Overview
This Python package provides implementations of Augmented Principal Component Analysis (AugmentedPCA) - a family of linear factor models that find a set of factors aligned with an augmenting objective in addition to the canonical PCA objective of finding factors that represent the data variance. AugmentedPCA can be split into two general families of models: adversarial AugmentedPCA and supervised AugmentedPCA.
Supervised AugmentedPCA
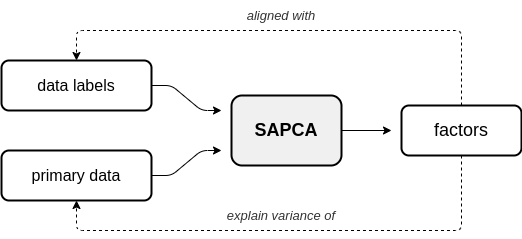
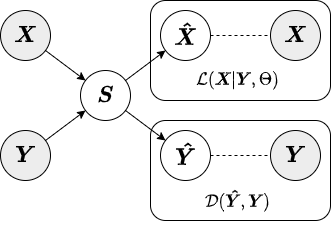
In supervised AugmentedPCA (SAPCA), the augmenting objective is to make the factors aligned with the data labels, or some outcome, in addition to having the factors explain the variance of the original observed or primary data. SAPCA is useful when predictivity of latent components with respects to a set of data labels or outcomes is desired. SAPCA is equivalent to a supervised autoencoder (SAE) with a single hidden layer. Therefore, SAPCA can be applied to situations where the properties of latent representations enforced via deep SAEs are desired, yet where limited data or training inconsistencies are a concern. Below is a diagram depicting the relationship between primary data, supervision data, and the resulting SAPCA factors.
Adversarial AugmentedPCA
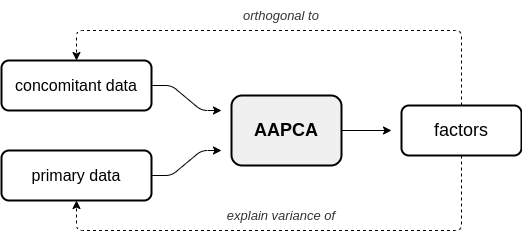
In adversarial AugmentedPCA (AAPCA), the augmenting objective is to make the factors orthogonal to a set of concomitant data, in addition to having the factors explain the variance of the original observed or primary data. AAPCA can be used in situations where one wishes to enforce invariance of latent components to a set of concomitant data, and is equivalent to an adversarial autoencoder with a single hidden layer. Below is a diagram depicting the relationship between primary data, concomitant data, and the resulting AAPCA factors.
Documentation
Documentation for AugmentedPCA is available on this documentation site.
Provided documentation includes:
-
Motivation - Motivation behind AugmentedPCA models and the different approximate inference strategies.
-
Model formulation - Overview of different models and approximate inference strategies as well as more in-depth mathematical descriptions.
-
Tutorials - Step-by-step guide on how to use the different offered AugmentedPCA models.
-
Examples - Use case examples for the different models.
Dependencies
The AugmentedPCA package is written in Python, and requires Python >= 3.6 to run. AugmentedPCA relies on the following libraries and version numbers:
Installation
To install the latest stable release, use pip. Use the following command to install:
$ pip install augmented-pca
Issue Tracking and Reports
Please use the GitHub issue tracker associated with the AugmentedPCA repository for issue tracking, filing bug reports, and asking general questions about the package or project.
Quick Introduction
A quick guide to using AugmentedPCA is given in this section. For a more in-depth guide, see our documentation.
Importing AugmentedPCA Models
APCA models can be imported from the models.py module. Below we show an example of importing the AAPCA model.
# Import all AugmentedPCA models
from apca.models import AAPCA
Alternatively, all offered AugmentedPCA models can be imported at once.
# Import all AugmentedPCA models
from apca.models import *
Instantiating AugmentedPCA Models
APCA models are instantiated by assigning either an SAPCA or AAPCA object to a variable. During instantiation, one has the option to define parameters n_components, mu, which represent the number of components and the augmenting objective strength, respectively. Additionally, approximate inference strategy can be defined through the inference parameter.
# Define model parameters
n_components = 2 # factors will have dimensionality of 2
mu = 1.0 # augmenting objective strength equal to 1
inference = 'encoded' # encoded approximate inference strategy
# Instantiate adversarial AugmentedPCA model
aapca = AAPCA(n_components=n_components, mu=mu, inference=inference)
Fitting AugmentedPCA Models
APCA models closely follow the style and implemention of scikit-learn's PCA implementation, with many of the same methods and functionality. Similar to scikit-learn models, AugmentedPCA models are fit using the fit() method. fit() takes two parameters: X which represents the matrix of primary data and Y which represents the matrix of augmenting data.
# Import numpy
import numpy as np
# Generate synthetic data
# Note: primary and augmenting data must have same number of samples/same first dimension size
n_samp = 100
X = np.random.randn(n_samp, 20) # primary data, 100 samples with dimensionality of 20
Y = np.random.randn(n_samp, 3) # concomitant data, 100 samples with dimensionality of 3
# Fit adversarial AugmentedPCA instance
aapca.fit(X=X, Y=Y)
Alternatively, AugmentedPCA models can be fit using the fit_transform() method, which takes the same parameters as the fit() method but also returns a matrix of components or factors.
