当前位置:网站首页>Learning Android II from scratch - activity
Learning Android II from scratch - activity
2022-04-23 04:47:00 【Scattered moon】
Catalog
Basic knowledge
-
Any... In the project Activity All should be rewrite onCreate() Method , And now our FirstActivity This method has been overridden in , This is a Android Studio It's automatic
-
Android The design of program stresses the separation of logic and view , It's better for each one Activity Can correspond to a layout . Layout is used to display the content of the interface .
-
Check Generate Layout File Indicates that it will automatically be FirstActivity Create a corresponding Layout file , Check Launcher Activity Indicates that the FirstActivity Set as... Of the current project Lord Activity
-
Destroy one activity,finish() Method
-
startActivity() Method , Used to start Activity
-
Android Medium Activity It can be layered . Every time we start one new Activity, Will cover the original Activity above , And then click Back The key will destroy the top Activity, Below One Activity It will reappear .
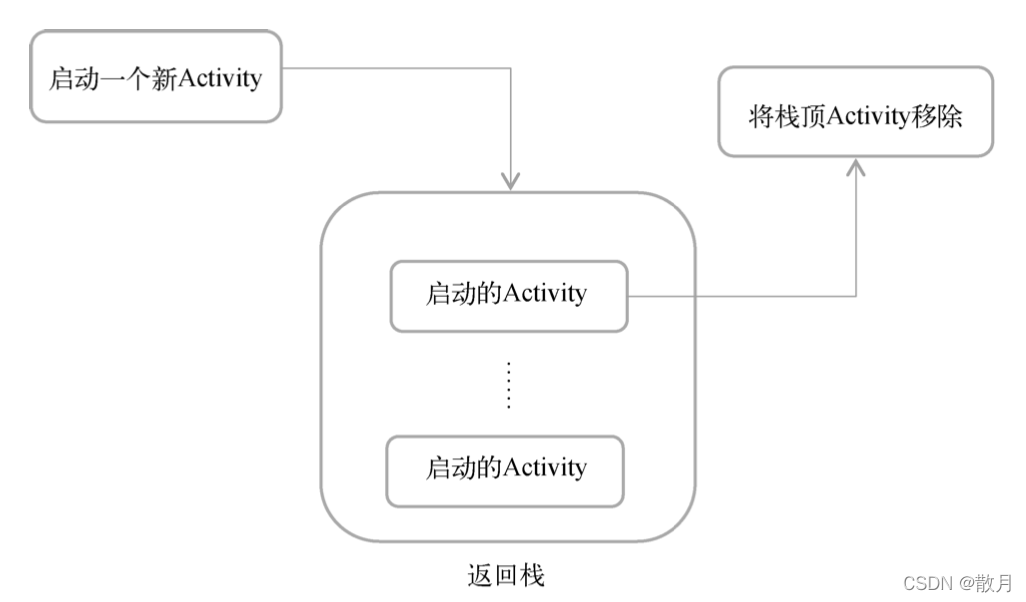
-
activity Four kinds of state : function 、 Pause 、 stop it 、 The destruction
button
activity in :
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val button1: Button = findViewById<Button>(R.id.button1)
button1.setOnClickListener {
Toast.makeText(this, "You clicked Button 1", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
- Toast yes Android A very good reminder provided by the system
Toast.makeText(this, "You clicked Button 1", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()The first parameter is Context, That is to say Toast Required context , because Activity Is itself a Context object , therefore It's coming in directly here this that will do . The second parameter is Toast Displayed text content . The third parameter is Toast When displayed Long , There are two built-in constants to choose from :Toast.LENGTH_SHORT and Toast.LENGTH_LONG. - **setOnClickListener()** Method register a listener for the button , When you click the button, the onClick() Method .
button.setOnClickListener {}
menu
- res New under the directory menu Catalog
- rewrite onCreateOptionsMenu() Method
- rewrite onOptionsItemSelected() Method
Intent( Jump 、 To transfer data )
- Show intent
Intent Overload with multiple constructors , One of them is Intent(Context packageContext, Class<? > cls). This constructor takes two arguments : The first parameter Context Ask for a startup Activity Up and down writing ; The second parameter Class Used to specify the target you want to start Activity, With this constructor, you can build Intent Of “ Intention ”.
val intent = Intent(this, SecondActivity::class.java)
startActivity(intent)
- Implicit Intent
button1.setOnClickListener {
val intent = Intent("com.example.activitytest.ACTION_START")
intent.addCategory("com.example.activitytest.MY_CATEGORY")
startActivity(intent)
}
<activity android:name=".SecondActivity" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.activitytest.ACTION_START" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="com.example.activitytest.MY_CATEGORY"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
- Show a web page
button1.setOnClickListener {
val intent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW)
intent.data = Uri.parse("https://www.baidu.com")
startActivity(intent)
}
- Call dialing
button1.setOnClickListener {
val intent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_DIAL)
intent.data = Uri.parse("tel:10086")
startActivity(intent)
}
- Next Activity To transfer data
button1.setOnClickListener {
val data = "Hello SecondActivity"
val intent = Intent(this, SecondActivity::class.java)
intent.putExtra("extra_data", data)
startActivity(intent)
}
val extraData = intent.getStringExtra("extra_data")
Log.d("SecondActivity", "extra data is $extraData")
- Returns data to the previous Activity,startActivityForResult(intent, 1) Method
button1.setOnClickListener {
val intent = Intent(this, SecondActivity::class.java)
startActivityForResult(intent, 1)
}
override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data)
when (requestCode) {
1 -> if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
val returnedData = data?.getStringExtra("data_return")
Log.d("FirstActivity", "returned data is $returnedData")
} }
}
button2.setOnClickListener {
val intent = Intent()
intent.putExtra("data_return", "Hello FirstActivity")
setResult(RESULT_OK, intent)
finish()
}
override fun onBackPressed() {
val intent = Intent()
intent.putExtra("data_return", "Hello FirstActivity")
setResult(RESULT_OK, intent)
finish()
}
activity The survival period of 7 Callback methods
- onCreate(). It will be Activity Called the first time it is created . In this method Activity Of Initialization operation , Such as loading layout 、 Binding events, etc .
- onStart(). This method is Activity Call when it changes from invisible to visible .
- onResume(). This method is Activity Called when you are ready to interact with the user . At this time Activity One Locate at the top of the return stack , And in operation .
- onPause(). This method is used when the system is ready to Start or restore another Activity Called when . We usually Will consume some... In this method CPU Resources released , And save some key data , But the execution speed of this method must be fast , Otherwise, it will affect the new stack top Activity Use .
- onStop(). This method is Activity Called when it is completely invisible . It and onPause() The main area of the method Don't lie in , If you start new Activity It's a dialog like Activity, that onPause() The method will be implemented That's ok , and onStop() Method does not execute .
- onDestroy(). This method is Activity By Call before destruction , after Activity The state of will change to destroyed state .
- onRestart(). This method is Activity The call is made from the stop state to the running state , That is to say Activity Has been rebooted .
3 Species survival time
- Complete life span .Activity stay onCreate() Methods and onDestroy() Method What you're going through is complete survival . In general , One Activity Will be in onCreate() Method to complete various initialization operations , And in the onDestroy() Method to release memory .
- Visible lifetime .Activity stay onStart() Methods and onStop() Method What you're going through is visible survival . Within the visible lifetime ,Activity Always visible to users , Even though it may not be possible to interact with users . I Through these two methods, we can reasonably manage the resources visible to users . For example onStart() Method to load resources , And in the onStop() Method to release resources , So as to ensure that it is in a stopped state Activity It won't take up too much memory .
- Front desk lifetime .Activity stay onResume() Methods and onPause() Method What we're going through is the life span of the front desk . Within the life of the front desk ,Activity Always running , At this time Activity It can interact with users , What we usually see and contact most is in this state Activity.
Activity Best practices
- Know which one you are now Activity, There is no need to let BaseActivity stay AndroidManifest.xml Register in , So choose to create a normal Kotlin Class 了 . And then let BaseActivity Inherited from AppCompatActivity, And rewrite onCreate() Method . Give Way BaseActivity Become ActivityTest All... In the project Activity Parent class of , because BaseActivity It's inherited from AppCompatActivity Of , So all in the project Activity The existing functionality of is not affected , They still inherit Activity All properties in .
open class BaseActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
Log.d("BaseActivity", javaClass.simpleName)
} }
- sign out activity,controller class
- To transfer data
companion object {
fun actionStart(context: Context, data1: String, data2: String) {
val intent = Intent(context, SecondActivity::class.java)
intent.putExtra("param1", data1)
intent.putExtra("param2", data2)
context.startActivity(intent)
} }
Activity2.actionStart(this, "data1", "data2")
版权声明
本文为[Scattered moon]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204220555418254.html
边栏推荐
- Eight misunderstandings that should be avoided in data visualization
- Agile practice | agile indicators to improve group predictability
- Unity RawImage背景无缝连接移动
- test
- Record your own dataset with d435i, run orbslam2 and build a dense point cloud
- What's the difference between error and exception
- Leetcode005 -- delete duplicate elements in the array in place
- Code007 -- determine whether the string in parentheses matches
- Innovative practice of short video content understanding and generation technology in meituan
- leetcode007--判断字符串中的括号是否匹配
猜你喜欢

