当前位置:网站首页>[programming practice / embedded competition] learning record of embedded competition (II): picture streaming based on TCP
[programming practice / embedded competition] learning record of embedded competition (II): picture streaming based on TCP
2022-04-23 08:04:00 【Pluse Lin】
0. Preface
After the last experiment , The head of the competition team gave me a new task : Try to simulate the lower computer to send picture bitstream to the upper computer , And receive it and show it on web front end .
Confirmed , The lower computer converts the picture into pixels RGB Value transfer , Transmit the length and width of the picture in turn 、 The pixel value of each pixel from the upper left corner to the lower right corner , That is, each byte is the color value of the pixel , Not like png、jpg Wait for picture coding . At present, the team leader asked me to send out the grayscale image , Therefore, my later processing part is based on gray image . The principle of transmitting color pictures is similar .
1. Picture coding
The focus of this experiment is how to receive client The transmitted bit stream is processed and put into the front end , Therefore, the data format is not the focus , But for the convenience of follow-up explanation , Here is the format of the picture of this experiment :

( This is much like the byte counting method of data link layer in computer network , It's not ?)
among ,width Field occupancy 1 or 2 byte , Indicates the width of the picture ,height occupy 1 or 2 byte , Indicates the length of the picture ,pixels Is the pixel bit , Because this experiment is a gray image , So only one channel is needed , It can also be changed to 3 Channels .
When receiving data , You can confirm the appearance of the picture through the first two fields , And how many pixel values there are , Because it is often not the same picture at a time , It may be multiple frames of the video , So you need to draw the boundary of each picture .
In this study ,width、height The length of the field is taken as 1 byte
2. Picture transmission mode
Follow the above format , I will 3 Zhang 255*255 The gray-scale image is saved in the form of binary coding , Got it 3 File
After that, you will use the network debugging assistant to select a file and send it
3. Picture receiving and coding processing
The first is the receiving part of the picture , because TCP server At most... Can be received at a time 1024B The data of ( This should be related to the data link layer MTU The maximum is 1500B of , But I don't know why 1024B), Therefore, we need to cache the received data , When a frame of picture is received , Process and save , In order to offer web server Use .
because TCP server and web server It's two threads , Therefore, there is the problem of mutual exclusion , Here, semaphores are used for control , If you're not familiar with semaphores , You can learn from Baidu search semaphores , No more here .
Also, why not use post Request to web server Send picture encoding , Because the picture encoding is a binary bit stream , It seems difficult to code to json in , It can't be converted into a string , Therefore, it can only be realized by sharing variables between threads .
The code is as follows , Slightly bloated , This is also the place that can be improved in the follow-up
class DataBuffer:
def __init__(self):
self.tempdata=bytes(0)
self.pic=bytes(0)
# Control read mutex
self.mutex=threading.Semaphore(1)
# The notice can take
self.pic_mutex=threading.Semaphore(1)
# Maximum
self.max_size=0x7fffffff
def insert_data(self,data:bytes):
self.mutex.acquire()
# if(len(self.tempdata)==0):
# self.max_size=int(data[0])*int(data[1])+2
self.tempdata+=data
# No matter how big the picture is, its size will not exceed 0x7fffffff
if(self.max_size>=0x7fffffff):
self.max_size=int(self.tempdata[0])*int(self.tempdata[1])+2
if(len(self.tempdata)>=self.max_size):
next_length=len(self.tempdata)-self.max_size
self.pic_mutex.acquire()
width,height,self.pic=hex_to_jpgstream(self.tempdata)
if(next_length>0):
self.tempdata=data[-next_length:]
#self.max_size=int(self.tempdata[0])*int(self.tempdata[1])+2
else:
self.tempdata=bytes(0)
self.max_size=0x7fffffff
self.pic_mutex.release()
self.mutex.release()
def get_data(self):
self.pic_mutex.acquire()
pic=self.pic
self.pic_mutex.release()
return pic
def clearbuffer(self):
self.max_size=0x7fffffff
self.tempdata=bytes(0)
Buffer=DataBuffer()
class MyHandler(socketserver.BaseRequestHandler):
def handle(self):
global Buffer
while True:
data=self.request.recv(8192)
if not data:
break
else:
Buffer.insert_data(data)
The general process is :
- Every time I receive 1024 Bytes of data , Stored in cache variable tempdata in
- Decide whether to accept a picture ( Compare the received data volume with the picture size , The picture size is calculated from the picture format segment )
- If received , After processing, it is saved in the variable pic in , At the same time to modify tempdata For the data part of the next picture , And recalculate the picture size .
- web server When taking pictures , The gain is pic Instead of tempdata
The following is the image processing part , It mainly converts the picture coding into jpg Format to show on the front end
def hex_to_jpgstream(hexstream:bytes):
#hex -> np.array
#bytes[0]:width bytes[1]:height
width,height=int(hexstream[0]),int(hexstream[1])
img=[int(hexstream[i]) for i in range(2,len(hexstream))]
img=np.array(img).reshape((width,height))
#np.array->jpg stream
img=cv2.imencode(".jpg",img)[1]
img=img.tobytes()
#jpg stream => base64
# b64stream=base64.b64encode(img)
return width,height,img
4. The picture stream is displayed on the front end
The processing of image display at the front end is different from that of ordinary back-end parameter transmission , I was thinking of using it again Ajax Update by polling , But then it was considered that such a burden was too great , So use Response Corresponding return .
This is where yield grammar , Probably generated a generator , You can constantly return some data , This is also a method of video streaming
from flask import *
from MyServer import Buffer
app1=Flask(__name__)
data=None
@app1.route("/",methods=["GET","POST"])
def index_page():
return render_template("index0.html")
def gen():
while True:
pic=Buffer.get_data()
yield (b'--frame\r\n'
b'Content-Type: image/jpeg\r\n\r\n' + pic + b'\r\n')
@app1.route("/video_feed")
def video_feed():
return Response(gen(),mimetype="multipart/x-mixed-replace; boundary=frame")
The front end
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<img id="camera" src="{
{url_for('video_feed')}}">
</body>
</html>
Finally, the startup module , start-up TCP server and Web server
from flask import *
import threading
import socketserver
import time
from app_views import *
from MyServer import *
def start_TCP(host,port):
myserver=socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer((host,port),MyHandler)
myserver.serve_forever()
def start_flask(host,port):
app1.run(host=host,port=port)
def main():
th1=threading.Thread(target=start_flask,args=("192.168.71.1",5000))
th2=threading.Thread(target=start_TCP,args=("192.168.71.1",5001))
th1.start()
th2.start()
if __name__=="__main__":
main()
5. check before acceptance
start-up web The server and TCP The server
Send data in the network debugging assistant

