当前位置:网站首页>Define defines constants and macros, pointers and structures
Define defines constants and macros, pointers and structures
2022-04-23 05:00:00 【C xuexiaobai】
Catalog
#define Define constants and macros
The size of the pointer variable
#define Define constants and macros
#define Define constants
In variables and constants 2,#define Defined identifier constant in , I know that #define You can define constants .
Define a symbol called NUM, Here we can assign a value to it , You can print its value directly , You can also create an array , The size of the array is in NUM( here NUM Is a constant ).
#define NUM 100
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", NUM);
int n = NUM;
printf("%d\n", n);
int arr[NUM] = { 0 };
return 0;
} Operation certificate , Whether it's direct printing , Or use it NUM There is no problem creating an array .
Operation certificate , Whether it's direct printing , Or use it NUM There is no problem creating an array .
#define Defining macro
Macros have parameters
When I was looking for the sum of two numbers , We wrote a function to find , Here we write a macro to find the sum of two numbers .
#define ADD(x,y) ((x)+(y)) Define a macro called ADD,
ADD Is the macro name ,(x,y) Is an argument to a macro , Parameters are untyped ,((x)+(y)) It's a macro .
int Add(int x,int y) This is how functions are written
{
return x + y;
}
#define ADD(x,y) ((x)+(y))
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = ADD(a, b);
printf("%d\n", c);
return 0;
}
 Run to get results 30, Successfully complete the task of adding two numbers .
Run to get results 30, Successfully complete the task of adding two numbers .
Macros and functions are very similar , But macros are macros , Functions are functions , Just have a look here .
The pointer
Memory
Before talking about the pointer , I have to talk about memory first .
Memory is a very important memory on a computer , All programs in a computer run in memory .
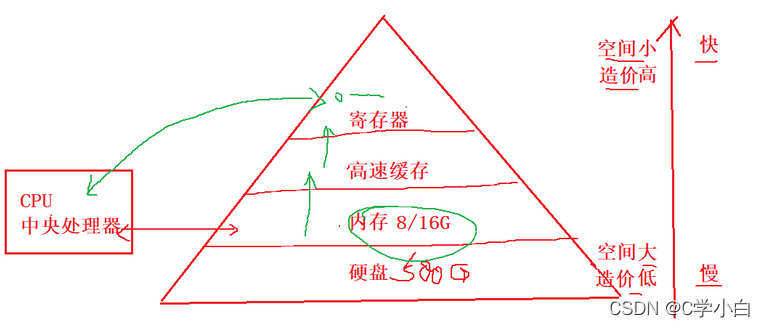 This is where we are register- The register mentioned .
This is where we are register- The register mentioned .
 control+alt+delete Open Task Manager , You can see the memory usage , Every program occupies memory , Are using memory , How do these programs work ? First, load it into memory .
control+alt+delete Open Task Manager , You can see the memory usage , Every program occupies memory , Are using memory , How do these programs work ? First, load it into memory .
When we buy computers, we say 8G/16G, What about this 8G/16G It's impossible to use it directly , So in order to use memory efficiently , Divide the memory into small memory units , The size of each memory unit is 1 Bytes .
These small memory units are like rooms in life , Every room has a Address .
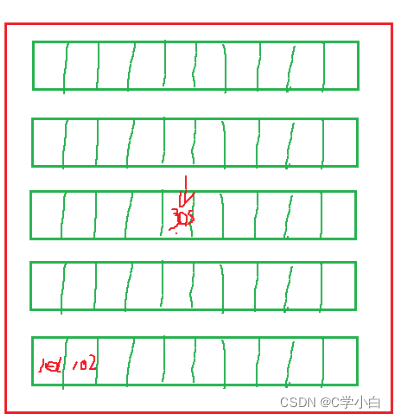 For example, there are five floors , Ten rooms on each floor , There are fifty rooms , Then if I say I'm in a room , Do you want to turn layer by layer , One room at a time , But it's time to number the fifty rooms ,101,102,103……, I said I was 305 when 305 It's the house number , At the same time, it is a Address .
For example, there are five floors , Ten rooms on each floor , There are fifty rooms , Then if I say I'm in a room , Do you want to turn layer by layer , One room at a time , But it's time to number the fifty rooms ,101,102,103……, I said I was 305 when 305 It's the house number , At the same time, it is a Address .
Life is like this , The same is true for memory , Just number each small memory cell , So it's very convenient for me to find these memory spaces .
 Memory will be divided into small memory units ( The size of a memory unit :1byte) Each memory unit has a number . This is a 32 The computer of bit , The address is generated by energizing the address line , Electricity will produce an electrical signal , The electrical signal is 1/0( Positive pulse or negative pulse );32 There are... On your computer 32 Root address line , At this time 32 Follow address line , Every address line has an electrical signal , that 32 The root address line may generate electrical signals at the same time :
Memory will be divided into small memory units ( The size of a memory unit :1byte) Each memory unit has a number . This is a 32 The computer of bit , The address is generated by energizing the address line , Electricity will produce an electrical signal , The electrical signal is 1/0( Positive pulse or negative pulse );32 There are... On your computer 32 Root address line , At this time 32 Follow address line , Every address line has an electrical signal , that 32 The root address line may generate electrical signals at the same time :
00000000000000000000000000000000——>0
00000000000000000000000000000001——>1
……
1111111111111111111111111111111111111
All combinations that produce electrical signals have 2 Of 32 Power individual
2 Of 32 Power The address sequence is 2 Of 32 Power Byte space
How big is that ? We turn on the computer's calculator and transfer it to the programmer , Click on BIN Binary , Input 100000000000000000000000000000000