Shanghai Hangxin technology sharing 𞓜 overview of safety characteristics of acm32 MCU
Spark FAQ sorting - must see before interview

Learning Android from scratch -- Introduction

Arduino UNO r3+LCD1602+DHT11

拼了!两所A级大学,六所B级大学,纷纷撤销软件工程硕士点!

PIP3 installation requests Library - the most complete pit sorting

The 14th issue of HMS core discovery reviews the long article | enjoy the silky clip and release the creativity of the video
【数据库】MySQL单表查询
![解决ValueError: Argument must be a dense tensor: 0 - got shape [198602], but wanted [198602, 16].](/img/99/095063b72390adea6250f7b760d78c.png)
解决ValueError: Argument must be a dense tensor: 0 - got shape [198602], but wanted [198602, 16].

Wechat payment function
随机推荐
Leetcode003 -- judge whether an integer is a palindrome number
Spark case - wordcount
La caméra Unity tourne avec la souris
leetcode004--罗马数字转整数
The unity camera rotates with the mouse
Mysql50 basic exercises
Spark small case - RDD, spark SQL
Leetcode006 -- find the longest common prefix in the string array
Better way to read configuration files than properties
C language: spoof games
C# List字段排序含有数字和字符
数据孤岛是什么?为什么2022年仍然存在数据孤岛?
Unity camera rotation with sliding effect (rotation)
Special topic of data intensive application system design
redis数据类型有哪些
Innovation training (IX) integration
Code007 -- determine whether the string in parentheses matches
Record the blind injection script
Go reflection rule
Painless upgrade of pixel series