当前位置:网站首页>数独 | 回溯-7
数独 | 回溯-7
2022-08-09 21:35:00 【acktomas】
数独 | 回溯-7
给定一个部分填充的 9×9 二维数组“grid[9][9]”,目标是将数字(从 1 到 9)分配给空单元格,以便每个行、列和大小为 3×3 的子网格包含恰好是从 1 到 9 的数字的一个实例。
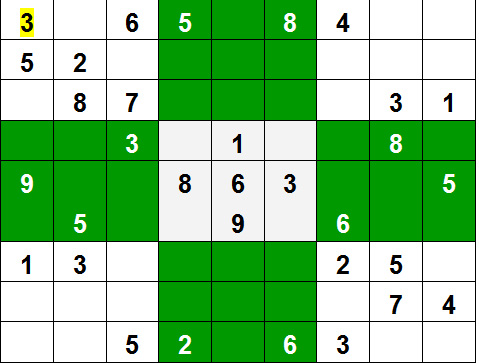
例子:
输入:
grid = { {3, 0, 6, 5, 0, 8, 4, 0, 0},
{5, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 8, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1},
{0, 0, 3, 0, 1, 0, 0, 8, 0},
{9, 0, 0, 8, 6, 3, 0, 0, 5},
{0, 5, 0, 0, 9, 0, 6, 0, 0},
{1, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 5, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 4},
{0, 0, 5, 2, 0, 6, 3, 0, 0} }
输出:
3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2
5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8
4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1
2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7
9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5
8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3
1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6
6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4
7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 9
说明:每行、每列和3*3的盒子
输出矩阵包含唯一数字。
输入:
gird = { { 3, 1, 6, 5, 7, 8, 4, 9, 2 },
{ 5, 2, 9, 1, 3, 4, 7, 6, 8 },
{ 4, 8, 7, 6, 2, 9, 5, 3, 1 },
{ 2, 6, 3, 0, 1, 5, 9, 8, 7 },
{ 9, 7, 4, 8, 6, 0, 1, 2, 5 },
{ 8, 5, 1, 7, 9, 2, 6, 4, 3 },
{ 1, 3, 8, 0, 4, 7, 2, 0, 6 },
{ 6, 9, 2, 3, 5, 1, 8, 7, 4 },
{ 7, 4, 5, 0, 8, 6, 3, 1, 0 } };
输出:
3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2
5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8
4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1
2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7
9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5
8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3
1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6
6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4
7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 9
说明:每行、每列和3*3的盒子
输出矩阵包含唯一数字。
推荐做法
**方法1:**简单。
**方法:**原来的方法是生成从 1 到 9 的所有可能的数字配置来填充空单元格。逐个尝试每个配置,直到找到正确的配置,即为每个未分配的位置填充从 1 到 9 的数字。填充所有未分配的位置后,检查矩阵是否正确。如果正确打印,则其他情况会再次出现。
算法:
- 创建一个检查给定矩阵是否为有效数独的函数。保留行、列和小盒子的 Hashmap。如果任何数字在 hashMap 中的频率大于 1,则返回 false,否则返回 true;
- 创建一个递归函数,该函数采用网格和当前行和列索引为参数。
- 检查一些基本情况。如果索引位于矩阵的末尾,即 i=N-1 且 j=N,则检查网格是否正确,如果正确则打印网格并返回 true,否则返回 false。另一种基本情况是当列的值为 N 时,即 j = N,然后移动到下一行,即 i++ 和 j = 0。
- 如果未分配当前索引,则将元素从 1 填充到 9,并使用下一个元素的索引(即 i、j+1)对所有 9 种情况进行重复。如果递归调用返回 true,则中断循环并返回 true。
- 如果分配了当前索引,则使用下一个元素的索引调用递归函数,即 i, j+1
执行:
# N is the size of the 2D matrix N*N
N = 9
# A utility function to print grid
def printing(arr):
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
print(arr[i][j], end = " ")
print()
# Checks whether it will be
# legal to assign num to the
# given row, col
def isSafe(grid, row, col, num):
# Check if we find the same num
# in the similar row , we
# return false
for x in range(9):
if grid[row][x] == num:
return False
# Check if we find the same num in
# the similar column , we
# return false
for x in range(9):
if grid[x][col] == num:
return False
# Check if we find the same num in
# the particular 3*3 matrix,
# we return false
startRow = row - row % 3
startCol = col - col % 3
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
if grid[i + startRow][j + startCol] == num:
return False
return True
