当前位置:网站首页>Digital image processing third edition Gonzalez notes Chapter 2
Digital image processing third edition Gonzalez notes Chapter 2
2022-04-23 03:37:00 【Blue area soldier】
Chapter two
The notes in chapter two

The horizontal axis is the angle between the straight line from the center of the lens to the retina and the visual axis , Refer to the following figure .

From this picture, we can see that there is a blind spot in people's eyes. There is no cone , There is no rod . But usually you don't feel this blind spot . One is because the brain of the brain , Another reason is that your binocular vision just covers the blind spot area , So feel this blind spot , Need to cover one eye . For details, please refer to the operation in this link https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/28105827

o It's the distance , object distance
f It's focal length ,focal distance
i It's like distance , image distance
Imaging in a camera is by changing the distance between the lens and the imaging plane , change i
Imaging in the eye is through the lens f.
Wavelength frequency formula of light

wavelength = The speed of light / frequency , c It's the speed of light ,v It's the frequency .
Energy formula of each component of electromagnetic spectrum

E It's energy ,h It's the Planck constant (6.62607015×10-34 J·s),v It's the frequency .
The common unit of energy is the electron volt , That is, an electron passes through 1 The kinetic energy of the change in the potential difference of volts . The commonly used Joule is a Coulomb positive charge passing through 1 The kinetic energy of the change in the potential difference of volts . An electron is charged about 1.6×10-19C The negative charge of .
It can be seen that energy is directly proportional to frequency , The higher the frequency , The more energy ( The microwave can heat , But decay fast , Long wave communication , But the energy is low ).
Monochromatic light refers to black, white and gray , Not color .
The electromagnetic spectrum of color light is 0.43μm( violet , micron ,10-3mm) To 0.79μm( Red ) Between .
Three basic quantities used to describe the quality of color light sources :
Luminous intensity (Radiance): The total amount of energy from the light source , In watts (W) Measure
Luminous flux (Luminance): In lumens (lm) Measure the energy the observer feels from the light source
brightness (brightness): It's a subjective description , Can't actually measure , It is one of the parameters to describe the feeling of color .
If required to “ See an object ”. That is, the electromagnetic wave can image the object . The electromagnetic wave length must be less than or equal to the size of the object .
Three main sensors :
Single , Strip , array
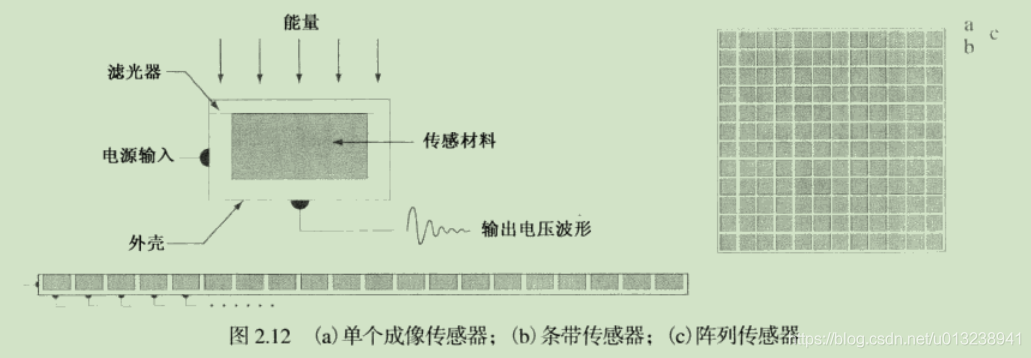
Some units of measurement in optics and images .
Lumen (lm)、 Lex (lux)、 Candela (cd)、 Candela per square meter (cd/m2)
These belong to photometry (Photometry) The unit of , It is based on the feeling of the human eye .
And radiometry (radiometry), Based on actual energy .
What's the difference between them ?
For example, there is an infrared light source , High energy , But it's all infrared light , The human eye is insensitive , Out of sight , This is the radiometric measurement is very strong , But in photometry , This light source is weaker . The conversion between the two types of parameters is carried out through a value , be called Luminous efficiency(Φ(λ)), Is a real valued function that converts light that does not pass through the wavelength .

