x x 与 X X X 模 m 1 m_1 m1 Congruence and x x x 与 X X X 模 m 2 m_2 m2 同余,那么 x x x 与 X X X 模 l c m ( m 1 , m 2 ) lcm(m_1, m_2) lcm(m1,m2) 同余.
算法流程总结
- Take two out of all equations
- 合并(If you can't merge output without a solution)
- There is only one equation left, directly solve the only one equation to get the answer
完结撒花!!!
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int __int128
#define in read()
#define MAXN 100100
inline int read(){
int x = 0; char c = getchar();
while(c < '0' or c > '9') c = getchar();
while('0' <= c and c <= '9'){
x = x * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar();
}
return x;
}
void write(int x){
if(x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;
if(x > 9) write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
int n = 0;
int a[MAXN] = {
0 };
int m[MAXN] = {
0 };
int k1 = 0, k2 = 0;
int exgcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y){
if(!b) {
x = 1, y = 0; return a; }
int d = exgcd(b, a % b, x, y);
int z = x; x = y, y = z - y * (a / b);
return d;
}
signed main(){
n = in; int ans = 0, lcm = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) m[i] = in, a[i] = in;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
k1 = 0, k2 = 0;
int d = exgcd(m[i], m[i + 1], k1, k2);
if((a[i + 1] - a[i]) % d != 0) {
puts("-1"); return 0; }
lcm = m[i] / d * m[i + 1];
a[i + 1] = k1 * (a[i + 1] - a[i]) / d * m[i] + a[i];
a[i + 1] = (a[i + 1] % lcm + lcm) % lcm; m[i + 1] = lcm;
}
int y = 0;
exgcd(1, m[n], ans, y);
write((ans * a[n] + m[n]) % m[n]);
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Shell编程规范与变量

字节跳动原来这么容易就能进去...
Likou 221 questions, the largest square
![[SQL brush questions] Day3----Special exercises for common functions that SQL must know](/img/b8/05589138441ada5d453297de7d181b.png)
[SQL brush questions] Day3----Special exercises for common functions that SQL must know
camera preview process --- from HAL to OEM
美创科技勒索病毒“零信任”防护和数据安全治理体系的探索实践
Common interview questions for APP UI automation testing, maybe useful~
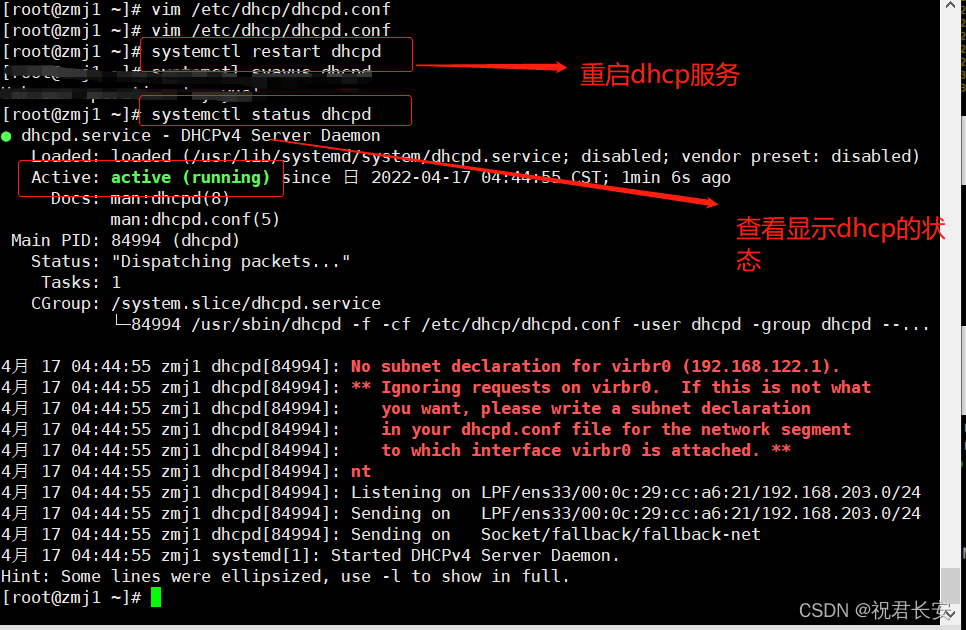
服务——DHCP原理与配置

ThreadLocal全面解析(一)

异常的了解
随机推荐
Use Cloudreve to build a private cloud disk
camera preview process --- from HAL to OEM
shell脚本
LeetCode-36-Binary search tree and doubly linked list
力扣215题,数组中的第K个最大元素
2022.8.9 Mock Competition
ArcGIS自动随机生成采样点的方法
深度学习之 12 循环神经网络RNN2
The use of TortoiseSVN little turtle
JVM classic fifty questions, now the interview is stable
labelme-屏蔽拖拽的事件
HighTec快捷键(Keys)设置位置
PROCEDURE :存储过程结构——《mysql 从入门到内卷再到入土》
测试4年感觉和1、2年时没什么不同?这和应届生有什么区别?
xshell (sed command)
自组织是管理者和成员的双向奔赴
GAN CFOP
黑猫带你学Makefile第12篇:常见Makefile问题汇总
2022.8.8好题选讲(数论场)
使用SylixOS虚拟串口,实现系统串口自由