# Takes a partially filled-in grid and attempts
# to assign values to all unassigned locations in
# such a way to meet the requirements for
# Sudoku solution (non-duplication across rows,
# columns, and boxes) */
def solveSudoku(grid, row, col):
# Check if we have reached the 8th
# row and 9th column (0
# indexed matrix) , we are
# returning true to avoid
# further backtracking
if (row == N - 1 and col == N):
return True
# Check if column value becomes 9 ,
# we move to next row and
# column start from 0
if col == N:
row += 1
col = 0
# Check if the current position of
# the grid already contains
# value >0, we iterate for next column
if grid[row][col] > 0:
return solveSudoku(grid, row, col + 1)
for num in range(1, N + 1, 1):
# Check if it is safe to place
# the num (1-9) in the
# given row ,col ->we
# move to next column
if isSafe(grid, row, col, num):
# Assigning the num in
# the current (row,col)
# position of the grid
# and assuming our assigned
# num in the position
# is correct
grid[row][col] = num
# Checking for next possibility with next
# column
if solveSudoku(grid, row, col + 1):
return True
# Removing the assigned num ,
# since our assumption
# was wrong , and we go for
# next assumption with
# diff num value
grid[row][col] = 0
return False
# Driver Code
# 0 means unassigned cells
grid = [[3, 0, 6, 5, 0, 8, 4, 0, 0],
[5, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 8, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1],
[0, 0, 3, 0, 1, 0, 0, 8, 0],
[9, 0, 0, 8, 6, 3, 0, 0, 5],
[0, 5, 0, 0, 9, 0, 6, 0, 0],
[1, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 5, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 4],
[0, 0, 5, 2, 0, 6, 3, 0, 0]]
if (solveSudoku(grid, 0, 0)):
printing(grid)
else:
print("no solution exists ")
# This code is contributed by sudhanshgupta2019a
输出
3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2
5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8
4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1
2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7
9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5
8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3
1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6
6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4
7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 9
复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度:
O(9^(n*n))。
对于每个未分配的索引,有 9 个可能的选项,因此时间复杂度为 O(9^(n*n))。 - 空间复杂度:
O(n*n)。
要存储输出数组,需要一个矩阵。
**方法2:**回溯。
方法:
像所有其他回溯问题一样,数独可以通过为空单元格一一分配数字来解决。在分配数字之前,请检查分配是否正确。检查当前行、当前列和当前 3X3 子网格中是否不存在相同的数字。检查正确后,分配数字,并递归检查此分配是否是一个解。如果分配没有产生一个解,请为当前空单元格尝试下一个数字。如果没有一个数字(1 到 9)获得一个解,则返回 false 并打印不存在解决方案。
算法:
- 创建一个函数,在分配当前索引后检查网格是否不正确。为行、列和盒子保留 Hashmap。如果任何数字在 hashMap 中的频率大于 1,则返回 false,否则返回 true;hashMap 可以通过使用循环来避免。
- 创建一个对网格的递归函数。
- 检查任何未分配的位置。如果存在则分配一个从 1 到 9 的数字,检查将数字分配给当前索引是否会使网格不正确,如果正确则递归调用从 0 到 9 的所有正确情况的函数。如果任何递归调用返回 true,则结束循环并返回true。如果没有递归调用返回 true,则返回 false。
- 如果没有未分配的位置,则返回 true。
执行:
# A Backtracking program
# in Python to solve Sudoku problem
# A Utility Function to print the Grid
def print_grid(arr):
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
print arr[i][j],
print ('n')
# Function to Find the entry in the Grid that is still not used. Searches the grid to find an entry that is still unassigned.