The human eye is right 555nm The wavelength at the corresponding is the most sensitive . therefore 555nm Situated Luminous efficiency As a relative standard 1.
Luminous flux (Luminous flux) Its unit is Lumen (lm). It can be compared to the power concept of radiometry , Is the flux of light felt by the human eye .
Luminous flux of monochromatic light Φ(λ):

Φe(λ) The wavelength is λ The true power of light .
v(λ) The wavelength of the upper body is λ Of light Luminous efficiency.
Km Is the conversion constant between lumens and watts . by 638lm/W, That is, the real power is 1W Of 555nm Light , Its light flux is 638 Lumen .
If you need to evaluate non monochromatic light , Like a fluorescent lamp , You have to consider all wavelengths .

Integrate all wavelengths .
Intensity of illumination (illuminance), The unit is Lex (lux). Used to describe an object / How much power the detector receives .
The unit in radiometry is W/m2( Just as luminous flux lumens correspond to radiometric power watts )
It is used to indicate whether the detector is severely irradiated .
Luminous intensity (Luminous intensity), Unit candela (cd). Used to describe how the human eye sees a Point source Whether it's bright or not .
The definition for , With a point light as the origin Solid Angle ( The unit is sphericity sr) How much power is there in the , Unit is W/sr.
Solid angle can be compared with plane angle , Is to make a sphere with a point as the center of the sphere , Intercept the spherical area with a cone at a certain angle , Than the square of the radius of the upper sphere .( The definition of solid angle is very similar to the radian angle of plane, isn't it )

Candela describes a point light source .
And nit (nit) It describes the surface light source , One of the parameters we often see when we buy monitors is nit (nit), Nit's unit is cd/m2.
The notes come from this answer , It's very clear , I suggest you read it .
Excuse me, nit (nit) And lumens (LM) What is the relationship between ? - Rick Answer - You know
https://www.zhihu.com/question/265367399/answer/357599187
sampling , Is to digitize the coordinate values , Images f(x,y) Medium x and y.
quantitative , Is to digitize the amplitude , Images f(x,y) Value .
The range of values crossed by grayscale is informally called dynamic range ( Understanding is that the upper and lower limits of gray scale can reach a range ), There are different usages on different occasions . Here, the dynamic range of the image system is defined as the ratio of the maximum measurable gray level to the minimum detectable gray level in the system . The upper limit depends on the saturation ,
Contrast : The difference between the highest gray level and the lowest gray level of the image .
Spatial resolution : Spatial resolution in digital image processing and what is often called wide * High pixel resolution ( This is just the size of the image itself ) Different , Spatial resolution is usually the sum of the logarithm of lines per unit distance The number of points per unit of distance is measured (dpi, Dots per inch ), Need and space units ( rice , mm , centimeter , Inch equidistant unit ) Combined measurement makes sense .
Gray scale resolution : If the gray level resolution is too low, false contour may appear

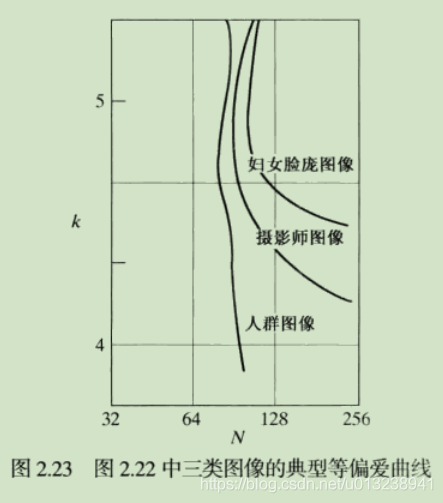
This graph describes different N and k Image , People's subjective preference curve .N Is the aforementioned spatial resolution of the image ( Namely N*N Size Image ),f Is the logarithm of gray scale amplitude , Namely 2k.
I think the method of this picture should be that every coordinate in the image generates an image , Then fix k, From the same N Choose the image with the best subjective quality ( Of course, there may be more than one person , Multiple votes , The one with the largest number of votes ).
2.5 There are some translation errors in the Chinese version , If you can't understand it, you can compare it with the English version .
p Of 4 Neighborhood , Just a pixel p The top, bottom, left and right pixels of ,N4(p).
p Of 8 Neighborhood ,4 Neighborhood plus four corners (ND(p)),N8(p).
2.5.2 In the festival :
V Is a set of gray values that define adjacency , It means the... Used to define adjacent pixels Gray value ( Only 0 To 255 in ) A collection of species .
Mixed adjacency :1)4 Adjacency is called mixed adjacency ,2)q stay p The four corners of a pixel , And p and q Of 4 The pixel gray level in the intersection of neighborhood is not in the gray value set V in .
8 Adjacency ambiguity means 8 Adjacency creates two pathways
https://blog.csdn.net/hankai1024/article/details/19085203
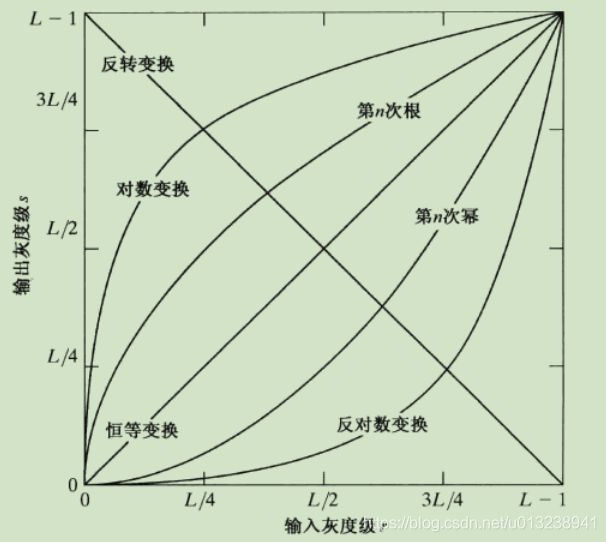
Some commonly used gray transformation processing functions
- Image reversal