And then click DEC It's the decimal system , The number obtained represents 4,294,967,296byte

Then divide by 1024 You can get KB, Divided by 1024 You can get MB, Divided by 1024 obtain GB


Finally, we calculate , If a memory unit is a byte , So in 32 On the computer , The management is 4GB Of memory
At present, we are all 64 The computer of bit , So computer memory is 8G/16G/32G It's all very common .
Here someone wants to ask why a memory unit doesn't use one bit Bit by bit ?
because 1bit Not quite reasonable , For example, I create a variable c,char c; c should 1byte,1byte Namely 8bit
Imagine 1bit A memory unit , Light one c Take up 8bit, Eight addresses ,char It's already C The smallest type in a language , that int Well , That's not 32 An address is gone , Just like sending express in life , I'll put it on the fifth square meter of the dormitory , Is there no need to , Is it OK to send it to the room .
So for all kinds of comprehensive considerations , Finally, a memory unit is specified as 1byte.
Why memory , Because creating variables is like applying for memory space
int a = 10; The meaning of this code is to apply for memory 4 Bytes , Store 10.
&a; take a The address of ,& It's the address symbol
Press F10 debugging , And open the window to monitor , Input a, The value is 10, Input &a, You can see a The address of
| name | value | type | |
|---|---|---|---|
| &a | 0x0116fd60 {10} | int * |

You can also view the memory , Also click debug —— window —— Memory ( Be careful : Only after debugging can you see )
Because I don't know what the address is , Enter... In the address window &a, enter , notice 0x0116fd60, Namely a The address of , Then adjust the column to 4, The line is 4 Bytes ——0a 00 00 00.

