当前位置:网站首页>Simple analysis of regularization principle (L1 / L2 regularization)
Simple analysis of regularization principle (L1 / L2 regularization)
2022-08-09 16:17:00 【pomelo33】
In machine learning and deep learning, in order to prevent the model from overfitting, there are usually two ways:
The first is to manually judge the importance of the data and retain the more important features, provided that there is sufficient prior knowledge.But at the same time, this is also equivalent to discarding part of the information in the data.
The second is regularization, which can automatically select important feature variables and automatically discard unnecessary feature variables by adopting certain constraints.
Commonly used regularization methods are:
L1/L2 regularization: A "penalty term" is added directly to the original loss function.
dropout: the most commonly used in deep learning, that is, randomly discarding some neurons during the training process.
Data augmentation: for example, flipping, translating, and stretching the original image to increase the training data set of the model.
Early termination method: Terminate the training early when the results obtained by the model training are relatively good.Human supervision and prior knowledge are required.
L2 regularization:
L2 regularization, that is, adding the sum of squares of weight parameters to the original loss function:
Ein is the training sample error without regularization, and λ is the regularization parameter.
Why add a weight parameter sum of squares?It is conceivable that when fitting a set of data, in general, it is easier to fit this set of data curves using higher-order polynomials.However, this will also make the model overly complex and prone to overfitting, that is, poor generalization ability.Therefore, the weights of the high-order parts can be limited to 0.This shifts the solution from higher-order problems to lower-order problems.But this method is more difficult to implement in practice.Therefore, a looser condition can be defined: 
This limitationThe meaning of the condition is also very simple, that is, the sum of the values of all weights is less than or equal to C.
So why is this penalty term (constraint) set to be the sum of all weights?Here is a brief explanation: 
As shown in the figure, the black ellipse is the area where Ein is minimized, and there is a blue point inside it which is the minimum value of Ein.The red circle is the restricted area, and the minimized point will move in the opposite direction of the gradient ▽Ein. Due to the restricted condition, the minimized point can only be within the red area.For the image above, the minimized point can only move along the red circle tangent.The loss function is minimized when the opposite direction of the gradient Ein coincides (i.e. parallel) with the direction of the center of the circle pointing to the minimized point (the direction of w).(Because the gradient ▽Ein has no component in the tangent direction, it will not move along the tangent any more).
So you get: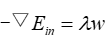
: (symbol is included in λ)

Considering this equation as a whole as a gradient, we getNew loss function: 
This is L2 regularization.Similarly, L1 regularization is based on the original loss function plus the absolute value of the weight parameter: 
The loss function actually contains two aspects: one is the training sample error.One is the regularization term.Among them, the parameter λ plays a balancing role.If λ is too large, the C of the constraint term is very small, that is, the area of the restricted area circle is very small, and the optimized result is far away from the real minimum point, resulting in underfitting.Vice versa, if λ is too small, the C of the constraint term is very large, that is, the area of the restricted area circle is very large, and the optimized result is very close to the real minimum point, and the effect of regularization is reduced, resulting in overfitting.Therefore, the choice of λ value is also very important.
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

光线的数值追踪

爱因斯坦的光子理论

Similar image detection method

What is a template engine?What are the common template engines?Introduction to common commands of thymeleaf.

启动报错:Caused by: org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException汇总解决

相干光(光学)

复数与复数域

Shell -- -- -- -- -- - common gadgets, sort and uniq, tr, the cut

What is the difference between the four common resistors?

Redis6.2.1配置文件详解
随机推荐
OpenCV - 矩阵操作 Part 3
Mysql两个引擎对比
Shell functions and arrays
思维导图FreeMind安装问题及简单使用
MySQL学习笔记
浅析Servlet三大容器的常用方法及其作用域
What are the implications of programmatic trading rules for the entire trading system?
6大论坛,30+技术干货议题,2022首届阿里巴巴开源开放周来了!
卷积神经网络表征可视化研究综述(1)
注释,标识符,数据类型
量子力学初步
量化投资者是如何获取实时行情数据的呢?
Seize the opportunity of quantitative trading fund products, and quantitative investment has room for development?
二维数组实现八皇后问题
focal loss原理及简单代码实现
[Basic version] Integer addition, subtraction, multiplication and division calculator
Bessel function
What are the misunderstandings about the programmatic trading system interface?
单向链表几个比较重要的函数(包括插入、删除、反转等)
职业量化交易员对量化交易有什么看法?