当前位置:网站首页>C语言的运算符
C语言的运算符
2022-04-23 05:48:00 【Chshyz】
C语言运算符
文末附运算符的优先表和ASCII表
一、算术运算符
- 加(+)减(—)乘(*)除(/)
- 模(余)运算符(%):不允许出现浮点型,余数正负取决于被除数正负
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i, b, a, c;
i= 4, b=3;
a= i+b;
c= i*a;
float p, k;
p= i/b;
k= i%a;
printf("a=%d,c=%d,p=%f,k=%f\n",a,c,p,k);
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
a=7,c=28,p=1.000000,k=4.000000
- 自增(++i,–i;i++,i–)
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i;
i= 4;
printf("%d\n",++i);
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
5
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i;
i= 4;
printf("%d\n",i--);
//printf("%d\n",i); 输出是
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
4
二、关系运算符
- 大于(>)小于(<)等于(==)
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b, max;
printf ("please enter a and b\n");
scanf ("%d %d",&a, &b);
if (a>b) max=a;
if (a<b) max=b;
if (a==b) max=a;
printf ("max=%d\n",max);
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
please enter a and b
55 66
max=66
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
please enter a and b
44 44
max=44
- 小于或等于(<=)大于或等于(>=)不等于(!=)赋值(-=、+=、*=);
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int a = 10;
a +=a *=a -=20;
printf("%d\n",a);
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./ass
200
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b, max;
printf ("please enter a and b\n");
scanf ("%d %d",&a, &b);
if (a>=b) max=a;
if (a<=b) max=b;
printf ("max=%d\n",max);
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
please enter a and b
55 66
max=66
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
please enter a and b
77 77
max=77
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b, max;
printf ("please enter a and b\n");
scanf ("%d %d",&a, &b);
if (a!=b);
if (a>b) max=a;
if (a<b) max=b;
printf ("max=%d\n",max);
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
please enter a and b
44 44
max=0
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
please enter a and b
44 55
max=55
三、逻辑运算符(并且、或者、除非)
PS:优先级从上至下
- 逻辑非(! NOT)
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num = 0;
printf ("Please enter num value: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
if (num != 69) {
printf ("num %d is not equal to 69.\n", num);
}
return 0;
}
~
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
Please enter num value: 69
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
Please enter num value: 1
num 1 is not equal to 69.
- 逻辑与(&& AND)
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b, x, y;
printf ("please enter a and b,x and y\n");
scanf ("a=%d,b=%d,x=%d,y=%d",&a, &b, &x, &y);
