当前位置:网站首页>Deep analysis of C language function
Deep analysis of C language function
2022-04-23 20:47:00 【Computer white】
Point a praise , Pay attention to each other , Learning together !!!

Two 、 Classification of functions
3、 The parameters of the function
3.1 The actual parameter ( Actual parameters ):
3.2 Formal parameters ( Shape parameter ):
3.3 Use memory to interpret formal parameters , Actual parameters
5、 Nested calls and chained access to functions
6. Function declaration and definition
One 、 What is a function
We often see the concept of function in Mathematics . But you know C Functions in language ?Wikipedia definition of function : Subroutinesstay Computer science in , Subroutines ( English :Subroutine, procedure, function, routine, method, subprogram, callable unit), It's a piece of code in a large program , Consists of one or more statement blocks . It's responsible for a particular task , And compared to other code , With relative independence .
Generally, there will be input parameters and return values , Provide encapsulation of the process and hiding of details . These codes are usually integrated into Software library . Function in Process oriented Has appeared in the language of . It's the structure (Struct) and class (Class) The forerunner of . Itself is the classification of relevant statements and the abstraction of a process .
Two 、 Classification of functions
1. Library function
2. Custom function
2.1 Library function
Why are there library functions :
At the beginning ,C Language has no library functions ,C Language library functions are not C Part of the language itself , It is from compiler According to the needs of ordinary users , Prepare and provide a set of programs for users .C Library functions greatly facilitate users , It also adds C The inadequacy of language itself . Writing C Language program time , Use library functions , It can not only improve the running efficiency of the program , It can also improve the quality of programming .
notes : Use library functions , Must contain #include Corresponding header file .
2.2 Custom function
C Library functions in language are not omnipotent , This leads to more important Custom function . Custom functions are the same as library functions , There's a function name , Return value types and function parameters . But the difference is that we design it ourselves , To give him “ mission ”, This gives programmers a lot of room to play !
Composition of functions :
ret_type fun_name(para1, * )
{
statement;// Statement item
}
ret_type Return type
fun_name Function name
para1 Function parameter Here is an example ( Get the largest number ):
#include <stdio.h>
// Enter two numbers , Get the maximum number
int get_max(int x, int y) {
return (x>y)?(x):(y);
//exp1 ? exp2 : exp3( Conditional operators )
// If x>y, Output x, Otherwise output y
}
int main()
{
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 20;
int max = get_max(num1, num2);
printf("max = %d\n", max);
}3、 The parameters of the function
3.1 The actual parameter ( Actual parameters ):
When calling a function with parameters , There is a data transfer relationship between the main function and the called function . When calling a function in the keynote function , The arguments in parentheses after the function name are called “ The actual parameter ”( abbreviation “ Actual parameters ”).
The argument can be Constant 、 Variable or expression , Whatever the type of argument is , It's going on Function call when , They all have to have certain values , In order to transmit these values to Shape parameter . Therefore, an assignment should be used in advance , Input and so on so that the argument gets a definite value .
3.2 form Parameters ( Shape parameter ):
Is to define the function name and The body of the function Parameters used when , The purpose is to receive the parameters passed in when the function is called .
Formal parameters refer to the variables in brackets after the function name , Because formal parameters are instantiated only when the function is called .( Within distribution Storage unit ), So it's called formal parameter . Formal parameters are automatically destroyed when the function call is completed . So formal parameters are only valid in functions .
The following is a code example to illustrate : Enter two numbers , Exchange the values of two numbers , And the output
#include <stdio.h>
// This code segment does not realize the exchange of two numbers
void Swap(int x, int y) {
int tmp = 0;
tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
}
int main()
{
int num1 = 1;
int num2 = 2;
Swap(num1, num2);// Custom function
printf("num1 = %d\nnum2 = %d\n", num1, num2);
return 0;
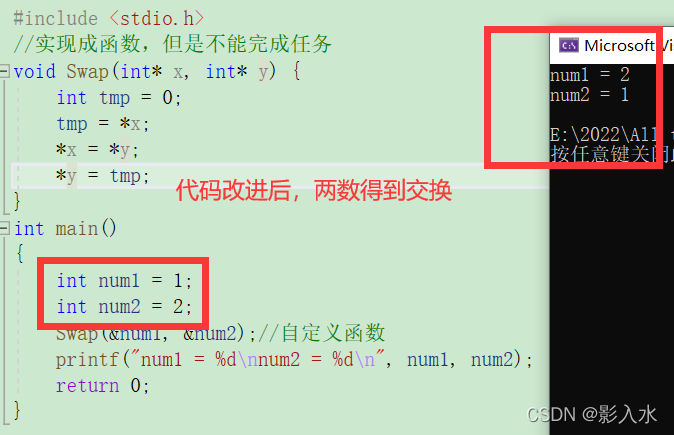
}The output result of the code instance

