当前位置:网站首页>NVIDIA CUDA Highly Parallel Processor Programming (VII): Parallel Mode: Prefix and
NVIDIA CUDA Highly Parallel Processor Programming (VII): Parallel Mode: Prefix and
2022-08-08 07:04:00 【To advance the Po】
背景
前缀和(prefix sum)也叫扫描(scan),Close scan(inclusive scan)操作对 n 元数组[x0, x1, x2, …, xn-1] 进行二元运算#,返回输出数组 [x0, (x0#x1),…, (x0#x1#x2# …# xn-1)].Scan on(exclusive scan) Similar to closed scan,返回数组 [0, x0, (x0#x1),…, (x0#x1#x2# …# xn-2)].Shifts the closed scan output array all one bit to the right,第 0 an array assignment 0 That is, the output array of the open scan is obtained.
Serial implementation of the closed scan algorithm:
void sequential_scan(float *x, float *y, int Max_i){
y[0] = x[0];
for(int i=1;i < Max_i;i++){
y[i] = y[i-1]+x[i];
}
}
That is a simple dynamic programming.
Simple parallel scan
The following is an in-place scan algorithm implemented through a reduction tree:
- Declare the array in shared memoryXY,and set the length to n 的 x The values in the array are assigned to XY 数组.
- 进行迭代,在第 n 次迭代时,后 n − 2 n − 1 n-2^{n-1} n−2n−1 Add the number in front of it respectively 2 n − 1 2^{n-1} 2n−1个数.
- 当 2 n − 1 2^{n-1} 2n−1 大于n时,停止迭代.