# Fit adversarial AugmentedPCA instance and generate components
S = aapca.fit_transform(X=X, Y=Y)
Approximate Inference Strategies
In this section, we give a brief overview of the different approximate inference strategies offered for AugmentedPCA. Inference strategy should be chosen based on the data on which the AugmentedPCA model will be used as well as the specific use case. Both SAPCA and AAPCA models use the jointly-encoded approximate inference strategy by default.
Local
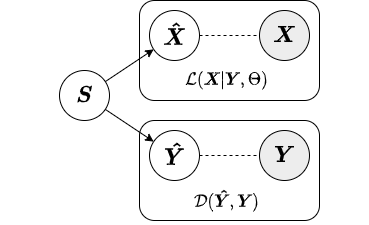
In the local approximate inference strategy, the factors (local variables associated with each observation) are included in both the likelihood relating and the augmenting objective. Below is a diagram from our paper depicting the local inference strategy.
Because the local variables are included in the augmenting objective, given new data we must have both primary and augmenting data to obtain factors. Thus, the local inference strategy should only be used for inference on new data when both primary and augmenting data are available. Below we show an example of how to fit a SAPCA model with local approximate inference strategy to training data and obtain factors for test data.
# Import numpy
import numpy as np
# Import supervised AugmentedPCA
from apca.models import SAPCA
# Generate synthetic data and labels
n_samp = 100
X = np.random.randn(n_samp, 20)
Y = np.random.randint(low=0, high=1, size=(n_samp, 1), dtype=int)
# Generate test/train splits
train_pct = 0.7
idx = np.arange(start=0, stop=101, step=1, dtype=int)
np.random.shuffle(idx)
n_train = int(train_pct * len(idx))
train_idx = idx[:n_train]
test_idx = idx[n_train:]
# Split data into test/train sets
X_train = X[train_idx, :]
X_test = X[test_idx, :]
Y_train = Y[train_idx, :]
Y_test = Y[test_idx, :]
# Instantiate supervised AugmentedPCA model with local approximate inference strategy
sapca = SAPCA(n_components=3, mu=5.0, inference='local')
# Fit supervised AugmentedPCA model
sapca.fit(X=X_train, Y_train)
# Generate components for test set
# Note: both primary and augmenting data are needed to obtain factors
S_test = sapca.transform(X=X_test, Y=Y_test)
Note that when factors are generated for the test set that the transform() method requires both the primary data X_test and labels Y_test be passed as parameters. For a more in-depth description of the local approximate inference strategy, see our paper or the corresponding documentation section.
Encoded
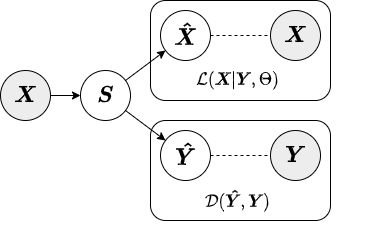
In the encoded approximate inference strategy, a linear encoder is used to transform the data into factors or components. This inference strategy is termed "encoded" because the augmenting objective is enforced via an encoding function. Below is a diagram depicting the encoded inference strategy.
In contrast to the local inference strategy, when factors are generated for the test set under the encoded inference strategy the transform() method only requires the primary data X_test. Below we show an example of how to fit a SAPCA model with encoded approximate inference strategy to training data and obtain factors for test data.
# Instantiate supervised AugmentedPCA model model with encoded approximate inference strategy
sapca = SAPCA(n_components=3, mu=5.0, inference='encoded')
# Fit supervised AugmentedPCA model
# Note: both primary and augmenting data are required to fit the model
sapca.fit(X=X_train, Y_train)
# Generate components for test set
# Note: only primary data are needed to obtain factors
S_test = sapca.transform(X=X_test)
For a more in-depth description of the encoded approximate inference strategy, see our paper or the corresponding documentation section.
Jointly-Encoded
The jointly-encoded approximate inference strategy is similar to the encoded in that the augmenting objective is enforced through a linear encoding matrix. However, in the jointly-encoded inference strategy both the primary and augmenting data are required for computing factors, similar to the local inference strategy. Below is a diagram depicting the jointly-encoded inference strategy.
Similar to the local inference strategy, when factors are generated for the test set under the jointly-encoded inference strategy the transform() method requires both the primary data X_test and augmenting data Y_test. Below we show an example of how to fit a SAPCA model with jointly-encoded approximate inference strategy to training data and obtain factors for test data.
# Instantiate supervised AugmentedPCA model model with encoded approximate inference strategy
sapca = SAPCA(n_components=3, mu=5.0, inference='encoded')
# Fit supervised AugmentedPCA model
# Note: both primary and augmenting data are required to fit the model
sapca.fit(X=X_train, Y_train)
# Generate components for test set
# Note: both primary and augmenting data are needed to obtain factors
S_test = sapca.transform(X=X_test)
For a more in-depth description of the jointly-encoded approximate inference strategy, see our paper or the corresponding documentation section.
Citation
Please cite our paper if you find this package helpful in your research:
@inproceedings{carson2021augmentedpca,
title={{AugmentedPCA}: {A} {P}ython {P}ackage of {S}upervised and {A}dversarial {L}inear {F}actor {M}odels},
author={{Carson IV}, William E. and Talbot, Austin and Carlson, David},
year={2021},
month={December},
booktitle={{P}roceedings of {L}earning {M}eaningful {R}epresentations of {L}ife {W}orkshop at {NeurIPS} 2021}}
Funding
This project was supported by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering and the National Institute of Mental Health through the National Institutes of Health BRAIN Initiative under Award Number R01EB026937.