当前位置:网站首页>Machine learning II: logistic regression classification based on Iris data set
Machine learning II: logistic regression classification based on Iris data set
2022-04-23 07:19:00 【Amyniez】
Step1: Library function import
# Basic function library
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Drawing function library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
Iris data set (iris) It includes 5 A variable , among 4 Characteristic variables ,1 A target classification variable . share 150 Samples , The target variable is the category of flowers , They all belong to three subgenera of iris , Namely Iris iris (Iris-setosa), Color fleur-de-lis (Iris-versicolor) and Iris Virginia (Iris-virginica). It contains four characteristics of three Iris species , Namely Calyx length (cm)、 Calyx width (cm)、 Petal length (cm)、 Petal width (cm), These morphological features have been used in the past to identify species .
| Variable | describe |
|---|---|
| sepal length | Calyx length (cm) |
| sepal width | Calyx width (cm) |
| petal length | Petal length (cm) |
| petal width | Petal width (cm) |
| target | Three subgenera of iris ,‘setosa’(0), ‘versicolor’(1), ‘virginica’(2) |
Step2: data fetch / load
# utilize sklearn The built-in iris Data is loaded as data , And make use of Pandas Turn into DataFrame Format
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
data = load_iris() # Get the data features
iris_target = data.target # Get the tag corresponding to the data
iris_features = pd.DataFrame(data=data.data, columns=data.feature_names) # utilize Pandas Turn into DataFrame Format
Step3: Simple view of data information
## utilize .info() View the overall information of the data
iris_features.info()
<class ‘pandas.core.frame.DataFrame’>
RangeIndex: 150 entries, 0 to 149
Data columns (total 4 columns):
Column Non-Null Count Dtype
0 sepal length (cm) 150 non-null float64
1 sepal width (cm) 150 non-null float64
2 petal length (cm) 150 non-null float64
3 petal width (cm) 150 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(4)
memory usage: 4.8 KB
## Do a simple data view , We can use .head() Head .tail() The tail
iris_features.head()
iris_features.tail()

## The corresponding category label is , among 0,1,2 Represent the 'setosa', 'versicolor', 'virginica' Three different types of flowers .
iris_target
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2])
## utilize value_counts Function to see the number of each category
pd.Series(iris_target).value_counts()
2 50
1 50
0 50
dtype: int64
## Some statistical description of the features
iris_features.describe()

From the statistical description, we can see the variation range of different numerical characteristics .
Step4: Visual description
# Combine tag and feature information
iris_all = iris_features.copy() ## Make a light copy , Prevent modification of original data
iris_all['target'] = iris_target
# Scatter visualization of feature and tag combination
sns.pairplot(data=iris_all,diag_kind='hist', hue= 'target')
plt.show()

Draw a box diagram :
- Five elements of box diagram : .
- 1、 Median : That is, the half quantile . So the calculation method is to put a set of data ( The median here , Especially an ordered sequence arranged from large to small ) Divide equally into two parts , Take the middle number . If the original sequence length n Is odd , So the median is (n+1)/2; If the original sequence length n It's even , So the median is n/2,n/2+1, The value of the median is equal to the arithmetic mean of the numbers at these two positions .
- 2、 Upper quartile Q1: emphasize , How to find the quartile , Is to divide the sequence equally into four parts . At present, the specific calculation has (n+1)/4 And (n-1)/4 Two kinds of , In general use (n+1)/4.
for example : An ordered sequence test = c(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8), adopt summary(test) To get test The median of this sequence , Upper quartile , Lower quartile and arithmetic mean . First, the sequence length n=8,(1+n)/4=2.25, Explain that the upper quartile is in the 2.25 Number of positions , So the first 2.25 The number is the second number 0.25+ The third number 0.75, namely 20.25+3*0.75=0.5+2.25=2.75. - 3、 Lower quartile Q3: The calculation method of the position of the lower quartile is the same as above , nothing but (1+n)/43=6.75, This is a place between the sixth position and the seventh position . The corresponding specific value is 0.756+0.25*7=6.25.
- 4、 Internal limit : above T The extreme distance to which a line segment extends , yes Q3+1.5IQR( among ,IQR=Q3-Q1) And the maximum value after excluding outliers , Below T The extreme distance to which a line segment extends , yes Q1-1.5IQR And the minimum value after excluding outliers, whichever is the maximum .
(1,6,2,7,4,2,3,3,8,25,30)
IQR=Q3-Q1=7.5-2.5=5
Upper and inner limits =Q3+1.5IQR=7.5+1.55=15, And eliminate two abnormal addresses 30,25 The maximum after 8, Take the minimum of both , So the upper and inner limits are 8
Lower internal limit =Q1-1.5IQR=2.5-1.55=-5, And eliminate two abnormal addresses 30,25 The minimum after 1, Take the maximum of both , So the lower limit is 1 - 5、 External limit : The calculation method of outer limit and inner limit is the same , The only difference is with : above T The extreme distance to which a line segment extends , yes Q3+3IQR( among ,IQR=Q3-Q1) And the maximum value after excluding outliers , Below T The extreme distance to which a line segment extends , yes Q1-3IQR And the minimum value after excluding outliers, whichever is the maximum .
for col in iris_features.columns:
sns.boxplot(x='target', y=col, saturation=0.5,palette='pastel', data=iris_all)
plt.title(col)
plt.show()


