当前位置:网站首页>ITK 读取一个目录中的一个序列,然后改变头信息,将多张dcm图像写成一个dcm文件。
ITK 读取一个目录中的一个序列,然后改变头信息,将多张dcm图像写成一个dcm文件。
2022-08-10 22:14:00 【peanut_wu】
/ Software Guide : BeginCodeSnippet
#include "itkImageFileReader.h"
#include "itkImageFileWriter.h"
#include "itkImage.h"
#include "itkMetaDataObject.h"
#include "itkGDCMImageIO.h"
// Software Guide : EndCodeSnippet
#include <list>
#include <fstream>
int
main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
if (argc < 5)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0]
<< " DicomImage OutputDicomImage Entry Value\n";
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Software Guide : BeginLatex
//
// We declare the image type by selecting a particular pixel type and image
// dimension.
//
// Software Guide : EndLatex
// Software Guide : BeginCodeSnippet
using InputPixelType = short;
constexpr unsigned int Dimension = 2;
using InputImageType = itk::Image<InputPixelType, Dimension>;
// Software Guide : EndCodeSnippet
// Software Guide : BeginLatex
//
// We instantiate the reader type by using the image type as template
// parameter. An instance of the reader is created and the file name to be
// read is taken from the command line arguments.
//
// Software Guide : EndLatex
// Software Guide : BeginCodeSnippet
using ReaderType = itk::ImageFileReader<InputImageType>;
auto reader = ReaderType::New();
reader->SetFileName(argv[1]);
// Software Guide : EndCodeSnippet
// Software Guide : BeginLatex
//
// The GDCMImageIO object is created in order to provide the services for
// reading and writing DICOM files. The newly created image IO class is
// connected to the reader.
//
// Software Guide : EndLatex
// Software Guide : BeginCodeSnippet
using ImageIOType = itk::GDCMImageIO;
auto gdcmImageIO = ImageIOType::New();
reader->SetImageIO(gdcmImageIO);
// Software Guide : EndCodeSnippet
// Software Guide : BeginLatex
//
// The reading of the image is triggered by invoking \code{Update()} in the
// reader.
//
// Software Guide : EndLatex
try
{
// Software Guide : BeginCodeSnippet
reader->Update();
// Software Guide : EndCodeSnippet
}
catch (const itk::ExceptionObject & e)
{
std::cerr << "exception in file reader " << std::endl;
std::cerr << e.GetDescription() << std::endl;
std::cerr << e.GetLocation() << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Software Guide : BeginLatex
//
// We take the metadata dictionary from the image that the reader had loaded
// in memory.
//
// Software Guide : EndLatex
// Software Guide : BeginCodeSnippet
InputImageType::Pointer inputImage = reader->GetOutput();
using DictionaryType = itk::MetaDataDictionary;
DictionaryType & dictionary = inputImage->GetMetaDataDictionary();
// Software Guide : EndCodeSnippet
// Software Guide : BeginLatex
//
// Now we access the entries in the metadata dictionary, and for particular
// key values we assign a new content to the entry. This is done here by
// taking
// \{key,value\} pairs from the command line arguments. The relevant method
// is \code{EncapsulateMetaData} that takes the dictionary and for a given
// key provided by \code{entryId}, replaces the current value with the
// content of the \code{value} variable. This is repeated for every
// potential pair present in the command line arguments.
//
// Software Guide : EndLatex
// Software Guide : BeginCodeSnippet
for (int i = 3; i < argc; i += 2)
{
std::string entryId(argv[i]);
std::string value(argv[i + 1]);
itk::EncapsulateMetaData<std::string>(dictionary, entryId, value);
}
// Software Guide : EndCodeSnippet
// Software Guide : BeginLatex
//
// Now that the dictionary has been updated, we proceed to save the image.
// This output image will have the modified data associated with its DICOM
// header.
//
// Using the image type, we instantiate a writer type and construct a
// writer. A short pipeline between the reader and the writer is connected.
// The filename to write is taken from the command line arguments. The image
// IO object is connected to the writer.
//
// Software Guide : EndLatex
// Software Guide : BeginCodeSnippet
using Writer1Type = itk::ImageFileWriter<InputImageType>;
auto writer1 = Writer1Type::New();
writer1->SetInput(reader->GetOutput());
writer1->SetFileName(argv[2]);
writer1->SetImageIO(gdcmImageIO);
// Software Guide : EndCodeSnippet
// Software Guide : BeginLatex
//
// Execution of the writer is triggered by invoking the \code{Update()}
// method.
//
// Software Guide : EndLatex
try
{
// Software Guide : BeginCodeSnippet
writer1->Update();
// Software Guide : EndCodeSnippet
}
catch (const itk::ExceptionObject & e)
{
std::cerr << "exception in file writer " << std::endl;
std::cerr << e.GetDescription() << std::endl;
std::cerr << e.GetLocation() << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Software Guide : BeginLatex
//
// Remember again, that modifying the header entries of a DICOM file
// involves very serious risks for patients and therefore must be done with
// extreme caution.
//
// Software Guide : EndLatex
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}边栏推荐
- 美味石井饭菜
- Shell编程之条件语句(二)
- Black cat takes you to learn Makefile Part 11: When the header file a.h changes, how to recompile all the .c files that depend on the header file a.h
- Shell programming specification and variables
- Common interview questions for APP UI automation testing, maybe useful~
- camera preview process --- from HAL to OEM
- Pro-test is effective | A method to deal with missing features of risk control data
- The perfect alternative to domestic Gravatar avatars Cravatar
- 音乐播放器(未完成版本)
- Power system power flow calculation (Newton-Raphson method, Gauss-Seidel method, fast decoupling method) (Matlab code implementation)
猜你喜欢
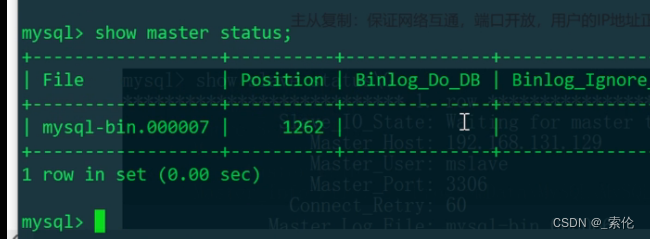
MySQL: MySQL Cluster - Principle and Configuration of Master-Slave Replication
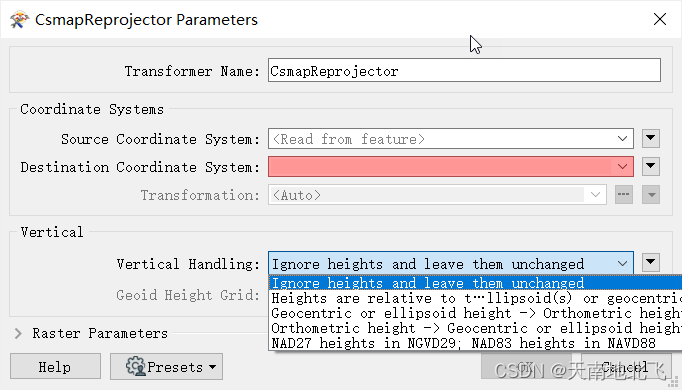
fme csmapreprojector转换器使用高程异常模型进行高程基准转换
音乐播放器(未完成版本)