# If found, the reference parameters row, col will be set the location that is unassigned, and true is returned.
# If no unassigned entries remains, false is returned.
# 'l' is a list variable that has been passed from the solve_sudoku function to keep track of incrementation of Rows and Columns
# 查找网格中仍未使用的条目的功能,搜索网格以查找仍未分配的条目。
# 如果找到,则将引用参数row、col设置为未赋值的位置,并返回true。
# 如果没有未分配的条目,则返回 false。
# 'l' 是一个从solve_sudoku函数传递的列表变量,用于跟踪行和列的增量
def find_empty_location(arr, l):
for row in range(9):
for col in range(9):
if(arr[row][col]== 0):
l[0]= row
l[1]= col
return True
return False
# Returns a boolean which indicates whether any assigned entry in the specified row matches the given number.
# 返回一个布尔值,指示指定行中的任何分配条目是否与给定数字匹配。
def used_in_row(arr, row, num):
for i in range(9):
if(arr[row][i] == num):
return True
return False
# Returns a boolean which indicates whether any assigned entry in the specified column matches the given number.
# 返回一个布尔值,指示指定列中的任何分配条目是否与给定数字匹配。
def used_in_col(arr, col, num):
for i in range(9):
if(arr[i][col] == num):
return True
return False
# Returns a boolean which indicates whether any assigned entry within the specified 3x3 box matches the given number
# 返回一个布尔值,指示指定 3x3 盒子中的任何分配条目是否与给定数字匹配
def used_in_box(arr, row, col, num):
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
if(arr[i + row][j + col] == num):
return True
return False
# Checks whether it will be legal to assign num to the given row, col
# Returns a boolean which indicates whether it will be legal to assign num to the given row, col location.
# 检查给指定的row和col分配数字是否合法,
# 返回一个布尔值,指示将数字分配给指定row和col 位置是否合法。
def check_location_is_safe(arr, row, col, num):
# Check if 'num' is not already
# placed in current row,
# current column and current 3x3 box
return not used_in_row(arr, row, num) and
not used_in_col(arr, col, num) and
not used_in_box(arr, row - row % 3,
col - col % 3, num)
# Takes a partially filled-in grid and attempts to assign values to all unassigned locations in such a way to meet the requirements for Sudoku solution (non-duplication across rows, columns, and boxes)
# 采用部分填充的网格并尝试以满足数独解决方案要求的方式为所有未分配的位置分配值(跨行、列和框不重复)
def solve_sudoku(arr):
# 'l' is a list variable that keeps the
# record of row and col in
# find_empty_location Function
l =[0, 0]
# If there is no unassigned
# location, we are done
if(not find_empty_location(arr, l)):
return True
# Assigning list values to row and col
# that we got from the above Function
row = l[0]
col = l[1]
# consider digits 1 to 9
for num in range(1, 10):
# if looks promising
if(check_location_is_safe(arr,
row, col, num)):
# make tentative assignment
arr[row][col]= num
# return, if success,
# ya !
if(solve_sudoku(arr)):
return True
# failure, unmake & try again
arr[row][col] = 0
# this triggers backtracking
return False
# Driver main function to test above functions
if __name__=="__main__":
# creating a 2D array for the grid
grid =[[0 for x in range(9)]for y in range(9)]
# assigning values to the grid
grid =[[3, 0, 6, 5, 0, 8, 4, 0, 0],
[5, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 8, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1],
[0, 0, 3, 0, 1, 0, 0, 8, 0],
[9, 0, 0, 8, 6, 3, 0, 0, 5],
[0, 5, 0, 0, 9, 0, 6, 0, 0],
[1, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 5, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 4],
[0, 0, 5, 2, 0, 6, 3, 0, 0]]
# if success print the grid
if(solve_sudoku(grid)):
print_grid(grid)
else:
print "No solution exists"
