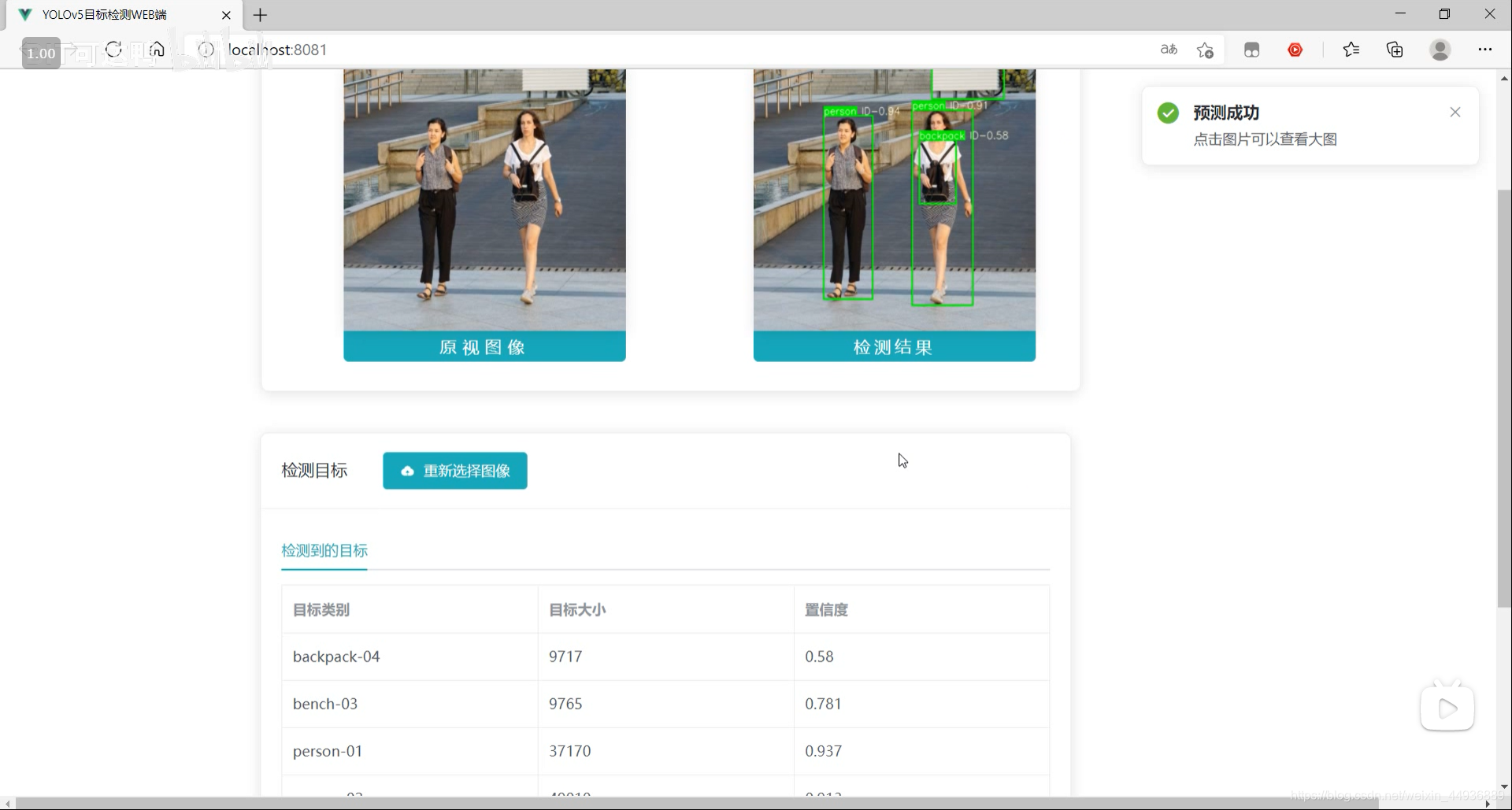
1. 效果:
视频链接:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Wr4y1K7Sh
最终效果:
源码已经上传 Github:
https://github.com/Sharpiless/Yolov5-Flask-VUE
2. YOLOv5模型训练:
训练自己的数据集可以看我这篇博客:
【小白CV】手把手教你用YOLOv5训练自己的数据集(从Windows环境配置到模型部署)
这里演示的话我就用官方训练好的 yolov5m.pt 模型。
3. YOLOv5模型预测:
预测接口:
import torch
import numpy as np
from models.experimental import attempt_load
from utils.general import non_max_suppression, scale_coords, letterbox
from utils.torch_utils import select_device
import cv2
from random import randint
class Detector(object):
def __init__(self):
self.img_size = 640
self.threshold = 0.4
self.max_frame = 160
self.init_model()
def init_model(self):
self.weights = 'weights/yolov5m.pt'
self.device = '0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
self.device = select_device(self.device)
model = attempt_load(self.weights, map_location=self.device)
model.to(self.device).eval()
model.half()
# torch.save(model, 'test.pt')
self.m = model
self.names = model.module.names if hasattr(
model, 'module') else model.names
self.colors = [
(randint(0, 255), randint(0, 255), randint(0, 255)) for _ in self.names
]
def preprocess(self, img):
img0 = img.copy()
img = letterbox(img, new_shape=self.img_size)[0]
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1)
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(self.device)
img = img.half() # 半精度
img /= 255.0 # 图像归一化
if img.ndimension() == 3:
img = img.unsqueeze(0)
return img0, img
def plot_bboxes(self, image, bboxes, line_thickness=None):
tl = line_thickness or round(
0.002 * (image.shape[0] + image.shape[1]) / 2) + 1 # line/font thickness
for (x1, y1, x2, y2, cls_id, conf) in bboxes:
color = self.colors[self.names.index(cls_id)]
c1, c2 = (x1, y1), (x2, y2)
cv2.rectangle(image, c1, c2, color,
thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(
cls_id, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3
cv2.rectangle(image, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(image, '{} ID-{:.2f}'.format(cls_id, conf), (c1[0], c1[1] - 2), 0, tl / 3,
[225, 255, 255], thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
return image
def detect(self, im):
im0, img = self.preprocess(im)
pred = self.m(img, augment=False)[0]
pred = pred.float()
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, self.threshold, 0.3)
pred_boxes = []
image_info = {}
count = 0
for det in pred:
if det is not None and len(det):
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(
img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
for *x, conf, cls_id in det:
lbl = self.names[int(cls_id)]
x1, y1 = int(x[0]), int(x[1])
x2, y2 = int(x[2]), int(x[3])
pred_boxes.append(
(x1, y1, x2, y2, lbl, conf))
count += 1
key = '{}-{:02}'.format(lbl, count)
image_info[key] = ['{}×{}'.format(
x2-x1, y2-y1), np.round(float(conf), 3)]
im = self.plot_bboxes(im, pred_boxes)
return im, image_info
处理完保存到服务器本地临时的目录下:
import os
def pre_process(data_path):
file_name = os.path.split(data_path)[1].split('.')[0]
return data_path, file_name
import cv2
def predict(dataset, model, ext):
global img_y