2. Logarithmic transformation


In the Fourier transform of the image , Fourier spectrum is usually calibrated by logarithmic transformation .
3. Power law ( gamma ) Transformation
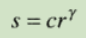


Gamma correction , stay CRT There are grayscale in the screen - Voltage correction , Through this function, you can better see the details of some gray range images .
2.1

The human eye needs to be able to identify print points , Then the image size of the print point in the retina must be larger than the fovea , So you can list expressions

So the final answer is 0.05mm The lower retina can no longer distinguish this point .
2.3
Direct basis wavelength = The speed of light / frequency obtain
wavelength = 2.998×108(m/s)÷77(Hz) About equal to 3.8935×106(m)
2.4
A single sensor cannot detect the shape , Because the detection of a single sensor requires two-dimensional movement in the tested area , And cells , Bacteria, etc. are too small , The required accuracy is too high . So we need array sensors .

2.5

2.6
Based on the lowest cost , You can choose to pair red 、 green 、 Blue sensitive single imaging sensor , By judging the output voltage , Select the color corresponding to the maximum voltage , If the voltage difference does not play , Just choose white .
2.7
I can't understand the question .
I'll do it later .
版权声明
本文为[Blue area soldier]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204220602025733.html
边栏推荐
- Download and configuration of idea
- Section 2 map and structure in Chapter 6
- Problem a: face recognition
- Codeforces Round #784 (Div. 4)题解 (第一次AK cf (XD
- Applet - canvas drawing Poster
- 2021-08-31
- 2022 group programming ladder simulation match 1-8 are prime numbers (20 points)
- 抽象类、接口、常用关键字
- 第四次作业
- MySQL is completely uninstalled and MySQL service is cleaned up
猜你喜欢

Punch in: 4.22 C language chapter - (1) first knowledge of C language - (11) pointer

Visual programming -- how to customize the mouse cursor

標識符、關鍵字、數據類型
PYMOL-note

AWS from entry to actual combat: creating accounts

Identifier, keyword, data type
Unity Basics

Un aperçu des flux d'E / s et des opérations de fichiers de classe de fichiers

Unity basics 2

Design and implementation of redis (2): how to handle expired keys
随机推荐
Test questions and some space wars
对象和类的概念
Source code and update details of new instance segmentation network panet (path aggregation network for instance segmentation)
Flink customizes the application of sink side sinkfunction
Talent Plan 学习营初体验:交流+坚持 开源协作课程学习的不二路径
MySQL zip installation tutorial
2022 团体程序设计天梯赛 模拟赛 L2-4 哲哲打游戏 (25 分)
Vscode delete uninstall residue
Leetcode punch in diary day 01
The art of concurrent programming (2): synchronized usage scenarios
将编译安装的mysql加入PATH环境变量
The art of concurrent programming (3): an in-depth understanding of the principle of synchronized
標識符、關鍵字、數據類型
AWS from entry to actual combat: creating accounts
String input problem
Using jsonserialize to realize data type conversion gracefully
Identificateur, mot - clé, type de données
C-11 problem h: treasure chest 2
File upload vulnerability summary and upload labs shooting range documentary
Design and implementation of redis (3): persistence strategy RDB, AOF