if (a==b && x==y){
printf ("a=b,x=y\n");
}
else
printf ("sorry,I donot konw.\n");
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
please enter a and b,x and y
a=1,b=2,x=1,y=1
sorry,I donot konw.
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./o
please enter a and b,x and y
a=1,b=1,x=2,y=2
a=b,x=y
- 逻辑或(|| OR)
四、位运算符
- 右移(>>)左移(<<)
- 按位与(&)
- 按位或(|)
- 按位异或(^)
- 取反(~)
五、赋值运算符
- 等号(=)
- 扩展赋值运算符
+= 加赋值 (a += 3 等价于 a = a + 3)
-= 减赋值
*= 乘赋值
/= 除赋值
%= 求余赋值
&= 按位与赋值
| = 按位或赋值
^= 按位异或赋值
<<= 左移位赋值(>>= 右移位赋值)
<> 当右操作数又是一个赋值表达式时,形成多重赋值表达式
六、条件运算符
PS:条件运算符优先级高于赋值、逗号运算符,低于其他运算符。
- 关系表达式 ? 表达式1 : 表达式2
三目运算符:条件 ? 结果1 : 结果2
例子:
判断a小于或者大于b,输出最大值max
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int a, b, max;
scanf("a=%d,b=%d",&a,&b);
max=a>b?a:b;
printf("max=%d\n",max);
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# gcc -o swap swap.c
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./swap
a=2,b=3
max=3
七、逗号运算符(,)
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int i = 1;
int a = (i+100,i++,i);
printf("%d\n",a);
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./comma
2
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int i = 1;
int a = (i=i+100,i++,i);
printf("%d\n",a);
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./comma
102
八、指针运算符
- 指针变量(*)
定义:基类型 * 指针变量名;
例子1:通过指针变量访问整型变量
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b; #定义两个int变量
int * pointer_1, * pointer_2; #定义两个指针变量,指向int变量
a = 100; b = 10;
pointer_1 = &a; #把变量a的地址赋给指针pointer_1
pointer_2 = &b;
printf ("a = %d, b = %d \n", a, b);
printf (" * pointer_1 = %d, * pointer_2 = %d \n", * pointer_1, * pointer_2); #输出的指针变量所指向的整型变量的值
return 0;
}
~
[root@chenshuyi c]# gcc -o pointer1 pointer1.c
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./pointer1
a = 100, b = 10
* pointer_1 = 100, * pointer_2 = 10
[root@chenshuyi c]# vi pointer1.c
例子2:比大小
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
int * p1, * p2, * p, a, b;
scanf ("%d, %d", &a, &b);
p1 = &a; p2 = &b;
if (a < b) {
p = p1; p1 = p2; p2 = p;
}
printf ("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
printf ("max = %d, min = %d\n", * p1, * p2);
return 0;
}
r
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./pointer2
4,6
a = 4, b = 6
max = 6, min = 4
例子3:算术
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
int maxsum = 123;
double temp = 888.8889922111111;
temp += (float)maxsum;
printf ("%7.3f, %d\n", (float)temp, (int)temp);
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# gcc -o compulsion compulsion.c
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./compulsion
1011.889, 1011
九、求字节数运算符(sizeof)