From this, we can conclude that the above code does not realize the function we want , What's the matter , Let's continue to discuss ( Formal parameters are automatically destroyed when the function call is completed )
We can improve the above code , The following code example :
#include <stdio.h>
// This code segment realizes the exchange of two numbers
void Swap(int* x, int* y) {
int tmp = 0;
tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
int main()
{
int num1 = 1;
int num2 = 2;
Swap(&num1, &num2);// Custom function
printf("num1 = %d\nnum2 = %d\n", num1, num2);
return 0;
}
Let's summarize :
The first code diagram :( The value passed is ) Call function Swap when , stay Swap Inside the function , The values of two numbers are exchanged , But what? ,x y It's a parameter , Formal parameters will be automatically destroyed after the function call is completed , That's what happened Swap After the scope of the function ,x y Will be destroyed , Will not be saved , Therefore, the function of exchanging two numbers will not be realized .
Chapter II code diagram :( It's the address ) After the analysis of the first code diagram , I also know that the formal parameters will be automatically destroyed after the function call is completed , So we sent the address , hold num1 and num2 Pass your memory address to x and y, stay Swap Function ,x and y Can find num1 and num2 Memory address of , Thus directly to num1 and num2 Make changes .
3.3 Use memory to interpret formal parameters , Actual parameters
The following is a code example :
#include <stdio.h>
// Unable to fulfill the requirements
void Swap1(int x, int y) {
int tmp = 0;
tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
}
// Achieve the desired results
void Swap2(int *px, int *py) {
int tmp = 0;
tmp = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = tmp;
}
int main()
{
int num1 = 1;
int num2 = 2;
Swap1(num1, num2);
printf("Swap1::num1 = %d num2 = %d\n", num1, num2);
Swap2(&num1, &num2);
printf("Swap2::num1 = %d num2 = %d\n", num1, num2);
return 0;
}above Swap1 and Swap2 Parameters in function x,y,px,py All are Formal parameters . stay main Function passed to Swap1 Of num1 , num2 He Zhuan to Swap2 Functional &num1 , &num2 yes The actual parameter .
Here we analyze the real and formal parameters of the function :
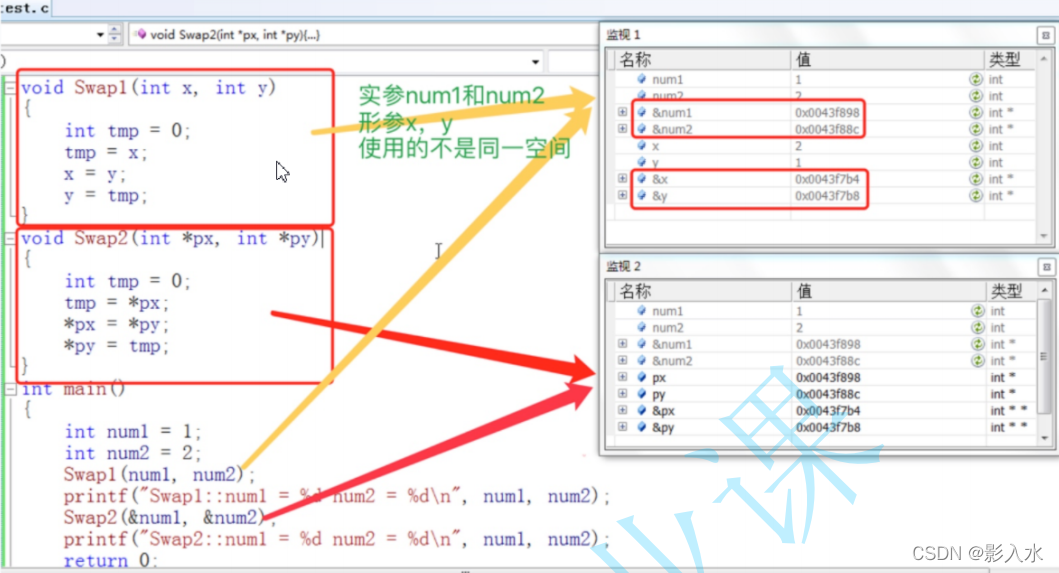
The memory allocation corresponding to the code is as follows :