The decimal system is made up of 0~9 It's made up of numbers , Octal is made up of 0~7 It's made up of numbers , Hexadecimal should have been 0~15 The numbers make up , But the back 10~15 Will it repeat , So here we use a~f They correspond to each other 10~15, therefore 10 Just use a Express

So in memory 0a 00 00 00, What's left is 10( As for why it is stored upside down , We'll talk about it later , Now just know that looking back on the memory is the number you saved )
a Your address can also be printed , For printing integers %d, Print the address with %p,printf("%p\n", &a);

At this time a The address of is 002CFF1C, Because every time you run the program ,a Variables will be recreated , So the address changed , It's different from the last time , Because binary printing is too long , It doesn't seem convenient enough , So print it out in hexadecimal .
Can you save the address ? Certainly. , How to write it
int* p = &a; hold a Put your address in a variable p Inside ,p The type of is called int*
there p It's called Pointer to the variable
Why is it called pointer variable ?
We talked about memory units earlier , Memory units are numbered , The number is the address , Addresses are also called pointers
So the pointer is the address , Is the number of the memory unit , and p Is used to save this address , This number is , That also means that it's used to store pointers , So use it to Store the pointer ( Address ) The variable of is called pointing variable

Be careful : The name of the variable is p, instead of *p, and p The type is int*
And so on , Then create char ch = 'w'
pc =&ch; At that time pc What is the type of , yes char*
int* p = &a; p There's... In it a The address of , that p You have a chance to find a, How to find it then
*p = 20; * Dereference operator , It means through p Address stored in , find p The object that is pointed to ,*p Namely p Object to point to .

Printed out 20, Prove that we passed the address in the pointer , then Dereference found a, And successfully changed a Value .
That's it , The two operators missing from the unary operator ——& and *.
Be careful : Distinguish between pointer and pointer variable , The pointer is the address , Pointing to the variable is used to store the address , As we say orally p It's a pointer , This pointer actually refers to a pointer variable , Pay attention to oral expression
The size of the pointer variable
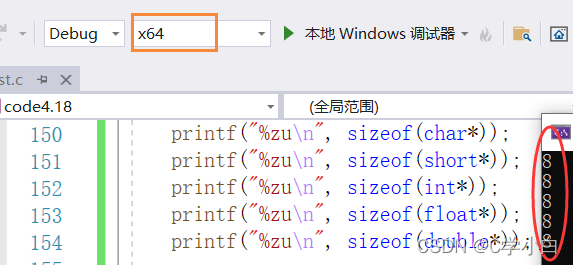
int* p;char* p2; There are different types of pointer creation , What are the sizes of different types

As a result, we found that all of them are 4, Then why are they all 4 Well ?
because No matter what kind of pointer it is , Are creating pointer variables , Pointer variables are used to store addresses , The size of the pointer variable depends on how much space is needed when storing an address .32 Address on bit machine :32bit position - 4byte, So the size of the pointer variable is 4 Bytes ,64 Address on bit machine :64bit position - 8byte, So the size of the pointer variable is 8 Bytes .
It gets 4, Is in X86 The result of running under (X86 It means 32 Bit platform ), Now change it to X64( Namely 64 Bit platform ), The result is 8 了 .
Finally, let's talk about the writing method of creating pointer variables :char* pc; and char *pc;
vs Compilers like char* pc; Write it like this , When you finish writing, add a semicolon , Will automatically jump like this , Write it like this char* Together is a type , But when multiple pointers are defined consecutively ,int* p1, p2, p3; Do you think int* Defined p1, p2, p3 It's all pointers , It's not ,* Just for p1 It was used ,p2, p3 Just got int type , You have to think p1, p2, p3 It's all pointers , Will be int *p1, *p2, *p3; Write it like this , At this time * It's better for you to understand ,p2,p3 It's not a pointer .
These two ways of writing are not absolutely good , Mainly depends on personal habits
Structure
We talked about data types earlier (char,short,int,long,float,double), You have no problem using these types to represent a number , But now we're going to use these types to represent a person , Man is a complex object , To represent a person, you have to have a name , Age , Address , Telephone ……, That means a Book , A book must have a title , author , Press. , pricing , Book number ……
We found these complex objects , The built-in type cannot be described simply , At this time C Language gives you the ability to customize ,
One of the custom types is called Structure , The keyword of the structure is called struct.
Structure is the combination of some single types .
Then we describe a student
First define struct use {} Enclose the variables that need to be described ( Be careful {} After ; You can't drop it ), Then create a main function
The structure accesses its object with . The operator ( Structure object . Member name ), The premise of this usage is to get a structure object .
struct Stu
{
// member
char name[20];
int age;
char sex[10];
char tele[12];
};
int main()
{
struct Stu s = {"zhangsan", 20, "nan", "15596668862"};
// Structure object . Member name
printf("%s %d %s %s\n", s.name, s.age, s.sex, s.tele);
return 0;
}
Don't want to print directly , Take out s The address of , Pass to print function .
void print(struct Stu* ps)
{
printf("%s %d %s %s\n", (*ps).name, (*ps).age, (*ps).sex, (*ps).tele);
}
int main()
{
struct Stu s = {"zhangsan", 20, "nan", "15596668862"};
print(&s);
return 0;
}I think it's too troublesome to write like this , Change to
void print(struct Stu* ps)
{
// Structure pointer variable -> Member name
printf("%s %d %s %s\n", ps->name, ps->age, ps->sex, ps->tele);
}
int main()
{
struct Stu s = {"zhangsan", 20, "nan", "15596668862"};
print(&s);
return 0;
}Here's another operator ->, usage : Structure pointer variable -> Member name ( The premise of this usage is to get a pointer )