# The above code has been contributed by Harshit Sidhwa.
输出
3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2
5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8
4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1
2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7
9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5
8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3
1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6
6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4
7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 9
复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(9^(nn))。
对于每个未分配的索引,有 9 个可能的选项,因此时间复杂度为 O(9^(nn))。时间复杂度保持不变,但会有一些早期修剪,因此所花费的时间将远少于朴素算法,但上限时间复杂度保持不变。 - 空间复杂度: O(n*n)。
要存储输出数组,需要一个矩阵。
方法 3:使用位掩码。
**方法:**此方法是对上述两种方法的轻微优化。为每一行/列/框创建一个位掩码,并为网格中的每个元素将相应位掩码中位置“值”处的位设置为 1,用于 O(1) 检查。
算法:
- 创建 3 个大小为 N 的数组(一个用于行、列和框)。
- 框的索引从 0 到 8。(为了找到元素的框索引,我们使用以下公式:行 / 3 * 3 + 列 / 3)。
- 首先映射网格的初始值。
- 每次我们在网格中添加/删除元素时,将相应位掩码的位设置为 1/0。
执行:
# N is the size of the 2D matrix N*N
N = 9
# A utility function to print grid
def printing(arr):
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
print(arr[i][j], end = " ")
print()
# Checks whether it will be
# legal to assign num to the
# given row, col
def isSafe(grid, row, col, num):
# Check if we find the same num
# in the similar row , we
# return false
for x in range(9):
if grid[row][x] == num:
return False
# Check if we find the same num in
# the similar column , we
# return false
for x in range(9):
if grid[x][col] == num:
return False
# Check if we find the same num in
# the particular 3*3 matrix,
# we return false
startRow = row - row % 3
startCol = col - col % 3
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
if grid[i + startRow][j + startCol] == num:
return False
return True
# Takes a partially filled-in grid and attempts
# to assign values to all unassigned locations in
# such a way to meet the requirements for
# Sudoku solution (non-duplication across rows,
# columns, and boxes) */
def solveSudoku(grid, row, col):
# Check if we have reached the 8th
# row and 9th column (0
# indexed matrix) , we are
# returning true to avoid
# further backtracking
if (row == N - 1 and col == N):
return True
# Check if column value becomes 9 ,
# we move to next row and
# column start from 0
if col == N:
row += 1
col = 0
# Check if the current position of
# the grid already contains
# value >0, we iterate for next column
if grid[row][col] > 0:
return solveSudoku(grid, row, col + 1)
for num in range(1, N + 1, 1):
# Check if it is safe to place
# the num (1-9) in the
# given row ,col ->we
# move to next column
if isSafe(grid, row, col, num):
# Assigning the num in
# the current (row,col)
# position of the grid
# and assuming our assigned
# num in the position
# is correct
grid[row][col] = num
# Checking for next possibility with next
# column
if solveSudoku(grid, row, col + 1):
return True
# Removing the assigned num ,
# since our assumption
# was wrong , and we go for
# next assumption with
# diff num value
grid[row][col] = 0
return False
# Driver Code
# 0 means unassigned cells
grid = [[3, 0, 6, 5, 0, 8, 4, 0, 0],
[5, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 8, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1],
[0, 0, 3, 0, 1, 0, 0, 8, 0],
[9, 0, 0, 8, 6, 3, 0, 0, 5],
[0, 5, 0, 0, 9, 0, 6, 0, 0],
[1, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 5, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 4],
[0, 0, 5, 2, 0, 6, 3, 0, 0]]
if (solveSudoku(grid, 0, 0)):
printing(grid)
else:
print("no solution exists ")
# This code is contributed by sanjoy_62.
输出
3 1 6 5 7 8 4 9 2
5 2 9 1 3 4 7 6 8
4 8 7 6 2 9 5 3 1
2 6 3 4 1 5 9 8 7
9 7 4 8 6 3 1 2 5
8 5 1 7 9 2 6 4 3
1 3 8 9 4 7 2 5 6
6 9 2 3 5 1 8 7 4
7 4 5 2 8 6 3 1 9
复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度:
O(9^(n*n))。对于每个未分配的索引,有 9 个可能的选项,因此时间复杂度为O(9^(n*n))。时间复杂度保持不变,但检查一个数字是否可以正确使用要快得多,O(1)。 - 空间复杂度:
O(n*n)。为了存储输出数组,需要一个矩阵,并且位掩码需要 3 个额外的大小为 n 的数组。
边栏推荐
- Definition and Basic Operations of Sequence Tables
- Ali Ermi: Without accept, can a TCP connection be established?
- 基于网络数据流的未知密码协议逆向分析
- Skywalking系列学习之Trace Profiling源码分析
- 没有 accept,我可以建立 TCP 连接吗?