Translating scientific and technological papers, how to translate from Russian to Chinese

MySQL:MySQL的集群——主从复制的原理和配置
LeetCode Daily 2 Questions 02: Reverse the words in a string (1200 each)
![68: Chapter 6: Develop article services: 1: Content sorting; article table introduction; creating [article] article services;](/img/95/7f21ecda19030c2faecbe373893d66.png)
68: Chapter 6: Develop article services: 1: Content sorting; article table introduction; creating [article] article services;

Shell编程之条件语句(二)
3598. 二叉树遍历(华中科技大学考研机试题)
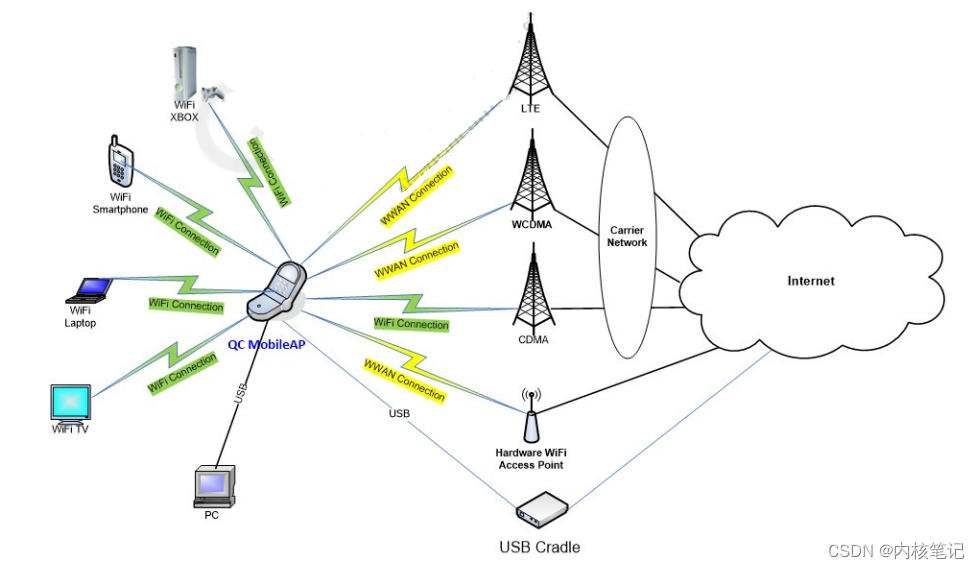
高通平台开发系列讲解(应用篇)QCMAP应用框架介绍
随机推荐
STL-deque
shell programming without interaction
过滤器
LeetCode每日两题01:反转字符串 (均1200道)方法:双指针
BM7 list entry in central
阿里云贾朝辉:云XR平台支持彼真科技呈现国风科幻虚拟演唱会
fme csmapreprojector转换器使用高程异常模型进行高程基准转换
uni-app微信小程序——下拉多选框
留言有奖|OpenBMB x 清华大学NLP:大模型公开课更新完结!
Service - DHCP principle and configuration
DC-9靶场下载及渗透实战详细过程(DC靶场系列)
Black cat takes you to learn Makefile Part 12: Summary of common Makefile problems
《DevOps围炉夜话》- Pilot - CNCF开源DevOps项目DevStream简介 - feat. PMC成员胡涛
Thread State 详解
LeetCode Daily Question (1573. Number of Ways to Split a String)
3598. 二叉树遍历(华中科技大学考研机试题)
亲测有效|处理风控数据特征缺失的一种方法
Redis
2021 IDEA creates web projects
Self-organization is a two-way journey between managers and members