- 当sizeof(与数据类型(如int,float,char …等)一起使用时,返回分配给该数据类型的内存量。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d\n",sizeof(char));
printf("%d\n",sizeof(int));
printf("%d\n",sizeof(float));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(double));
return 0;
}
- 当sizeof和表达式一起使用的时候,返回表达式的大小。
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 1, b = 3;
printf ("%d\n", sizeof ( a + b ));
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# gcc -o sizeof1 sizeof1.c
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./sizeof1
4
十、强制类型转换运算符
例1:小数转整数
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
float f = 8.88;
int i;
i = (int) f;
printf ("f = %f, i = %d \n", f, i);
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# gcc -o compulsion compulsion.c
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./compulsion
f = 8.880000, i = 8
例2:整数转小数
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
int maxsum = 123;
printf ("%lf\n", (double) maxsum);
return 0;
}
[root@chenshuyi c]# gcc -o compulsion compulsion.c
[root@chenshuyi c]# ./compulsion
123.000000
十一、成员运算符
- 成员运算符(.)
- 间接成员运算符(–>)
十二、下标运算符([ ])
PS:运算符的优先级和结合性
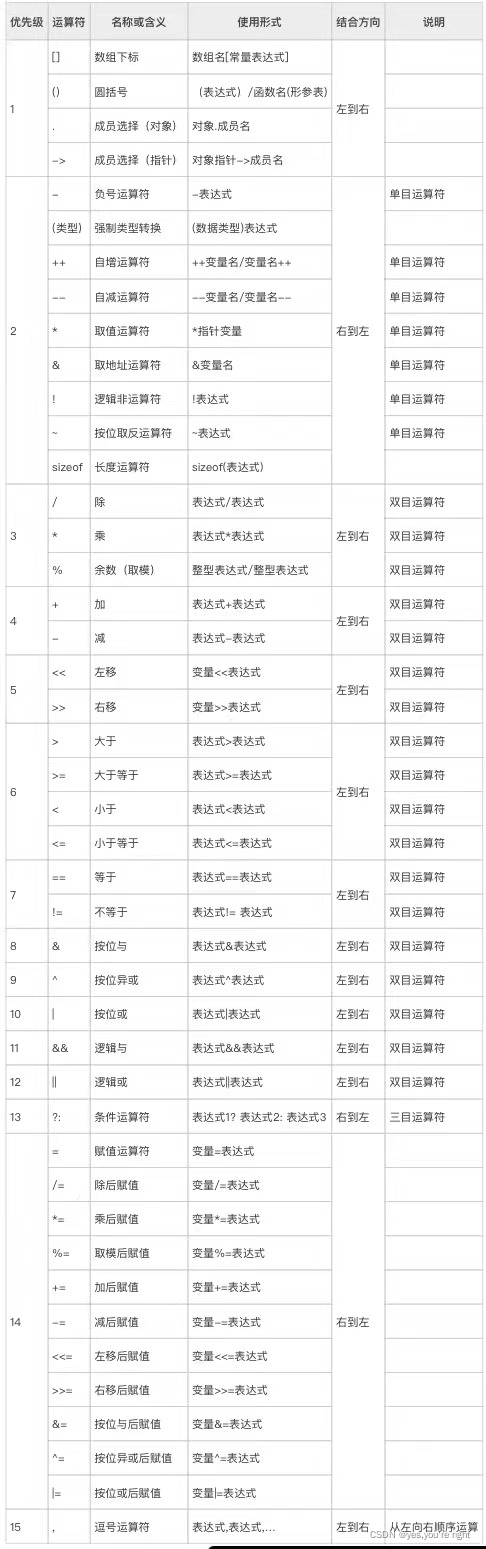
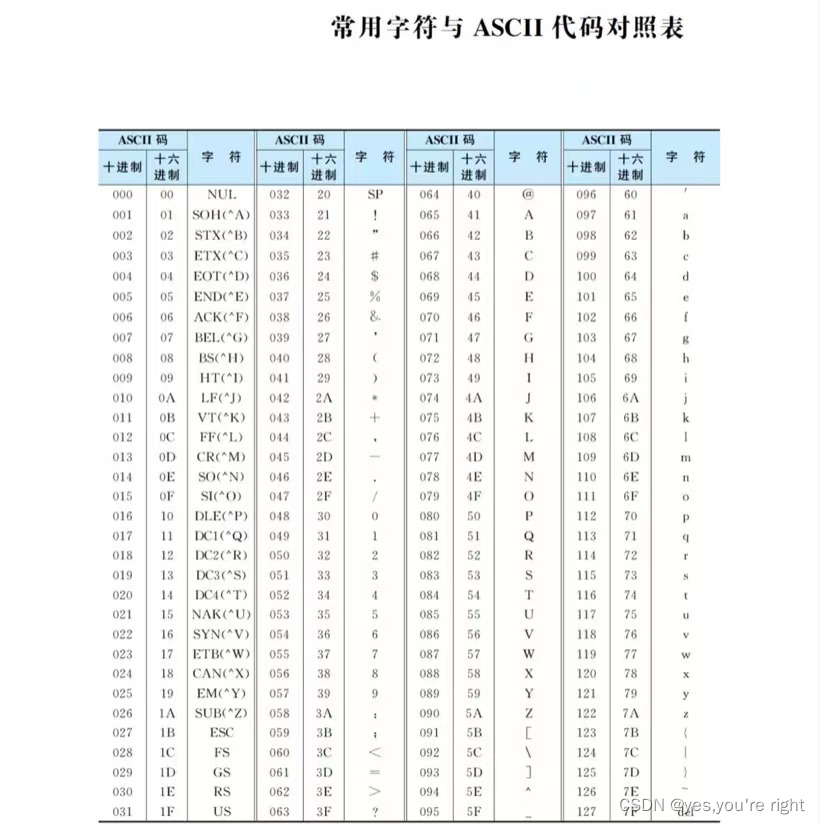
版权声明
本文为[Chshyz]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://blog.csdn.net/HelloWorld_4396/article/details/120032677
边栏推荐
- Easy to use data set and open source network comparison website
- POI and easyexcel exercises
- Rust 中的 Cell 共享可变指针
- Sakura substring thinking
- P1586 solution to tetragonal theorem
- [leetcode 67] sum of two binary numbers
- Addition, deletion, query and modification of data
- [leetcode169] most elements
- C语言实现2048小游戏方向合并逻辑
- Swagger2 generates API documents
猜你喜欢

1007 go running (hdu6808) in the fourth game of 2020 Hangzhou Electric Multi school competition

Addition, deletion, modification and query of MySQL table
类和对象的初始化(构造函数与析构函数)

Guaba and Computational Geometry

定位器
Robocode教程8——AdvancedRobot

SQL -- data definition
Robocode教程4——Robocode的游戏物理

Export the articles written in CSDN to PDF format
从源代码到可执行文件的过程
随机推荐
H. Are You Safe? Convex hull naked problem
[leetcode 401] binary Watch
代理服务器
MySQL table constraints and table design
grub boot. S code analysis
爬取蝉妈妈数据平台商品数据
[leetcode 954] double pair array
日志
C array
C # Foundation
Miscellaneous 1
SQL -- data filtering and grouping
Rainbow (DP)
Robocode教程4——Robocode的游戏物理
Rust:如何实现一个线程池?
P1586 solution to tetragonal theorem
Gesture recognition research
Explanation of login page
Advanced operation of idea debug
Record the installation and configuration of gestermer on TX2, and then use GST RTSP server