The above algorithm can handle no more than one number of elements block 的线程数.
代码:
#include<cuda.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define SECTION_SIZE 256
__global__ void work_inefficient_scan_kernel(float *X, int input_size){
__shared__ float XY[SECTION_SIZE];
int i = blockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
//Load an array into a shared register.
if(i < input_size){
XY[threadIdx.x] = X[i];
}
//Perform a closed scan
for(unsigned int stride = 1;stride <= threadIdx.x;stride*=2){
__syncthreads();
XY[threadIdx.x] += XY[threadIdx.x - stride];
}
__syncthreads();
X[i] = XY[threadIdx.x];
}
void test(float *A, int n){
float *d_A, *d_B;
int size = n * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_A, size);
cudaMemcpy(d_A, A, size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
//用SECTION_SIZE作为blocksize startskernel.
work_inefficient_scan_kernel<<<ceil((float)n/SECTION_SIZE), SECTION_SIZE>>>(d_A, n);
cudaMemcpy(A, d_A, size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaFree(d_A);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
int n = atoi(argv[1]); //n 不能大于SECTION_SIZE
float *A = (float *)malloc(n * sizeof(float));
for(int i = 0; i < n;++i){
A[i] = 1.0;
}
test(A, n);
for(int i = 0;i < n; ++i){
printf("%f ", A[i]);
}
free(A);
return 0;
}
效率
Now let's analyze the above kernel 的工作效率.All threads will iterate log(SECTION_SIZE) 步.The number of threads that do not need to do additions in each iteration is equal to stride ,So we can calculate the amount of work done by the algorithm like this:
∑ ( N − s t r i d e ) , f o r s t r i d e s 1 , 2 , 4 , . . . , N / 2 \sum(N-stride), for \, strides \, 1,2,4,...,N/2 ∑(N−stride),forstrides1,2,4,...,N/2
The first part of each item has nothing to do with strides,So their sum is : N × l o g 2 ( N ) N \times log_2(N) N×log2(N);The second part is similar to the proportional sequence,他们的和为 N − 1 N-1 N−1.So the total number of addition operations is : N × l o g 2 ( N ) − ( N − 1 ) N \times log_2(N)-(N-1) N×log2(N)−(N−1)
The total number of additions done by the serial scan algorithm is N − 1 N-1 N−1,Serial and parallel are different N The number of additions to the value:
| N | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 | 1024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N − 1 N-1 N−1 | 15 | 31 | 63 | 127 | 255 | 51 | 1023 |
| N × l o g 2 ( N ) − ( N − 1 ) N \times log_2(N)-(N-1) N×log2(N)−(N−1) | 49 | 129 | 321 | 769 | 1793 | 4097 | 9217 |
元素个数为 1024 时,Parallel does more than serial 9 double addition.随着 N 的增大,This coefficient will continue to grow.
Efficient parallel scan
This algorithm consists of two parts,The first part is the reduction and summation,The second part distributes the partial sum with an inverted tree.
把一个长度为 N Array reduction sum of (The top half of the image below),一般需要 (N/2) + (N/4) + … + 2 + 1 = N - 1 次操作.
归约求和:
A version without a control flow branch:
for(unsigned int stride = 1;stride <= blockDim.x;stride *= 2){
__syncthreads();
int index = (threadIdx.x + 1)*stride*2 - 1;
if(index < SECTION_SIZE)
XY[index] += XY[index - stride];
}
The values in the array after reduction are shown in the first row of the figure below:
It can be seen from the inverted tree,第一次将 XY[7] 加到 XY[11] 上,The second time will be respectively XY[3], XY[7], XY[11] 加到 XY[5] , XY[9], XY[13] 上,第三次除 XY[0] The even-numbered element is added to the preceding element.
可以看出,相加的 stride 从 SECTION_SIZE/4 下降到 1.We need to set the location to stride 的倍数 - 1 的 XY Elements are added up to one distance apart stride on the element at the position.具体代码如下:
for(unsigned int stride = SECTION_SIZE/4; stride > 0; stride /= 2){
__syncthreads();
int index = (threadIdx.x + 1)*stride*2 - 1;
if(index + stride < SECTION_SIZE)
XY[index + stride] += XY[index];
}
Either in the reduction phase or in the distribution phase,The number of threads is not exceeded SECTION_SIZE/2.So can start one onlySECTION_SIZE/2 个线程的 block.因为一个 block 中可以有 1024 个线程,So there can be at most in each scan part 2048 个元素.So a thread has to load 2 个元素.
完整Brent_Kung_scan代码:
#include<cuda.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define SECTION_SIZE 2048
__global__ void Brent_Kung_scan_kernel(float *X, int input_size){
__shared__ float XY[SECTION_SIZE];
//Load an array into a shared register,One thread loads two elements.
int i = 2 * blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if(i < input_size) XY[threadIdx.x] = X[i];
else XY[threadIdx.x] = 0.0f;
if(i + blockDim.x < input_size) XY[threadIdx.x + blockDim.x] = X[i + blockDim.x];
else XY[threadIdx.x + blockDim.x] = 0.0f;
//Reduction and summation without control flow
for(unsigned int stride = 1;stride <= blockDim.x;stride *= 2){
__syncthreads();
int index = (threadIdx.x + 1)*stride*2 - 1;
if(index < SECTION_SIZE)
XY[index] += XY[index - stride];
}
//Distribution section and
for(unsigned int stride = SECTION_SIZE/4; stride > 0; stride /= 2){
__syncthreads();
int index = (threadIdx.x + 1)*stride*2 - 1;
if(index + stride < SECTION_SIZE)
XY[index + stride] += XY[index];
}
__syncthreads();
if(i < input_size) X[i] = X[threadIdx.x];
if(i + blockDim.x < input_size) X[i + blockDim.x] = XY[threadIdx.x + blockDim.x];
}
void test(float *A, int n){
float *d_A;
int size = n * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_A, size);
cudaMemcpy(d_A, A, size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
Brent_Kung_scan_kernel<<<ceil((float)n/(SECTION_SIZE/2)), SECTION_SIZE/2>>>(d_A, n);
cudaMemcpy(A, d_A, size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaFree(d_A);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
int n = atoi(argv[1]);
float *A = (float *)malloc(n * sizeof(float));
for(int i = 0; i < n;++i){
A[i] = 1.0;
}
test(A, n);
for(int i = 0;i < n; ++i){
printf("%f ", A[i]);
}
free(A);
return 0;
}
对于 N 个元素的数组,操作总数为 (N/2) + (N/4) + … + 4 + 2 -1 约为 N - 2,So the final operand is 2 × N − 3 2 \times N-3 2×N−3.The table below compares the differences N The number of operations performed under.
| N | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 | 1024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N − 1 N-1 N−1 | 15 | 31 | 63 | 127 | 255 | 51 | 1023 |
| N × l o g 2 ( N ) − ( N − 1 ) N \times log_2(N)-(N-1) N×log2(N)−(N−1) | 49 | 129 | 321 | 769 | 1793 | 4097 | 9217 |
| 2 × N − 3 2 \times N-3 2×N−3 | 29 | 61 | 125 | 253 | 509 | 1021 | 2045 |
Due to the number of operations now with N 成正比,而不是与 N × l o g 2 ( N ) N \times log_2(N) N×log2(N) 成正比,So the total number of operations performed by an efficient algorithm will not exceed twice the serial number.As long as there are at least twice as many execution units,Parallel algorithms can perform better than serial.
Parallel scans of larger lengths
The algorithm above can only handle at most 2048 个元素,We need a parallel algorithm that can handle more elements,The following hierarchical scan is one such method.
- First use the one from the previous section for the entire array Brent_Kung_scan_kernel 进行处理,Scanning occurs within each block,Only the results of the scan within the block remain in the result array after the scan,We call these segments scan blocks.
- Save the last number of each block to length m 的辅助数组 S 中,对 S 进行扫描.
- 将 S 的前 m - 1 Each element is added to the end of the result array m - 1 in each element of a scan block.

