Adaptive wavelets
Adaptive wavelets 
Wavelets which adapt given data (and optionally a pre-trained model). This yields models which are faster, more compressible, and more interpretable.
Quickstart
Installation:
pip install awaveor clone the repo and runpython setup.py installfrom the repo directory
Then, can use the core functions (see simplest example in notebooks/demo_simple_2d.ipynb or notebooks/demo_simple_1d.ipynb). See the docs for more information on arguments for these functions.
Given some data X, you can run the following:
from awave.utils.misc import get_wavefun
from awave.transform2d import DWT2d
wt = DWT2d(wave='db5', J=4)
wt.fit(X=X, lr=1e-1, num_epochs=10) # this function alternatively accepts a dataloader
X_sparse = wt(X) # uses the learned adaptive wavelet
phi, psi, x = get_wavefun(wt) # can also inspect the learned adaptive wavelet
To distill a pretrained model named model, simply pass it as an additional argument to the fit function:
wt.fit(X=X, pretrained_model=model,
lr=1e-1, num_epochs=10,
lamL1attr=5) # control how much to regularize the model's attributions
Background
Official code for using / reproducing AWD from the paper "Adaptive wavelet distillation from neural networks through interpretations" (Ha et al. NeurIPS, 2021).
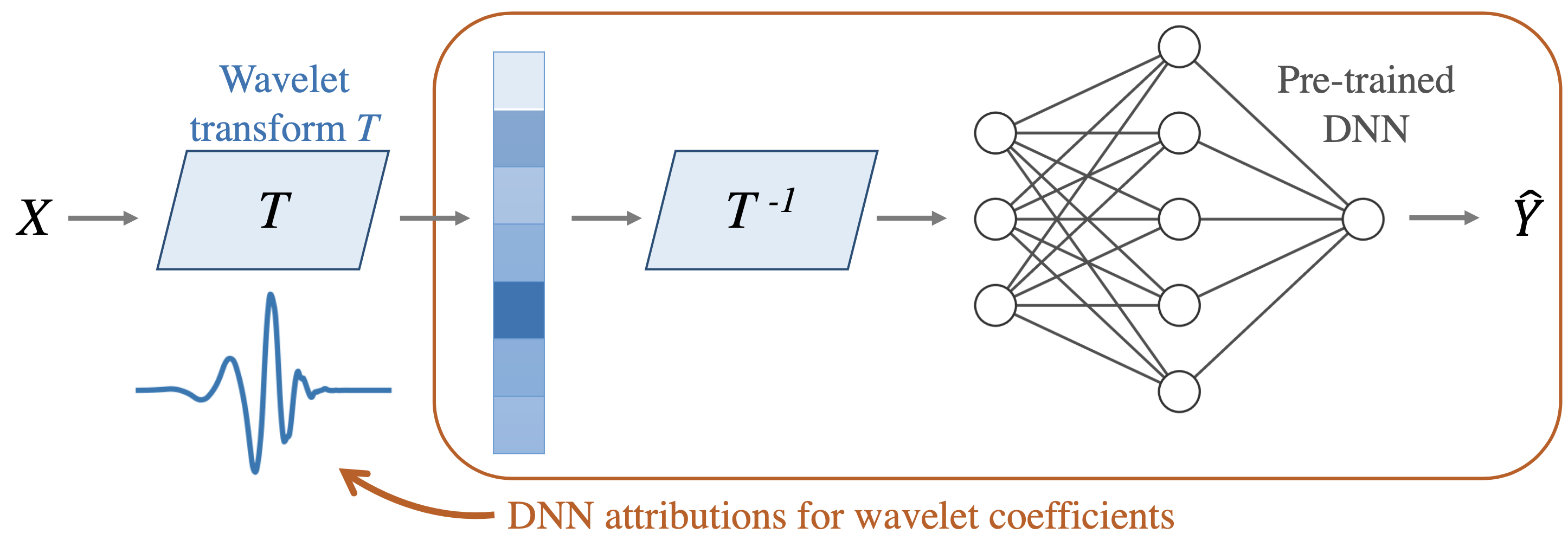
Abstract: Recent deep-learning models have achieved impressive prediction performance, but often sacrifice interpretability and computational efficiency. Interpretability is crucial in many disciplines, such as science and medicine, where models must be carefully vetted or where interpretation is the goal itself. Moreover, interpretable models are concise and often yield computational efficiency. Here, we propose adaptive wavelet distillation (AWD), a method which aims to distill information from a trained neural network into a wavelet transform. Specifically, AWD penalizes feature attributions of a neural network in the wavelet domain to learn an effective multi-resolution wavelet transform. The resulting model is highly predictive, concise, computationally efficient, and has properties (such as a multi-scale structure) which make it easy to interpret. In close collaboration with domain experts, we showcase how AWD addresses challenges in two real-world settings: cosmological parameter inference and molecular-partner prediction. In both cases, AWD yields a scientifically interpretable and concise model which gives predictive performance better than state-of-the-art neural networks. Moreover, AWD identifies predictive features that are scientifically meaningful in the context of respective domains.
Also provides an implementation for "Learning Sparse Wavelet Representations" (Recoskie & Mann, 2018)
Abstract: In this work we propose a method for learning wavelet filters directly from data. We accomplish this by framing the discrete wavelet transform as a modified convolutional neural network. We introduce an autoencoder wavelet transform network that is trained using gradient descent. We show that the model is capable of learning structured wavelet filters from synthetic and real data. The learned wavelets are shown to be similar to traditional wavelets that are derived using Fourier methods. Our method is simple to implement and easily incorporated into neural network architectures. A major advantage to our model is that we can learn from raw audio data.
Related work
- TRIM (ICLR 2020 workshop pdf, github) - using simple reparameterizations, allows for calculating disentangled importances to transformations of the input (e.g. assigning importances to different frequencies)
- ACD (ICLR 2019 pdf, github) - extends CD to CNNs / arbitrary DNNs, and aggregates explanations into a hierarchy
- CDEP (ICML 2020 pdf, github) - penalizes CD / ACD scores during training to make models generalize better
- DAC (arXiv 2019 pdf, github) - finds disentangled interpretations for random forests
- PDR framework (PNAS 2019 pdf) - an overarching framewwork for guiding and framing interpretable machine learning
If this package is useful for you, please cite the following!
@article{ha2021adaptive,
title={Adaptive wavelet distillation from neural networks through interpretations},
author={Ha, Wooseok and Singh, Chandan and Lanusse, Francois and Song, Eli and Dang, Song and He, Kangmin and Upadhyayula, Srigokul and Yu, Bin},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.09145},
year={2021}
}