Come here ,C The basic grammar of the language is over , I'm sure you're right C What knowledge of language should have an outline , It's just that this knowledge is not so deep , No problem , Then gradually take out the silk and peel the cocoon , A little bit to say .
版权声明
本文为[C xuexiaobai]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230457189928.html
边栏推荐
- 2022/4/22
- Making message board with PHP + MySQL
- Excel protects worksheets and workbooks from damage
- The programmer starts the required application with one click of window bat
- Introduction to raspberry pie 3B - system installation
- js 判断数字字符串中是否含有字符
- Solve valueerror: argument must be a deny tensor: 0 - got shape [198602], but wanted [198602, 16]
- MySQL 慢查询
- 信息学奥赛一本通 1212:LETTERS | OpenJudge 2.5 156:LETTERS
- The object needs to add additional attributes. There is no need to add attributes in the entity. The required information is returned
猜你喜欢

Innovation training (V) configuration information

使用model.load_state_dict()时,出现AttributeError: ‘str‘ object has no attribute ‘copy‘

Customize the navigation bar at the top of wechat applet (adaptive wechat capsule button, flex layout)

Deep learning notes - data expansion

《2021多多阅读报告》发布,95后、00后图书消费潜力攀升
【数据库】MySQL单表查询

Independent station operation | Facebook marketing artifact - chat robot manychat

Download PDF from HowNet (I don't want to use CAJViewer anymore!!!)

View analysis of scenic spots in ArcGIS

Sword finger offer: the median in the data stream (priority queue large top heap small top heap leetcode 295)
随机推荐
Innovation training (IX) integration
Details related to fingerprint payment
Innovation training (II) task division
Learning Android V from scratch - UI
Opencv + clion face recognition + face model training
selenium模式下切换窗口,抓取数据的实现
Customize the navigation bar at the top of wechat applet (adaptive wechat capsule button, flex layout)
JS determines whether the numeric string contains characters
js 判断数字字符串中是否含有字符
Implementation of switching windows and capturing data in selenium mode
Use AES encryption - reuse the wisdom of predecessors
Independent station operation | Facebook marketing artifact - chat robot manychat
COM in wine (2) -- basic code analysis
Pixel mobile phone brick rescue tutorial
vscode ipynb文件没有代码高亮和代码补全解决方法
Learning Android from scratch -- Introduction
深度学习笔记 —— 物体检测和数据集 + 锚框
Informatics Olympiad 1955: [11noip popularization group] Swiss round | openjudge 4.1 4363: Swiss round | Luogu p1309 [noip2011 popularization group] Swiss round
Innovation training (V) mid term inspection
Cross border e-commerce | Facebook and instagram: which social media is more suitable for you?