Input web Server address , I found that the picture display was successful
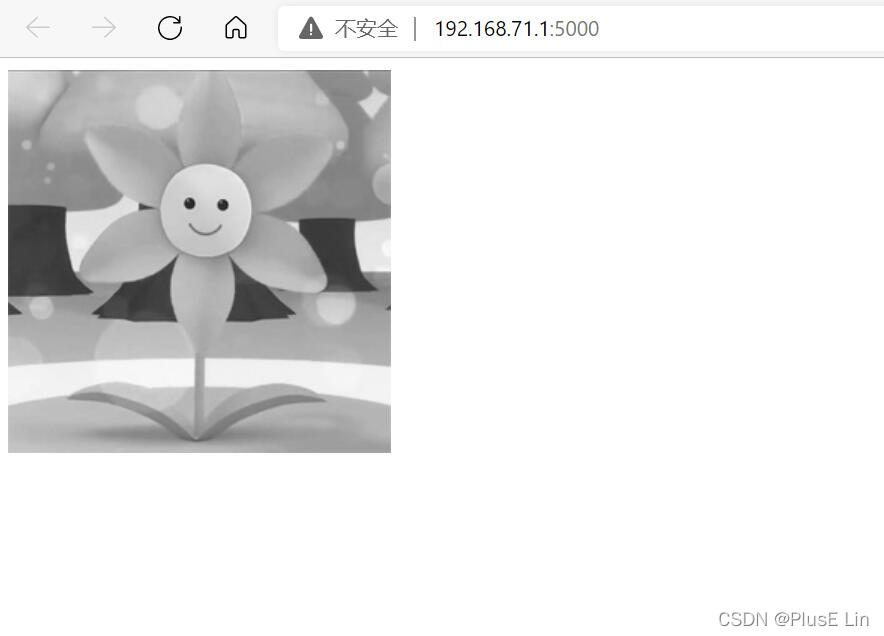
It proves that the experiment is successful
6. reflection
- Whether this method can be correctly applied to video ? In fact, in the next experiment, I will try
- Is there a better way to make TCP server and web server Shared data ? You can try other ways when you have a chance
Last , Thank you for watching. !
版权声明
本文为[Pluse Lin]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230629306585.html
边栏推荐
- 《内网安全攻防:渗透测试实战指南》读书笔记(五):域内横向移动分析及防御
- 一些关于网络安全的好教程或笔记的链接,记录一下
- 内网渗透系列:内网隧道之icmp_tran
- Interview learning route
- strcat()、strcpy()、strcmp()、strlen()
- Houdini fluid > > particle fluid export to unity note
- SAP STO With Billing流程与配置
- 面试学习路线
- Internal network security attack and defense: a practical guide to penetration testing (VII): cross domain attack analysis and defense
- ABAP ALV显示金额与导出金额不一致
猜你喜欢

About USB flash drive data prompt raw, need to format, data recovery notes

Construction of middleman environment mitmproxy
Chapter IV intangible assets

Intranet penetration series: dns2tcp of Intranet tunnel

CTF attack and defense world brush questions 51-

SAP self created table log function is enabled

Intranet penetration series: icmptunnel of Intranet tunnel (by master dhavalkapil)

Go语学习笔记 - 异常处理 | 从零开始Go语言

SAP STO With Billing流程与配置

云计算技能大赛 -- openstack私有云环境 第二部分
随机推荐
Intranet penetration series: dnscat2 of Intranet tunnel
第四章 无形资产
Intranet penetration series: icmpsh of Intranet tunnel
《内网安全攻防:渗透测试实战指南》读书笔记(五):域内横向移动分析及防御
About USB flash drive data prompt raw, need to format, data recovery notes
聊聊接口幂等与消费幂等的本质
Sto with billing cross company inventory dump return
随笔(不定时更新)
Chapter V investment real estate
访问数据库的时候出现错误 Operation not allowed for a result set of type ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY.详解
GUI,CLI与Unix哲学
Research on system and software security (4)
《内网安全攻防:渗透测试实战指南》读书笔记(八):权限维持分析及防御
学fpga(从verilog到hls)
Dvwa 靶场练习记录
《内网安全攻防:渗透测试实战指南》读书笔记(六):域控制器安全
内网渗透系列:内网隧道之dnscat2
从ES、MongoDB、Redis、RocketMQ出发谈分布式存储
upload-labs 靶场练习
feign如何集成hystrix