Here you can see Swap1 When the function is called , x , y Have your own space , As like as two peas, the same thing is true. . So we can simply think that : After the formal parameter is instantiated, it is actually equivalent to a temporary copy of the argument .
4、 Function call
4.1 Value transfer call
The formal and actual parameters of a function occupy different memory blocks , Modification of a parameter does not affect the argument .
4.2 Value transfer call
Address call is a way to call a function by passing the memory address of the created variable outside the function to the function parameter .
This parameter transfer method can establish a real relationship between the function and the variables outside the function , In other words, the variables outside the function can be directly manipulated inside the function .
Let's practice , Write a function , To realize binary search of an ordered array .
int binary_search(int arr[], int k, int sz)
{
int left = 0;
int right = sz - 1;// Memory is from 0 Starting number
while (left <= right)
{
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// The reason for this is because if you meet a super large number , Then the computer will make mistakes
// You can write like this int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (k > arr[mid])
left = mid++;
else if (k < arr[mid])
right = mid--;
else
return mid;
}
return -1;
}
int main(){
int k = 0;
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
scanf("%d", &k);
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int ret = binary_search(arr, k, sz);
if (-1==ret)
printf(" Can't find ");
else
printf(" eureka ,k The location of the for %d", ret);
return 0;
}5、 Nested calls and chained access to functions
Functions and functions can be combined according to actual needs , That is, calling each other .
5.1 Nested calls
The following code example :
#include <stdio.h>
void new_line()
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
void three_line()
{
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<3; i++)
{
new_line();
}
}
int main()
{
three_line();
return 0;
}Functions can be called nested , But you can't nest definitions , The following code example ( Error model )
int main()
{
test()
{
;
}
}5.2 Chained access
Take the return value of one function as the parameter of another function .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char arr[20] = "hello";
int ret = strlen(strcat(arr, "bit"));//strlen: Calculation \0 Number of previous strings ;strcat: take bit Overlay to
//arr Array
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}6. Function declaration and definition
Statement :
1. Tell the compiler that there is a function called , What are the parameters , What is the return type . But does it exist , function
The statement does not determine .
2. The declaration of a function usually precedes the use of the function . To satisfy the requirement of declaration before use .
3. The declaration of the function is usually placed in the header fileDefinition :
The definition of a function refers to the concrete implementation of a function , Explain the function realization .
summary
The recursion of functions and classical topics will be put in the next article .
版权声明
本文为[Computer white]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204210546128243.html
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

DOS command of Intranet penetration

Common problems in deploying projects with laravel and composer for PHP
Fastdfs思维导图

41. The first missing positive number
go interface
GO語言開發天天生鮮項目第三天 案例-新聞發布系統二
电脑越用越慢怎么办?文件误删除恢复方法

GO语言开发天天生鲜项目第三天 案例-新闻发布系统二

How to use PM2 management application? Come in and see

JS arrow function user and processing method of converting arrow function into ordinary function
随机推荐
2021-09-02 unity project uses rider to build hot change project failure record of ilruntime
On IRP from the perspective of source code
Lunch on the 23rd day at home
黑客的入侵方式你知道几种?
MySQL 存储过程和函数
3-5 obtaining cookies through XSS and the use of XSS background management system
Create vs project with MATLAB
Send email to laravel
The iswow64process function determines the number of program bits
Pikachuxss how to get cookie shooting range, always fail to return to the home page
Fastdfs思维导图
JS arrow function user and processing method of converting arrow function into ordinary function
Solve the Chinese garbled code of URL in JS - decoding
6-5 string - 2 String copy (assignment) (10 points) the C language standard function library includes the strcpy function for string copy (assignment). As an exercise, we write a function with the sam
Latex formula
LeetCode 1351、统计有序矩阵中的负数
Selenium displays webdriverwait
Unity asset import settings
C# 知识
How many hacking methods do you know?