当前位置:网站首页>SQL -- data definition
SQL -- data definition
2022-04-23 06:25:00 【Wood acridine】
Create table (Create table)
grammar :
Create table Database name Schema name Table name (
Name 1 data type PRIMARY KEY,
Name 2 data type not null,
………
);
If you do not specify a schema, it will be in the current database by default dbo In mode
example :create table stu(
id int identity primary key, -- identity Identity column primary key Primary key
name varchar (20) not null,
birthday datetime
);

Copy table
If the target table exists
grammar :insert into Target table [ Specified field ] select * from The original table ;
If the target table does not exist
grammar :select * into Target table from The original table ;
Identity column
Create identity column (identity)
grammar :identity [( The value of the first line , Incremental value added to the identification value of the previous line )]
Don't write , If you don't write, it defaults to (1,1), You can also customize it .
Allow only one identity column per table
example :create table a(
aid int identity(1,2) primary key,
aname varchar (50) not null
);

Reuse identity values
SQL server Identifiers cannot be reused . If you insert a row into the identifier and execute insert Statement failed or rolled back , Then the identification value will be lost , Will not be generated again . It will result in blank space in the identification column
Reset the identity column of the entire table ( Delete data )
truncate Delete all values in the table and reset the identifier , But the data in the table will be lost and cannot be retrieved .
grammar :truncate table Table name ;
Reset identity column ( Do not delete data )
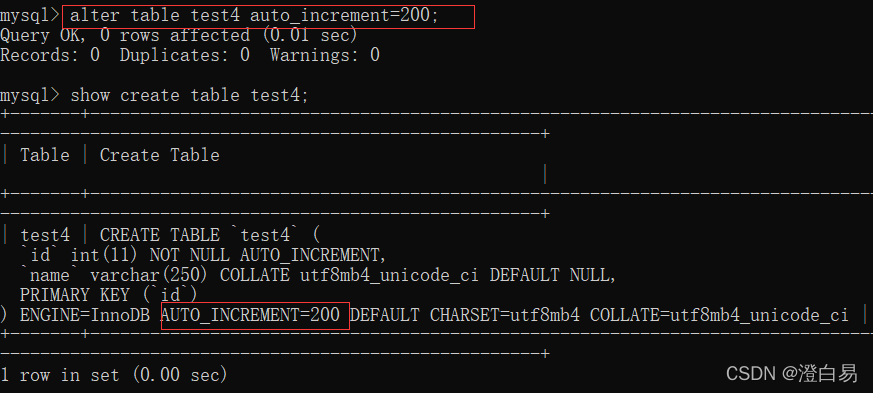
- dbcc checkident(‘ Table name ’,new_value) Reset new identifier ,new_value For the new value
- select ident_current(‘a’) The maximum value of the current table ID column
- select @@identity The maximum value of the current identity column . notes : Follow the wrong statement to query
Add columns... To the table
grammar :alter table Table name add Name data type constraint
example :alter table stu
add tel nvarchar (11) not null;

Modify the column
You can modify the data type , Column size 、not null constraint
grammar :alter table Table name alter column Name data type ;
example :alter table stu alter column tel varchar(22)

When changing the data type when there is data in the table , The data should be able to be transformed into the target type , If it doesn't change, it will report an error . The two data types must be compatible .
Delete column
grammar :alter table Table name drop column Name
example :alter table stu drop column tel;

Delete table (drop)
grammar :drop table [ if exists] Table name ;
add to if exists You can't report an error , Whether that table exists or not
Delete tables with foreign key constraints
Constraint referenced table . To delete this table , You must first delete the reference foreign key constraint or reference table .
grammar :
drop table Reference table ;
drop table Referenced table ;
If you use a single drop table Delete two tables , You must put the reference table first
grammar :drop table Reference table , Referenced table ;
Truncation table (truncate table)
truncate table Similar to no where Clause delete sentence . however truncate Statements execute faster , And use less system and transaction log resources .
And delect Comparative advantage :
- Use fewer transaction logs
delete Statement Deletes one line at a time , And insert an entry in the transaction log for each Deleted Row .truncate table Statement deletes data by releasing the data page used to store table data , And only insert page deallocation in the transaction log .
- Use fewer locks
When executing a statement with a row lock , Every row in the table is locked for deletion .truncate table Lock tables and pages , Not every line
- Reset identification
If the table to be truncated has an identity column , When you use truncate table Statement after deleting data , The calculator with the identity column will be reset to the starting value ( It's usually :1).
版权声明
本文为[Wood acridine]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204210616404940.html
边栏推荐
- Generate excel template (drop-down selection, multi-level linkage)
- Framework analysis 1 Introduction to system architecture
- MySQL advanced query
- A general U-shaped transformer for image restoration
- 2. Average length of words
- JDBC operation transaction
- RPC must know and know
- LockSupport. Park and unpark, wait and notify
- Doomsday (simple computational geometry)
- 6.Reversal
猜你喜欢

Delete and truncate

Filebrowser realizes private network disk

Substring Inversion (Easy Version)

Pytorch learning record (V): back propagation + gradient based optimizer (SGD, adagrad, rmsporp, Adam)
Illustrate the significance of hashcode
MySQL table constraints and table design

自動控制(韓敏版)

Gaussian processes of sklearn

PyTorch笔记——实现线性回归完整代码&手动或自动计算梯度代码对比

線性代數第一章-行列式
随机推荐
卡尔曼滤波与惯性组合导航
Rainbow (DP)
Use Matplotlib. In Jupiter notebook Pyplot server hangs up and crashes
[leetcode 383] ransom letter
[leetcode 19] delete the penultimate node of the linked list
Consistent hash algorithm used for redis cache load balancing
Pytorch notes - get familiar with the network construction method by building RESNET (complete code)
Pyqy5 learning (2): qmainwindow + QWidget + qlabel
Pytoch -- data loading and processing
Supply chain service terms
Pytorch learning record (V): back propagation + gradient based optimizer (SGD, adagrad, rmsporp, Adam)
線性代數第一章-行列式
Sakura substring thinking
Filebrowser realizes private network disk
3. Continuous integer
Framework analysis 2 Source code - login authentication
MySQL table constraints and table design
Example of ticket selling with reentrant lock
Gaussian processes of sklearn
Delete and truncate