当前的 CUDA 设备每个 block 中有1024个线程,每个 block 最多能处理 2048 个元素,grid x 维中有 65536 个线程块,最多可以处理 134217728 个元素.
Complete the work in the picture above and we design 3 个 kernel.
第一个 kernel The first thread that uses the block,Load the last element of the scan block into S 数组上.可以使用 Brent_Kung_scan_kernel 然后在其后面加上:
__syncthreads(); if(threadIdx.x == 0) S[blockIdx.x] = XY[SECTION_SIZE - 1];第二个 kernel 对 S 进行扫描.可以使用 Brent_Kung_scan_kernel.
第三个 kernel 将 S Write back to the original array.
最终代码如下:
#include<cuda.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define SECTION_SIZE 2048
__global__ void Brent_Kung_scan_kernel_1(float *X, float *S, int input_size){
__shared__ float XY[SECTION_SIZE];
//Load an array into a shared register,One thread loads two elements.
int i = 2 * blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if(i < input_size) XY[threadIdx.x] = X[i];
else XY[threadIdx.x] = 0.0f;
if(i + blockDim.x < input_size) XY[threadIdx.x + blockDim.x] = X[i + blockDim.x];
else XY[threadIdx.x + blockDim.x] = 0.0f;
//Reduction and summation without control flow
for(unsigned int stride = 1;stride <= blockDim.x;stride *= 2){
__syncthreads();
int index = (threadIdx.x + 1)*stride*2 - 1;
if(index < SECTION_SIZE)
XY[index] += XY[index - stride];
}
//Distribution section and
for(unsigned int stride = SECTION_SIZE/4; stride > 0; stride /= 2){
__syncthreads();
int index = (threadIdx.x + 1)*stride*2 - 1;
if(index + stride < SECTION_SIZE)
XY[index + stride] += XY[index];
}
__syncthreads();
if(i < input_size) X[i] = XY[threadIdx.x];
if(i + blockDim.x < input_size) X[i + blockDim.x] = XY[threadIdx.x + blockDim.x];
__syncthreads();
if(threadIdx.x == 0){
S[blockIdx.x] = XY[SECTION_SIZE - 1];
}
}
__global__ void Brent_Kung_scan_kernel_2(float *X, int input_size){
__shared__ float XY[SECTION_SIZE];
//Load an array into a shared register,One thread loads two elements.
int i = 2 * blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if(i < input_size) XY[threadIdx.x] = X[i];
if(i + blockDim.x < input_size) XY[threadIdx.x + blockDim.x] = X[i + blockDim.x];
//Reduction and summation without control flow
for(unsigned int stride = 1;stride <= blockDim.x;stride *= 2){
__syncthreads();
int index = (threadIdx.x + 1)*stride*2 - 1;
if(index < SECTION_SIZE)
XY[index] += XY[index - stride];
}
//Distribution section and
for(unsigned int stride = SECTION_SIZE/4; stride > 0; stride /= 2){
__syncthreads();
int index = (threadIdx.x + 1)*stride*2 - 1;
if(index + stride < SECTION_SIZE)
XY[index + stride] += XY[index];
}
__syncthreads();
if(i < input_size) X[i] = XY[threadIdx.x];
if(i + blockDim.x < input_size) X[i + blockDim.x] = XY[threadIdx.x + blockDim.x];
}
__global__ void kernel_3(float *X, float *S, int input_size){
//One thread processes two elements.
int i = 2*blockDim.x*blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x;
if(blockIdx.x > 0){
X[i] += S[blockIdx.x - 1];
X[blockDim.x + i] += S[blockIdx.x - 1];
}
}
void test(float *A, int n){
float *d_A, *S;
int size = n * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_A, size);
cudaMalloc(&S, ceil((float)n/SECTION_SIZE)*sizeof(float));
cudaMemcpy(d_A, A, size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
Brent_Kung_scan_kernel_1<<<ceil((float)n/(SECTION_SIZE)), SECTION_SIZE/2>>>(d_A, S, n);
Brent_Kung_scan_kernel_2<<<ceil((float)(ceil((float)n/SECTION_SIZE))/(SECTION_SIZE)), SECTION_SIZE/2>>>(S, n);
kernel_3<<<ceil((float)n/(SECTION_SIZE)), SECTION_SIZE/2>>>(d_A, S, n);
cudaMemcpy(A, d_A, size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaFree(d_A);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
int n = atoi(argv[1]);
float *A = (float *)malloc(n * sizeof(float));
for(int i = 0; i < n;++i){
A[i] = 1.0;
}
test(A, n);
// for(int i = 0;i < n; ++i){
// printf("%f ", A[i]);
// }
printf("%f ", A[n-1]);
free(A);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
Because the printing speed is too slow,So print the last element directly,Equal to the input length is correct.
When the length is 10 million, the calculation result is wrong.
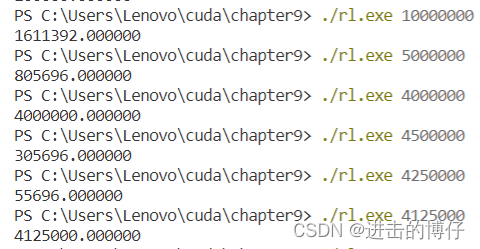
Find the length that can be calculated correctly at most approx 4125000,It might be hardware related,But it's unclear exactly what it's about.I'll add more as I learn more.
边栏推荐
- 如何使用conda,pip安装、更新、查看和卸载重装Pytorch?
- 正则爬取豆瓣Top250数据存储到CSV文件(6行代码)
- MongoDB配置文件.conf配置项介绍
- PURE(A Frustratingly Easy Approach for Entity and Relation Extraction)
- 必知必会的VGG网络(含代码)
- 线性回归---Fit A Line
- Yii2中MongoDB的使用方法-CURD
- 【图形学】四元数(二)
- Prompt for Extraction? PAIE:Prompting Arguement Interaction for Event Argument Extraction
- 多神经网络模型联合训练,神经网络模型怎么训练
猜你喜欢