The biggest advantage of box chart is : Not affected by outliers , It can describe the discrete distribution of data in a relatively stable way .
Using box graph, we can also get the distribution differences of different categories on different features .
# Select the first three features to draw a three-dimensional scatter map
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
iris_all_class0 = iris_all[iris_all['target']==0].values
iris_all_class1 = iris_all[iris_all['target']==1].values
iris_all_class2 = iris_all[iris_all['target']==2].values
# 'setosa'(0), 'versicolor'(1), 'virginica'(2)
ax.scatter(iris_all_class0[:,0], iris_all_class0[:,1], iris_all_class0[:,2],label='setosa')
ax.scatter(iris_all_class1[:,0], iris_all_class1[:,1], iris_all_class1[:,2],label='versicolor')
ax.scatter(iris_all_class2[:,0], iris_all_class2[:,1], iris_all_class2[:,2],label='virginica')
plt.legend()
plt.show()

Step5: utilize Logistic regression model In the second category Train and predict
## In order to correctly evaluate the model performance , Divide the data into training set and test set , And train the model on the training set , Verify model performance on a test set .
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
## Select the category as 0 and 1 The sample of ( Excluding categories of 2 The sample of )
iris_features_part = iris_features.iloc[:100]
iris_target_part = iris_target[:100]
## The test set size is 20%, 80%/20% branch
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris_features_part, iris_target_part, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 2020)
## from sklearn The logistic regression model is introduced into the model
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
## Definition Logistic regression model
clf = LogisticRegression(random_state=0, solver='lbfgs')
# Train the logistic regression model on the training set
clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
LogisticRegression(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1, l1_ratio=None, max_iter=100,
multi_class=‘auto’, n_jobs=None, penalty=‘l2’,
random_state=0, solver=‘lbfgs’, tol=0.0001, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
## Look at the corresponding w
print('the weight of Logistic Regression:',clf.coef_)
## Look at the corresponding w0
print('the intercept(w0) of Logistic Regression:',clf.intercept_)
the weight of Logistic Regression: [[ 0.45181973 -0.81743611 2.14470304 0.89838607]]
the intercept(w0) of Logistic Regression: [-6.53367714]
## In the training set and test set distribution, using the trained model to predict
train_predict = clf.predict(x_train)
test_predict = clf.predict(x_test)
from sklearn import metrics
## utilize accuracy( Accuracy )【 The proportion of the number of correctly predicted samples to the total number of predicted samples 】 Evaluate the effect of the model
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_train,train_predict))
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,test_predict))
## Look at the confusion matrix ( Statistical matrix of various situations of predicted value and real value )
confusion_matrix_result = metrics.confusion_matrix(test_predict,y_test)
print('The confusion matrix result:\n',confusion_matrix_result)
# The results are visualized using thermal maps
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix_result, annot=True, cmap='Blues')
plt.xlabel('Predicted labels')
plt.ylabel('True labels')
plt.show()
The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is: 1.0
The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is: 1.0
The confusion matrix result:
[[ 9 0]
[ 0 11]]

