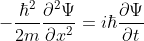当前位置:网站首页>Several important functions of singly linked list (including insertion, deletion, reversal, etc.)
Several important functions of singly linked list (including insertion, deletion, reversal, etc.)
2022-08-09 16:17:00 【Yellow duck 233】
The first is the definition of linked list
//单向链表的定义
struct SNode
{
int elem;
struct SNode* next;
};
The following is the insertion of the singly linked list、删除、反转、Reverse by one、Calculate the common substring length、合并两个有序链表、A function to determine whether the linked list has a cycle,Some are not well written descriptions
//0失败 1成功
//在指定结点node的后面插入一个结点
int insert_after(struct SNode* node, int elem)
{
assert(node != NULL);
struct SNode* newnode = (struct SNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct SNode));//Allocate memory for the new node
if(newnode == NULL) //Failed to create returns failure
return 0;
newnode->elem = elem;
newnode->next = node->next; //把node的next传给newnode
node->next = newnode; //让node的next指向newnode
return 1;
}
//删除指定结点nodethe last node of , *elemUsed to receive deleted values,可以为空
int delete_after(struct SNode* node, int* elem)
{
assert(node!=NULL); //The incoming node is NULL不运行
if(node->next == NULL) //nodeThe next node is empty
return 0;
struct SNode* delnode = node->next; //让delnode记录要删除的结点
if(elem != NULL) //The caller needs to return the deleted value record
*elem = delnode->elem;
node->next = delnode->next; //让node的next指向del原来next的指向
free(delnode); //一定要记得释放内存!!!
return 1;
}
//超级重点
//单向链表的反转
struct SNode* reverse(struct SNode* list)
{
assert(list != NULL);
//If the list has only one head node or only one node Then exit directly without reversing the order
if(list->next==NULL || list->next->next==NULL)
return list;
struct SNode* prev = NULL;
struct SNode* curr = list->next;
struct SNode* next = NULL;
while(curr != NULL)
{
next = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
list->next = prev; //Let the head node point to the node after the reverse order
return list;
}
//根据count反转单向链表
//It is equivalent to dividing the linked list into countA set of several singly linked lists,依次反转
struct SNode* reverse_count(struct SNode* list, size_t count)
{
assert(list != NULL);
if(list->next==NULL || list->next->next==NULL)
return list;
struct SNode* prev = NULL;
struct SNode* curr = list->next;
struct SNode* next = NULL;
struct SNode* last = list; //用于记录当前的“头结点”
struct SNode* first = NULL; //for recording next time“头结点”,之后要让last指向他
while(curr != NULL)
{
first = curr; //The first node before the inversion is the last node after the inversion
prev = NULL; //这一步不能忘,Each time is equivalent to a new linked list starting to reverse
for(size_t i = 0; i<count && curr!=NULL; i++) //When the number of the last group is not enoughcount个时curr来
to the end,退出循环
{
next = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
last->next = prev;//Make the last node of the previous group point to the reversed node
last = first; //last获得新的“头结点”, The last node after the inversion of the previous group is used as the beginning of the inversion of the next group
转的“头结点”
}
return list;
}
//合并两个升序的单向链表为一个,l1和l2都是升序的,合并到l3中保持有序 No need to create new nodes
void merage_list(struct SNode* l1, struct SNode* l2,struct SNode* l3)
{
assert(l1!=NULL && l2!=NULL && l3!=NULL);
struct SNode* node1 = l1->next;
struct SNode* node2 = l2->next;
struct SNode* curr = l3;
while(curr != NULL) //This increases the number of loop judgments,Conditions in parentheses can also be
//(node1!=NULL && node2!=NULL),So I will add a sentence below
{
if(node1->elem < node2->elem)
{
curr->next = node1;
curr = node1;
node1 = node1->next;
}
else
{
curr->next = node2;
curr = node2;
node2 = node2->next;
}
}
// curr->next = node1!=NULL ? node1 : node2;
l1->next = NULL;
l2->next = NULL;
}
//Calculate the number of nodes in the linked list is the length
size_t size_list(struct SNode* list)
{
assert(list != NULL);
size_t len = 0;
struct SNode* node = list->next;
while(node != NULL)
{
len++;
node = node->next;
}
return len;
}
//Find the length of the common substring of two linked lists
size_t common_subsequence(struct SNode* l1, struct SNode* l2)
{
assert(l1!=NULL && l2!=NULL);
size_t len1 = size_list(l1);
size_t len2 = size_list(l2);
struct SNode* node1 = l1->next;
struct SNode* node2 = l2->next;
if(len1 > len2) //Let the two linked lists be on the same starting line first,That is, let the long one take a few steps first
{
while(len1 != len2)
{
len1--;
node1 = node1->next;
}
}
else if(len1 < len2)
{
while(len1 != len2)
{
len2--;
node2 = node2->next;
}
}
//这时len1和len2已经相等
while(node1!=node2 && node1!=NULL && node2!=NULL)
{
len1--; //每次循环长度-1,Encounter the same or reach the last exit
node1 = node1->next;
node2 = node2->next;
}
return len1; //The rest is the common string length,为0It means that there are no substrings
}
//判断链表是否有环 Returns the length of the ring
size_t is_loop(struct SNode* list)
{
assert(list != NULL);
//Have two people start walking, one fast and one slow,If two people meet, it means there is a ring
struct SNode* quick = list->next;
struct SNode* slow = list->next;
size_t len = 0;
while(quick!=NULL && quick->next!=NULL) //因为quick一次走两步,所以要判断下quick的next
{
quick = quick->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(quick == slow)
{
//Let the slow, motionless, fast walk one more circle to calculate the length of the ring
do //Remember to use heredo{}while(); 因为quick和slowThe same cannot enter the cycle
{
quick = quick->next;
len++;
}while(quick != slow);
return len;
}
}
return 0;
}边栏推荐
- How to make your quantitative trading system have probabilistic advantages and positive return expectations?
- 深刻地认识到,编译器会导致编译结果的不同
- 爱因斯坦的光子理论
- 对程序化交易系统接口有什么误区?
- Bessel function
- 如何灵活运用量化交易接口的优势取长补短?
- What are the hot topics in quantitative programmatic trading?
- 启动报错:Caused by: org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException汇总解决
- 数组学习笔记
- VS2010:出现devenv.sln解决方案保存对话框
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
正则化原理的简单分析(L1/L2正则化)
docker安装nacos并且指定容器数据卷,数据库连接等
How do quantitative investors obtain real-time market data?
A Preliminary Study on Baidu Open Source e-chart
回收站一直显示未清空的图标问题
OpenSSF's open source software risk assessment tool: Scorecards
【C语言初阶】倒置字符串(输入 I like beijing. 输出beijing. like I)
名词概念总结(不定期更新~~)
常见编译问题
运算符学习
Shell functions and arrays
What do professional quantitative traders think about quantitative trading?
【小白必看】初始C语言(上)
常微分方程的幂级数解法
Similar image detection method
相干光(光学)
股票程序化交易如何理解自己的交易系统?
OpenCV - matchTemplate image template matching
[Mysql]--Transaction, transaction isolation level, dirty read, non-repeatable read, phantom read analysis
Bean的生命周期