【图形学】12 UnityShader语法入门
Stack queue OJ question sharing and explanation
jupyter notebook添加目录

用户管理 用户的增删改查 切换用户 用户组 用户组相关文件
win11+MX250+CUDA Tookit 10.1 update 2

File IO realizes the encryption operation of pictures

关于剪枝对象的分类(weights剪枝、神经元剪枝、filters剪枝、layers剪枝、channel剪枝、对channel分组剪枝、Stripe剪枝)

leetcode第84场双周赛
深度神经网络主要模型,深度神经网络预测模型

中序表达式转为后序表达式
随机推荐
【嵌入式Linux】SQLite数据库
PyTorch向量变换基本操作
P23 传值和传引用
【EagleEye】2020-ECCV-EagleEye: Fast Sub-net Evaluation for Efficient Neural Network Pruning-论文详解
有符号数和无符号数参与运算时的问题
多神经网络模型联合训练,神经网络模型怎么训练
leetcode第84场双周赛
如何使用conda,pip安装、更新、查看和卸载重装Pytorch?
P20 美颜相机的实现——基础铺垫2
cybox target machine wp
Unity3D物体上下左右旋转(不受物体自身坐标轴影响)
CSDN21天学习挑战赛之插入排序
【图形学】13 UnityShader语义(一)
Error日志 ERROR: Failed building wheel for jsonnet
TextCNN实现imdb数据集情感分类任务
[Unity] GPU动画实现(五)——渲染GPU动画
P04 并发小球V1 V2.1
简悦音乐播放器用到的相关技术点都在这里了(一)
ResNet 原理与代码复现
NVIDIA CUDA 高度并行处理器编程(四):性能优化习题