It can be found that the accuracy is 1, It means that all samples are correctly predicted .
Step6: utilize Logistic regression model In three categories ( Many classification ) On Train and predict
## The test set size is 20%, 80%/20% branch
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris_features, iris_target, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 2020)
## Definition Logistic regression model
clf = LogisticRegression(random_state=0, solver='lbfgs')
# Train the logistic regression model on the training set
clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
LogisticRegression(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1, l1_ratio=None, max_iter=100,
multi_class=‘auto’, n_jobs=None, penalty=‘l2’,
random_state=0, solver=‘lbfgs’, tol=0.0001, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
## Look at the corresponding w
print('the weight of Logistic Regression:\n',clf.coef_)
## Look at the corresponding w0
print('the intercept(w0) of Logistic Regression:\n',clf.intercept_)
## Because this is 3 classification , So here we get the parameters of three logistic regression models , The three logistic regression can be combined to realize the three classification .
the weight of Logistic Regression:
[[-0.45928925 0.83069886 -2.26606531 -0.9974398 ]
[ 0.33117319 -0.72863423 -0.06841147 -0.9871103 ]
[ 0.12811606 -0.10206463 2.33447679 1.9845501 ]]
the intercept(w0) of Logistic Regression:
[ 9.43880677 3.93047364 -13.36928041]
## In the training set and test set distribution, using the trained model to predict
train_predict = clf.predict(x_train)
test_predict = clf.predict(x_test)
## Since the logistic regression model is a probabilistic prediction model ( Previously described p = p(y=1|x,\theta)), All we can do with predict_proba Function predicts its probability
train_predict_proba = clf.predict_proba(x_train)
test_predict_proba = clf.predict_proba(x_test)
print('The test predict Probability of each class:\n',test_predict_proba)
## The first column represents the prediction of 0 The probability of a class , The second column represents the prediction of 1 The probability of a class , The third column represents the prediction of 2 The probability of a class .
## utilize accuracy( Accuracy )【 The proportion of the number of correctly predicted samples to the total number of predicted samples 】 Evaluate the effect of the model
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_train,train_predict))
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is:',metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,test_predict))
The test predict Probability of each class:
[[1.03461734e-05 2.33279475e-02 9.76661706e-01]
[9.69926591e-01 3.00732875e-02 1.21676996e-07]
[2.09992547e-02 8.69156617e-01 1.09844128e-01]
[3.61934870e-03 7.91979966e-01 2.04400685e-01]
[7.90943202e-03 8.00605300e-01 1.91485268e-01]
[7.30034960e-04 6.60508053e-01 3.38761912e-01]
[1.68614209e-04 1.86322045e-01 8.13509341e-01]
[1.06915332e-01 8.90815532e-01 2.26913667e-03]
[9.46928070e-01 5.30707294e-02 1.20016057e-06]
[9.62346385e-01 3.76532233e-02 3.91897289e-07]
[1.19533384e-04 1.38823468e-01 8.61056998e-01]
[8.78881883e-03 6.97207361e-01 2.94003820e-01]
[9.73938143e-01 2.60617346e-02 1.22613836e-07]
[1.78434056e-03 4.79518177e-01 5.18697482e-01]
[5.56924342e-04 2.46776841e-01 7.52666235e-01]
[9.83549842e-01 1.64500670e-02 9.13617258e-08]
[1.65201477e-02 9.54672749e-01 2.88071038e-02]
[8.99853708e-03 7.82707576e-01 2.08293887e-01]
[2.98015025e-05 5.45900066e-02 9.45380192e-01]
[9.35695863e-01 6.43039513e-02 1.85301359e-07]
[9.80621190e-01 1.93787400e-02 7.00125246e-08]
[1.68478815e-04 3.30167226e-01 6.69664295e-01]
[3.54046163e-03 4.02267805e-01 5.94191734e-01]
[9.70617284e-01 2.93824740e-02 2.42443967e-07]
[2.56895205e-04 1.54631583e-01 8.45111522e-01]
[3.48668490e-02 9.11966141e-01 5.31670105e-02]
[1.47218847e-02 6.84038115e-01 3.01240001e-01]
[9.46510447e-04 4.28641987e-01 5.70411503e-01]
[9.64848137e-01 3.51516748e-02 1.87917880e-07]
[9.70436779e-01 2.95624025e-02 8.18591606e-07]]
The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is: 0.9833333333333333
The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is: 0.8666666666666667
## Look at the confusion matrix
confusion_matrix_result = metrics.confusion_matrix(test_predict,y_test)
print('The confusion matrix result:\n',confusion_matrix_result)
# The results are visualized using thermal maps
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix_result, annot=True, cmap='Blues')
plt.xlabel('Predicted labels')
plt.ylabel('True labels')
plt.show()
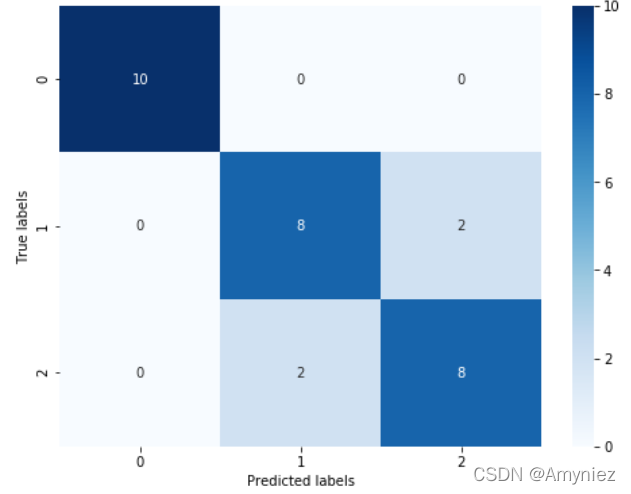
Through the results we can find , The prediction accuracy of the three classification results has declined , Its accuracy on the test set is : 86.67 % 86.67\% 86.67%, This is because ’versicolor’(1) and ‘virginica’(2) The characteristics of these two categories , We can also see from the visualization that , The boundary of its characteristics is fuzzy ( The boundary categories are mixed , There is no clear distinction between borders ), There are some mistakes in these two kinds of predictions .
版权声明
本文为[Amyniez]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230610096343.html
边栏推荐
- webView因证书问题显示一片空白
- torch.mm() torch.sparse.mm() torch.bmm() torch.mul() torch.matmul()的区别
- 机器学习笔记 一:学习思路
- cmder中文乱码问题
- 常见的正则表达式
- Component based learning (1) idea and Implementation
- Android interview Online Economic encyclopedia [constantly updating...]
- Viewpager2 realizes Gallery effect. After notifydatasetchanged, pagetransformer displays abnormal interface deformation
- Markdown basic grammar notes
- Thanos.sh灭霸脚本,轻松随机删除系统一半的文件
猜你喜欢
Cause: dx. jar is missing

Record WebView shows another empty pit
Itop4412 HDMI display (4.4.4_r1)

Gephi教程【1】安装

face_recognition人脸检测
this. getOptions is not a function

PaddleOCR 图片文字提取

webView因证书问题显示一片空白
![[recommendation of new books in 2021] enterprise application development with C 9 and NET 5](/img/1d/cc673ca857fff3c5c48a51883d96c4.png)
[recommendation of new books in 2021] enterprise application development with C 9 and NET 5

BottomSheetDialogFragment 与 ListView RecyclerView ScrollView 滑动冲突问题
随机推荐
5种方法获取Torch网络模型参数量计算量等信息
Android room database quick start
Keras如何保存、加载Keras模型
取消远程依赖,用本地依赖
torch.mm() torch.sparse.mm() torch.bmm() torch.mul() torch.matmul()的区别
Fill the network gap
torch. mm() torch. sparse. mm() torch. bmm() torch. Mul () torch The difference between matmul()
如何对多维矩阵进行标准化(基于numpy)
Five methods are used to obtain the parameters and calculation of torch network model
Gephi教程【1】安装
【2021年新书推荐】Learn WinUI 3.0
Binder mechanism principle
微信小程序 使用wxml2canvas插件生成图片部分问题记录
MarkDown基础语法笔记
【動態規劃】不同路徑2
Cancel remote dependency and use local dependency
Android exposed components - ignored component security
Tiny4412 HDMI display
【 planification dynamique】 différentes voies 2
Handlerthread principle and practical application