当前位置:网站首页>Why should sparse adjacency matrix be written in transposed form adj in pytorch geometric_ t
Why should sparse adjacency matrix be written in transposed form adj in pytorch geometric_ t
2022-04-21 13:53:00 【Big meow who wants to lie flat every day】
pytorch geometric Why should sparse adjacency matrix be written in the form of transpose adj_t
First contact pytorch geometric My little friend may have the same question as me , Why should the adjacency matrix in data be written in the form of transpose . Until I read the source code , I understand the author's writing , Because of the way information is transmitted , Here I share with you .
edge_index
First pytorch geometric There are two storage modes for edge information , The first is edge_index, its shape yes [2, N], among N Is the number of edges . first N The element of dimension stores the information of the origin of the edge , be called source, the second N The element of dimension stores the information of the target point of the edge , be called target. for instance , If we have such a directed graph , that edge_index That's true : tensor([[1, 2, 3, 4], [0, 0, 0, 0]]), Side is (1,0), (2,0), (3,0), (3,0)
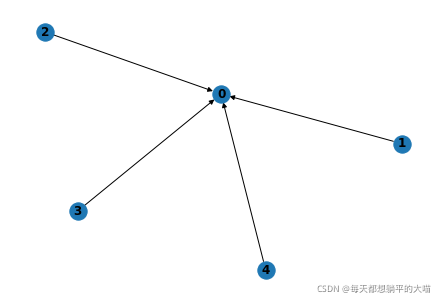
If the graph above is undirected , that 0 This node also points to 1,2,3,4 These nodes ,edge_index It should be : tensor([[1, 2, 3, 4,0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]), Side is (1,0), (2,0), (3,0), (3,0), (0,1), (0,2), (0,3), (0,4).
edge_index The reason for this is , stay pytorch geometric in , use scatter A kind of method can be easily realized , from source To target, This default edge transfer method .( Of course, you can also change the transmission mode from target Pass on to source.) If you still don't understand the above , Then remember , The way of edge transfer is from source To target Of , Later, in the process of looking at the source code , It will come to understand .
adj_t
pytorch geometric The second storage mode of edge information is adj_t, It's a sparse tensor. Here we see the author in adj Add... To the back t, It shows that it is the transpose of adjacency matrix . Why write it as transpose , Let's go up edge_index speak .
First, why do we need sparse adjacency matrix , Not directly edge_index? That's because if sparse adjacency matrix can be used, the computing speed can be greatly accelerated , To save memory . Of course, we also have some graph algorithms that cannot avoid explicit edge passing , such as GAT This kind of graph algorithm that needs to operate alone on the edge .
take edge_index When converting to adjacency matrix , Naturally, I will write the following form :
adj = SparseTensor(row=edge_index[0], col=edge_index[1], value=...,
sparse_sizes=(num_nodes, num_nodes))
But we all know that , Matrix computing AW It is the process of aggregating the characteristics of neighbors on a row , among A It's an adjacency matrix ,W Is the characteristic matrix . If it is just a small partner of the contact graph algorithm , I borrowed the following picture , You can see it , Each node finally generates embedding It's in A Sum of eigenvalues corresponding to neighbors in the row , therefore In essence, it aggregates the information corresponding to the column to the row . In the figure A Only neighbors E, But think about it D, It has B, C, E Three neighbors , So its characteristic is B, C, E Sum of three neighbor characteristics , Aggregate the columns B, C, E Corresponding information to... In the line D.

So there's a problem ,edge_index Information transmission in is source to target, That is to say edge_index[0] to edge_index[1], and adj Medium is col To row, This creates a problem of inconsistency . So when doing matrix calculation and transmitting information , The author will adj convert to adj_t, And make it the default form , This is consistent .
give an example
Look at an author's document about GIN Examples of implementations :https://pytorch-geometric.readthedocs.io/en/latest/notes/sparse_tensor.html?highlight=adj_t#memory-efficient-aggregations
from torch_sparse import matmul
class GINConv(MessagePassing):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(aggr="add")
def forward(self, x, edge_index):
out = self.propagate(edge_index, x=x)
return MLP((1 + eps) x + out)
def message(self, x_j):
return x_j
def message_and_aggregate(self, adj_t, x):
return matmul(adj_t, x, reduce=self.aggr)
You can see in the message_and_aggregate This step is in the process of information transmission , Default is used adj_t.
I'm talking to the new pytorch geometric Series of tutorials pytorch_geometric Code details , Welcome to comment and exchange .
版权声明
本文为[Big meow who wants to lie flat every day]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204211348394325.html
边栏推荐
- Cdh5 delete data node
- Fengqiu technology provides you with 10M Ethernet solution
- Machine learning notes - SVD singular value decomposition (3) applying SVD to images
- mysql-三星索引和cost值成本计算
- Beauty of ASM pile insertion
- Esgyndb about the performance improvement of delete with index
- 深度学习与图像识别:原理与实践 笔记Day_15
- c3p0的坑导致并发性能问题
- Promise -- several key problems
- 2021-11-06数据库
猜你喜欢

Unittest unit test (V)

Detailed explanation of JVM memory allocation mechanism

软件工程-基础篇刷题
JMM model of concurrent programming and three characteristics of concurrency

山东大学项目实训树莓派提升计划二期(七)对象和类

【leetcode】516. Longest palindrome subsequence

networkx与PyG计算度数degree时需避免的坑:自环selfloop和多重边

Software testing common problems development model PC QQ login test case bug related problems test case design common methods

Machine learning notes - Moore Penrose pseudo inverse

Use of JSON server
随机推荐
【leetcode】144.二叉树的前序遍历
山东大学项目实训树莓派提升计划二期(八)数组和ArrayList
Trafodion troubleshooting - error [1034] unable to obtain privileges
JVM內存分配機制詳解
并发编程之深入理解
2021-10-21软件测试理论
POI与EasyExcel读写测试
vite. Config configuration file
机器学习笔记 - Moore-Penrose 伪逆
networkx与PyG计算度数degree时需避免的坑:自环selfloop和多重边
认识与分析日志文件
Flex item properties
山东大学项目实训树莓派提升计划二期(五)book1内容分析与整理
Esgyndb tips on collecting core information
<2021SC@SDUSC>山东大学软件工程应用与实践JPress代码分析(十二)
OpenLDAP使用ldapadd手动添加用户
CDH5删除数据节点
Deep analysis and optimization of JVM memory model
Color gradient (columns, rings, etc.)
小案例的实现