x = dataset[0].replace('\\', '/')
file_name = dataset[1]
print(x)
print(file_name)
x = cv2.imread(x)
img_y, image_info = model.detect(x)
cv2.imwrite('./tmp/draw/{}.{}'.format(file_name, ext), img_y)
return image_info
from core import process, predict
def c_main(path, model, ext):
image_data = process.pre_process(path)
image_info = predict.predict(image_data, model, ext)
return image_data[1] + '.' + ext, image_info
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass
4. Flask 部署:
然后通过Flask框架写相应函数:
@app.route('/upload', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def upload_file():
file = request.files['file']
print(datetime.datetime.now(), file.filename)
if file and allowed_file(file.filename):
src_path = os.path.join(app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'], file.filename)
file.save(src_path)
shutil.copy(src_path, './tmp/ct')
image_path = os.path.join('./tmp/ct', file.filename)
pid, image_info = core.main.c_main(
image_path, current_app.model, file.filename.rsplit('.', 1)[1])
return jsonify({'status': 1,
'image_url': 'http://127.0.0.1:5003/tmp/ct/' + pid,
'draw_url': 'http://127.0.0.1:5003/tmp/draw/' + pid,
'image_info': image_info})
return jsonify({'status': 0})
这样前端发出POST请求时,会对上传的图像进行处理。
5. VUE前端:
主要是通过VUE编写前端WEB框架。
核心前后端交互代码:
// 上传文件
update(e) {
this.percentage = 0;
this.dialogTableVisible = true;
this.url_1 = "";
this.url_2 = "";
this.srcList = [];
this.srcList1 = [];
this.wait_return = "";
this.wait_upload = "";
this.feature_list = [];
this.feat_list = [];
this.fullscreenLoading = true;
this.loading = true;
this.showbutton = false;
let file = e.target.files[0];
this.url_1 = this.$options.methods.getObjectURL(file);
let param = new FormData(); //创建form对象
param.append("file", file, file.name); //通过append向form对象添加数据
var timer = setInterval(() => {
this.myFunc();
}, 30);
let config = {
headers: { "Content-Type": "multipart/form-data" },
}; //添加请求头
axios
.post(this.server_url + "/upload", param, config)
.then((response) => {
this.percentage = 100;
clearInterval(timer);
this.url_1 = response.data.image_url;
this.srcList.push(this.url_1);
this.url_2 = response.data.draw_url;
this.srcList1.push(this.url_2);
this.fullscreenLoading = false;
this.loading = false;
this.feat_list = Object.keys(response.data.image_info);
for (var i = 0; i < this.feat_list.length; i++) {
response.data.image_info[this.feat_list[i]][2] = this.feat_list[i];
this.feature_list.push(response.data.image_info[this.feat_list[i]]);
}
this.feature_list.push(response.data.image_info);
this.feature_list_1 = this.feature_list[0];
this.dialogTableVisible = false;
this.percentage = 0;
this.notice1();
});
},
这段代码在点击提交图片时响应:
<div slot="header" class="clearfix">
<span>检测目标span>
<el-button
style="margin-left: 35px"
v-show="!showbutton"
type="primary"
icon="el-icon-upload"
class="download_bt"
v-on:click="true_upload2"
>
重新选择图像
<input
ref="upload2"
style="display: none"
name="file"
type="file"
@change="update"
/>
el-button>
div>
6. 启动项目:
在 Flask 后端项目下启动后端代码:
python app.py
在 VUE 前端项目下,先安装依赖:
npm install
然后运行前端:
npm run serve
然后在浏览器打开localhost即可:
关注我的公众号:
感兴趣的同学关注我的公众号——可达鸭的深度学习教程: