当前位置:网站首页>Flink二阶段提交
Flink二阶段提交
2022-08-11 01:15:00 【江畔独步】
一、引申(什么是XA事务)
XA(eXtended Architecture)是指由X/Open 组织提出的分布式交易处理的规范。XA 是一个分布式事务协议,由Tuxedo 提出,所以分布式事务也称为XA 事务。XA 协议主要定义了事务管理器TM(Transaction Manager,协调者)和资源管理器RM(Resource Manager,参与者)之间的接口。其中,资源管理器往往由数据库实现,如Oracle、DB2、MySQL,这些商业数据库都实现了XA 接口,而事务管理器作为全局的调度者,负责各个本地资源的提交和回滚。XA 事务是基于两阶段提交(Two-phaseCommit,2PC)协议实现的,可以保证数据的强一致性,许多分布式关系型数据管理系统都采用此协议来完成分布式。阶段一为准备阶段,即所有的参与者准备执行事务并锁住需要的资源。当参与者Ready时,向TM 汇报自己已经准备好。阶段二为提交阶段。当TM 确认所有参与者都Ready 后,向所有参与者发送COMMIT 命令。
XA 事务允许不同数据库的分布式事务,只要参与在全局事务中的每个结点都支持XA 事务。Oracle、MySQL 和SQL Server 都支持XA 事务。
XA 事务由一个或多个资源管理器(RM)、一个事务管理器(TM)和一个应用程序(ApplicationProgram)组成。
资源管理器:提供访问事务资源的方法。通常一个数据库就是一个资源管理器。
事务管理器:协调参与全局事务中的各个事务。需要和参与全局事务的所有资源管理器进行通信。
应用程序:定义事务的边界。
XA 事务的缺点是性能不好,且无法满足高并发场景。一个数据库的事务和多个数据库间的XA 事务性能会相差很多。因此,要尽量避免XA 事务,如可以将数据写入本地,用高性能的消息系统分发数据,或使用数据库复制等技术。只有在其他办法都无法实现业务需求,且性能不是瓶颈时才使用XA。
二、Flink二阶段提交
2.1 引入 EXACTLY_ONCE 语义
EXACTLY_ONCE语义简称EOS,指的是每条输入消息只会影响最终结果一次,注意这里是影响一次,而非处理一次,Flink一直宣称自己支持EOS,实际上主要是对于Flink应用内部来说的,对于外部系统(端到端)则有比较强的限制
外部系统写入支持幂等性
外部系统支持以事务的方式写入
Flink在1.4.0版本引入了TwoPhaseCommitSinkFunction接口,并在Kafka Producer的connector中实现了它,支持了对外部Kafka Sink的EXACTLY_ONCE语义。
详见:End-to-End Exactly-Once Processing in Apache Flink
2.2 Kafka幂等性和事务性
在kafka 0.11版本中已经提出,kafka 将对事务和幂等性的支持,使得kafka 端到端exactly once语义成为可能。幂等性与事务性都是Kafka发展过程中非常重要的。
在正常情况下,produce向Broker投递消息,broker将消息追加写到对应的流(即某一个topic的某一partition)中,并向Producer返回ACK信号,表示确认收到。
1、幂等性的实现
kafka 为了实想幂等性,他在底层的设计架构中引入了Producer和SequenceNumber。
(1)、ProducerID:在每一个新的Producer初始化时,或被分配一个唯一的ProducerID,这个ProducerID对客户端使用者是不可见的。
(2)、sequenceNumber:对于每个producerID,Producer发送数据的每个Topic和Partition都对饮一个从0开始递增的SequenceNumber值。
2、当引入幂等性后解决的问题。
同样的数据发送到kafka中会对数据增加Pid 和sequenceId
2、事务
在数据端对端数据保证中,另个一个我们特别关注的问题就是事务。即原子性操作。对应的结果是同时成功或者同时失败,kafka的事务注重的生产和消费的的原子性操作。典型的例子为。
一系列的Producer生产消息和消费消息提交Offsets的操作在一个事务中。
例如产生的场景包括:
(1)、producer多次发送消息封装在一个原子性操作,即要求同时成功,或者同时失败。
(2)、在消费者&生产者的模式下,因为consumer在 commit offsets出现问题时,导致重复消费消息时,需要将这个模式下的Consumer和Commit offsets操作和Producer一系列生产消息的操作封装成一个原子性操作。
(3)、kafka的事务总体可以分为三方面的内容:
- 1)、只有Producer生产消息,这种场景需要事务的介入;
- 2)、消费消息和生产消息并存,比如Consumer&Producer模式,这种场景是一般Kafka项目中比较常见的模式,需要事务介入;
- 3)、但是只有Consumer消费消息,这种操作在实际项目中意义不大,和手动Commit Offsets的结果一样,而且这种场景不是事务的引入目的。
事务提供的5种API方法:
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Producer<K,V>接口中:
// 1. 初始化事务,需要注意确保transation.id属性被分配
void initTransactions();
// 2. 开启事务
void beginTransaction() throws ProducerFencedException;
// 3. 为Consumer提供的在事务内Commit Offsets的操作
void sendOffsetsToTransaction(Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets,
String consumerGroupId) throws ProducerFencedException;
// 4. 提交事务
void commitTransaction() throws ProducerFencedException;
// 5. 放弃事务,类似于回滚事务的操作
void abortTransaction() throws ProducerFencedException;
2.3 Flink二阶段提交
场景描述
两阶段提交(two-phase commit, 2PC)是最基础的分布式一致性协议,应用广泛。
2PC介绍:
2PC 在分布式系统中,为了让每个节点能够感知其他所有节点的事务执行情况,需要我们引入一个中心节点来统一所有节点的执行逻辑和进度,这个中心节点叫做协调者(Coordinator),而其中向中心节点汇报或者被中心节点调度的其他节点叫做参与者(Participant)。
2PC原理
①、请求阶段
- 1、协调者向所有参与者发送准备请求与事务内容,询问是否可以准备事务提交,并等待参与者的响应。
- 2、参与者执行事务中的包含操作,并记录undo日志(用于回滚)和redo日志(用于重放),但是不真正提交。
- 3、参与者向协调者返回事务才做的执行结果,执行陈工返回yes,否则返回no.
②、提交阶段(分成成功和失败两种情况)
情况1: 若所有的参与者都返回yes,说明事务可以提交。
- 1、协调者向所有参与者发送commit请求。
- 2、参与者收到commit 请求后,将事务真正的提交上去,并释放占用的事务资源,并向协调者返回ack。
- 3、协调者收到所有参与者ack消息,事务成功完成。
情况2:若有参与者返回no或者超时未返回,说明事务终端,需要回滚。
- 1、协调者向所有参与者发送rollback请求。
- 2、参与者收到rollback请求后,根据undo日志回滚到事务执行前的状态,释放占用的事务资源,并向协调者返回ack。
- 3、协调者收到所有参与者的ack消息,事务回滚完成。

2pc 的优缺点
2PC的优点在于原理非常简单,容易理解及实现。
缺点主要有3个,列举如下:
(1)协调者存在单点问题。如果协调者挂了,整个2PC逻辑就彻底不能运行。
(2)、执行过程是完全同步的。各参与者在等待其他参与者响应的过程中都处于阻塞状态,大并发下有性能问题。
(3)、仍然存在不一致风险。如果由于网络异常等意外导致只有部分参与者收到了commit请求,就会造成部分参与者提交了事务而其他参与者未提交的情况。
不过,现在人们在分布式一致性领域做了很多工作,以ZooKeeper为代表的分布式协调框架也数不胜数,2PC有了这些的加持,可靠性大大提升了,也就能够真正用在要求高的生产环境中了。
Flink基于2PC的实现
2PC 的最常见应用场景其实是关系型数据库,比如mysql InnoDB 存储引擎的XA事务系统。
Flink作为流式处理引擎,自然也提供了对exactly once语义的保证。flink的内部意图检查点机制和轻量级分布式快照算法ABS 保证exactly once .。二我们要实现端到端的精确一次的输出逻辑,则需要施加以下两种限制之一:幂等性写入(idempotent write)、事务性写入(transactional write)。
在Spark Streaming中,要实现事务性写入完全靠用户自己,框架本身并没有提供任何实现。但是在Flink中提供了基于2PC的SinkFunction,名为TwoPhaseCommitSinkFunction,帮助我们做了一些基础的工作。

flink 官方推荐所有需要保证exactly once 的sink 逻辑都继承该抽象类。它具体定义如下四个抽象方法。需要我们去在子类中实现。
// 开始一个事务,返回事务信息的句柄
protected abstract TXN beginTransaction() throws Exception;
// 预提交(即提交请求)阶段的逻辑
protected abstract void preCommit(TXN transaction) throws Exception;
// 正式提交阶段的逻辑
protected abstract void commit(TXN transaction);
// 取消事务
protected abstract void abort(TXN transaction);
public class FlinkKafkaProducer<IN>
extends TwoPhaseCommitSinkFunction< IN, FlinkKafkaProducer.KafkaTransactionState, FlinkKafkaProducer.KafkaTransactionContext> {
/** * Semantics that can be chosen. * <li>{@link #EXACTLY_ONCE} * <li>{@link #AT_LEAST_ONCE} * <li>{@link #NONE} */
public enum Semantic {
/** * Semantic.EXACTLY_ONCE the Flink producer will write all messages in a Kafka transaction * that will be committed to Kafka on a checkpoint. * * <p>In this mode {@link FlinkKafkaProducer} sets up a pool of {@link * FlinkKafkaInternalProducer}. Between each checkpoint a Kafka transaction is created, * which is committed on {@link FlinkKafkaProducer#notifyCheckpointComplete(long)} . If * checkpoint complete notifications are running late, {@link FlinkKafkaProducer} can run * out of {@link FlinkKafkaInternalProducer}s in the pool. In that case any subsequent * {@link FlinkKafkaProducer#snapshotState(FunctionSnapshotContext)} requests will fail and * {@link FlinkKafkaProducer} will keep using the {@link FlinkKafkaInternalProducer} from * the previous checkpoint. To decrease the chance of failing checkpoints there are four * options: * <li>decrease number of max concurrent checkpoints * <li>make checkpoints more reliable (so that they complete faster) * <li>increase the delay between checkpoints * <li>increase the size of {@link FlinkKafkaInternalProducer}s pool */
EXACTLY_ONCE,
/** * Semantic.AT_LEAST_ONCE the Flink producer will wait for all outstanding messages in the * Kafka buffers to be acknowledged by the Kafka producer on a checkpoint. */
AT_LEAST_ONCE,
/** * Semantic.NONE means that nothing will be guaranteed. Messages can be lost and/or * duplicated in case of failure. */
NONE
}
下面以Flink与Kafka的集成来说明2PC的具体流程。注意这里的Kafka版本必须是0.11及以上,因为只有0.11+的版本才支持幂等producer以及事务性,从而2PC才有存在的意义。Kafka内部事务性的机制如下框图所示。
flink 实现两阶段提交具体实现为:
FlinkKafkaProducer.commit()方法实际上是代理了KafkaProducer.commitTransaction()方法,正式向Kafka提交事务。
Flink版本:1.13.6
@Override
protected void commit(FlinkKafkaProducer.KafkaTransactionState transaction) {
if (transaction.isTransactional()) {
try {
transaction.producer.commitTransaction();
} finally {
recycleTransactionalProducer(transaction.producer);
}
}
}
该方法的调用点位于 TwoPhaseCommitSinkFunction.notifyCheckpointComplete()方法中,顾名思义,当所有的检查点都成功后,会调用这个方法。
@Override
public final void notifyCheckpointComplete(long checkpointId) throws Exception {
// the following scenarios are possible here
//
// (1) there is exactly one transaction from the latest checkpoint that
// was triggered and completed. That should be the common case.
// Simply commit that transaction in that case.
//
// (2) there are multiple pending transactions because one previous
// checkpoint was skipped. That is a rare case, but can happen
// for example when:
//
// - the master cannot persist the metadata of the last
// checkpoint (temporary outage in the storage system) but
// could persist a successive checkpoint (the one notified here)
//
// - other tasks could not persist their status during
// the previous checkpoint, but did not trigger a failure because they
// could hold onto their state and could successfully persist it in
// a successive checkpoint (the one notified here)
//
// In both cases, the prior checkpoint never reach a committed state, but
// this checkpoint is always expected to subsume the prior one and cover all
// changes since the last successful one. As a consequence, we need to commit
// all pending transactions.
//
// (3) Multiple transactions are pending, but the checkpoint complete notification
// relates not to the latest. That is possible, because notification messages
// can be delayed (in an extreme case till arrive after a succeeding checkpoint
// was triggered) and because there can be concurrent overlapping checkpoints
// (a new one is started before the previous fully finished).