- 企业数据打通有什么好处?不同行业怎么解决数据打通难题?
- LED闪烁 闪灯芯片IC 手电筒IC 闪灯控制IC 闪烁IC流水灯
- Two methods of implementing inverted strings in C language
- [Graphic and textual] How to reinstall Win7 system
- Acrel5000web能耗系统在某学院的应用-Susie 周
猜你喜欢
![[Generic Programming] Full Detailed Explanation of Templates](/img/9d/7864f999cb2e4edda2ee7723558135.png)
[Generic Programming] Full Detailed Explanation of Templates
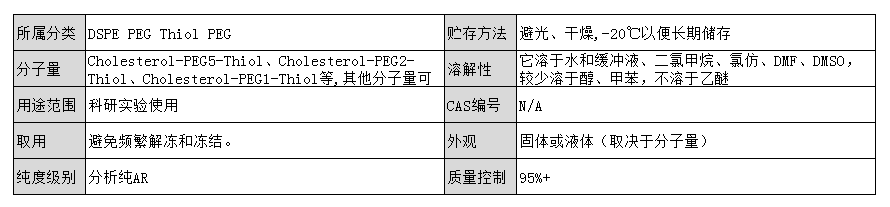
Cholesterol-PEG-Thiol, CLS-PEG-SH, Cholesterol-PEG-Sulfhydryl for improved solubility

普源精电上半年扭亏为盈,高端产品持续发力!你看好仪器界“华为”吗?

10个 Istio 流量管理 最常用的例子,你知道几个?
Ankerui supports Ethernet communication, profibus communication embedded energy meter APM guiding technical requirements-Susie Week

Install Mysql8.0 on windos, and solve the problem of re-login exception ERROR 1045 (28000)

LoRa无线技术在物联网应用市场的概况和发展
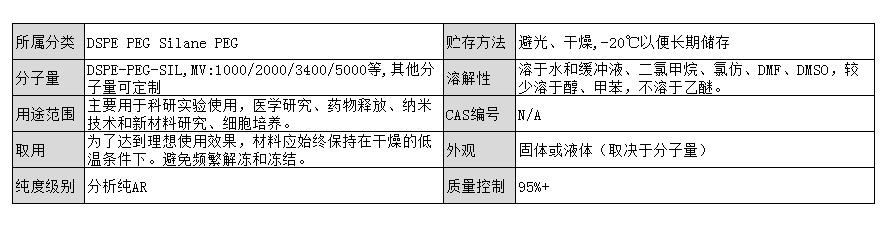
DSPE-PEG-Silane,DSPE-PEG-SIL,磷脂-聚乙二醇-硅烷修饰二氧化硅颗粒用

Lyapp exponents and bifurcation diagrams for fractional chaotic systems
Simulation of Water Temperature Control System Based on Fuzzy PID Controller
随机推荐
UE4_定序器控制蓝图对象
小黑leetcode清爽雨天之旅,刚吃完宇飞牛肉面、麻辣烫和啤酒:112. 路径总和
【Efficient Tools】Remote Control Software ToDesk (Favorites)
字符串哈希(2014 SERC J题)
What are the benefits of enterprise data integration?How do different industries solve the problem of data access?
【图文并茂】如何进行Win7系统的重装
C语言之实现倒置字符串的两种方法
Application of Acrel5000web Energy Consumption System in a College-Susie Week
C语言预处理命令是什么?
浅谈Numpy中的shape、reshape函数的区别
Unity_平滑移动
Cholesterol-PEG-Thiol,CLS-PEG-SH,胆固醇-聚乙二醇-巯基用于改善溶解度
Definition and Basic Operations of Linear Tables
Deceptive Dice(期望计算)
基于网络数据流的未知密码协议逆向分析
fixed investment fund
LED闪烁 闪灯芯片IC 手电筒IC 闪灯控制IC 闪烁IC流水灯
Excel如何打出正负号?Excel打出正负号的方法
Acrel5000web能耗系统在某学院的应用-Susie 周
Word怎么制作双面席卡?使用Word制作双面席卡方法