//
// ==> There should never be a case where we have no pending transaction here
//
Iterator<Map.Entry<Long, TransactionHolder<TXN>>> pendingTransactionIterator =
pendingCommitTransactions.entrySet().iterator();
Throwable firstError = null;
while (pendingTransactionIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Long, TransactionHolder<TXN>> entry = pendingTransactionIterator.next();
Long pendingTransactionCheckpointId = entry.getKey();
TransactionHolder<TXN> pendingTransaction = entry.getValue();
if (pendingTransactionCheckpointId > checkpointId) {
continue;
}
LOG.info(
"{} - checkpoint {} complete, committing transaction {} from checkpoint {}",
name(),
checkpointId,
pendingTransaction,
pendingTransactionCheckpointId);
logWarningIfTimeoutAlmostReached(pendingTransaction);
try {
commit(pendingTransaction.handle);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (firstError == null) {
firstError = t;
}
}
LOG.debug("{} - committed checkpoint transaction {}", name(), pendingTransaction);
pendingTransactionIterator.remove();
}
if (firstError != null) {
throw new FlinkRuntimeException(
"Committing one of transactions failed, logging first encountered failure",
firstError);
}
}
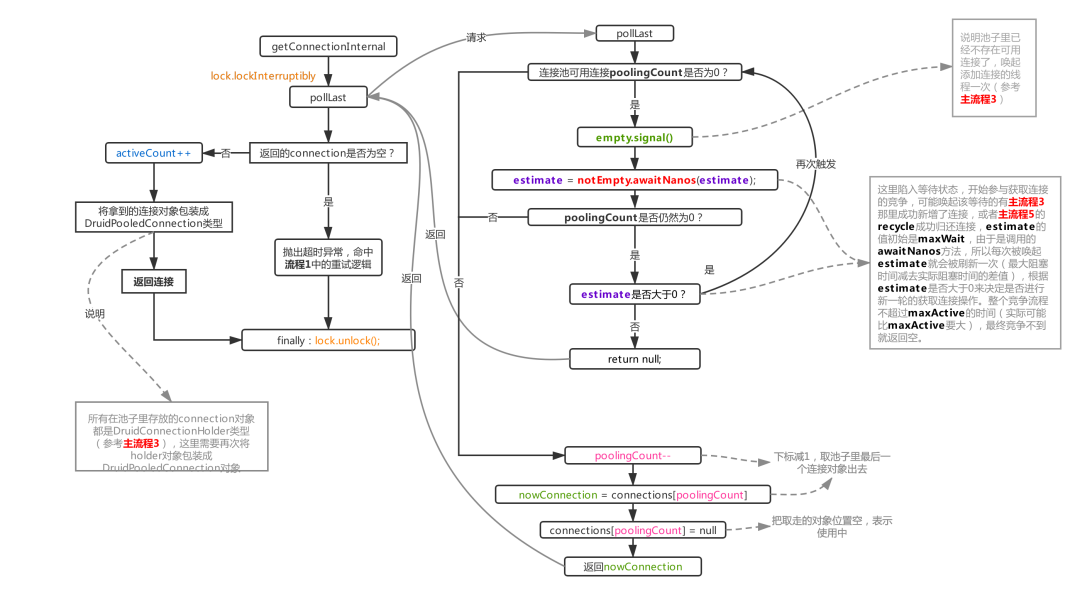
从代码中可以看出,该方法每次从赈灾等待提交的事务句柄中取出一个,检查他的检查点ID,并调用commit()方法提交,这个阶段流程图为:

可见,只有在所有的检查点都成功的这个前提下,写入才会成功。这符合前文描述2PC的流程。其中jobmanager为协调者,各个算子为参与者,并且中有sink一个参与者会执行提交。一旦有了检查点失败,notifyCheckpointComplete()方法不会执行,如果重试不成功,则最后会调用abort()方法回滚事务,如下:
@Override
protected void abort(FlinkKafkaProducer.KafkaTransactionState transaction) {
if (transaction.isTransactional()) {
transaction.producer.abortTransaction();
recycleTransactionalProducer(transaction.producer);
}
}
参考list:
边栏推荐
- MySQL进阶查询
- 构建资源的弹性伸缩
- 如何做到构建的提速,再提速
- 编程技巧│selenium 更新 chromedriver 驱动
- 使用mysql语句操作数据表(table)
- Data Filters in ABP
- [Server data recovery] Data recovery case of lvm information and VXFS file system corruption caused by raid5 crash
- apache+PHP+MySQL+word press, page error when installing word press?
- Linux install redis database
- 22. Inventory service
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
HCIP-R&S By Wakin自用笔记(3)OSPF之引入外部路由、Forwarding-Address、汇总、特殊区域
#yyds Dry Goods Inventory#[Yugong Series] August 2022 Go Teaching Course 008-Integer of Data Types
Exception: try catch finally throws throw
std::format格式化自定义类型
深度解析volatile关键字(保证够全面)
③ 关系数据库标准语言SQL 数据查询(SELECT)
Jvm. Profiling tools (jconsole, jvisualvm, arthas, jprofiler, mat)
C# JObject解析JSON数据
QT+VTK+PCL拟合圆柱并计算起始点、中止点
How to check if the online query suddenly slows down
R language multiple linear regression, ARIMA analysis of the impact of different candidates in the United States on the economic GDP time series
J9 Digital Theory: DAO governance is more like an ecological process: governance is native to the network and continues to evolve
HW-蓝队工作流程(1)
leetcode 前K个高频单词
The statistical data analysis, interview manual"
[GXYCTF2019]BabySQli
Web APIs BOM - A Comprehensive Case of Operating Browsers
Elastic scaling of construction resources
MySQL indexes and transactions
① 数据库介绍 及 关系型数据库的关系代数表达式