当前位置:网站首页>Customize my_ Strcpy and library strcpy [analog implementation of string related functions]
Customize my_ Strcpy and library strcpy [analog implementation of string related functions]
2022-04-23 16:57:00 【Toilet look algorithm】

It's hard to study , The result was cool ![]()
️ reminder :
You children's shoes must pay attention to your body on the road of inner rolling , Don't sit in front of the computer all day , Multi motion .
Catalog
One 、 Using library functions strcpy Realize string copy
Two 、 Customize my_strcpy Realize string copy
3、 ... and 、my_strcpy Copy string optimized version
Four 、my_strcpy Copy string depth optimization
One 、 Using library functions strcpy Realize string copy
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
char arr1[20] = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx";
char arr2[20] = "hello";
strcpy(arr1, arr2);//arr1 Destination space start address ,arr2 Source space start address
printf("%s\n", arr1);
return 0;
} Current code print hello It's over , because strcpy Functions not only put hello Copy it , Together with the following \0 Also copied together , The end of string flag is \0, It will only print out hello 了 .

Two 、 Customize my_strcpy Realize string copy
The array name is the address of the first element , That is to say char The address of
use my_strcpy take src Point to copy to dest The space it points to
When put h After copying , To copy other content, make dest and src Point to the next content
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void my_strcpy(char* dest, char* src)//dest Means the destination ,src Means the source
{
while (*src != '\0')
{
*dest = *src;
dest++;
src++;
}
*dest = *src;
}
int main()
{
char arr1[20] = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx";
char arr2[20] = "hello";
my_strcpy(arr1, arr2);//arr1 Destination space start address ,arr2 Source space start address
printf("%s\n", arr1);
return 0;
}


There is something you don't understand about pointers , You can read my previous articles
3、 ... and 、my_strcpy Copy string optimized version
1. The first one is
*dest++ = *src++ yes hello A copy of the
*dest = *src yes \0 A copy of the
️ 2. The second kind
First the h Assign to *dest,h Of ASCII Value is not equal to 0. Later, we will e、l、l、o Assign to *dest, Their ASCII Values are not equal to 0, But will \0 Assign to *dest When ,\0 Of ASCII The value is 0, Expression is false , So the cycle is over .
Four 、my_strcpy Copy string depth optimization
1. Use assert() Assertion
If arr1 perhaps arr2 yes Null pointer (NULL), Means dest perhaps src There is no point anywhere , At this time, if you dereference again, there will be a problem .
terms of settlement :assert()// Assertion
Our program should be able to Check arr1 and arr2 Is it a null pointer , If so, prompt , If not, run .assert() and if() Very similar , It's just assert() The expression in parentheses It's true , Nothing happens , For false , Just a hint of error .
for example :
assert(src != NULL)in addition assert Use the header file
#include<assert.h>
️
Be careful :assert() For real, nothing happens , If it is false, it will prompt an error , This sum if The statement is just the opposite , Be careful not to confuse when using .
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
void my_strcpy(char* dest, char* src)//dest Means the destination ,src Means the source
{
assert(src != NULL);// Assertion
while (*dest++ = *src++)
{
}
}
int main()
{
char arr1[20] = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx";
char arr2[20] = "hello";
my_strcpy(arr1, NULL);//arr1 Destination space start address ,arr2 Source space start address
printf("%s\n", arr1);
return 0;
}
arr1 and arr2 It could be NULL, So assert both
The code is as follows :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
void my_strcpy(char* dest, char* src)//dest Means the destination ,src Means the source
{
assert(dest != NULL);// Assertion dest
assert(src != NULL);// Assertion src
while (*dest++ = *src++)
{
}
}
int main()
{
char arr1[20] = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx";
char arr2[20] = "hello";
my_strcpy(arr1, arr2);//arr1 Destination space start address ,arr2 Source space start address
printf("%s\n", arr1);
return 0;
}️2. add to const

If The starting address of the source space and the starting address of the target space are reversed , It has been written. *src++ = *dest++, The string copy is reversed , take arr1 String in ( a pile x) copy to arr2 In the middle , The program will crash , because arr2 can't let go arr1 The content of

When we reverse the source space start address and the target space start address , How can we find it in time ?
terms of settlement :const
Add a... Before the address of the source space const
for example :
void my_strcpy(char* dest, const char* src)
When we add const after , Then compile the code , take *dest Copy to *src, The program will report an error ; And even if it's written backwards , Programs can also run , add const After that, the program can't even run , There will be no running errors .
Then add one from const Is a good protection
️
Be careful : If *dest and *src No reverse , Even with const The program will not report a mistake
The code is as follows :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
void my_strcpy(char* dest, const char* src)//dest Means the destination ,src Means the source
{
assert(dest != NULL);
assert(src != NULL);// Assertion
while (*dest++ = *src++)
{
}
}
int main()
{
char arr1[20] = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx";
char arr2[] = "hello";
my_strcpy(arr1, arr2);//arr1 Destination space start address ,arr2 Source space start address
printf("%s\n", arr1);
return 0;
}️ 3.const Modify a pointer
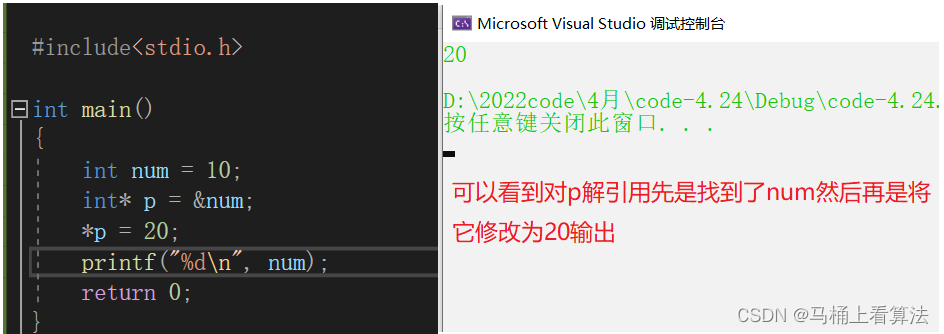
Now? requirement num The value of cannot be changed , To be in num On the left Add a const, That's what it says :
const int num = 10;const The function of is to modify variables , This variable is called a constant variable , Has constant properties , Cannot be modified , But it's essentially a variable .
When we run the code, we will find , Even with const,num The value of has been changed .
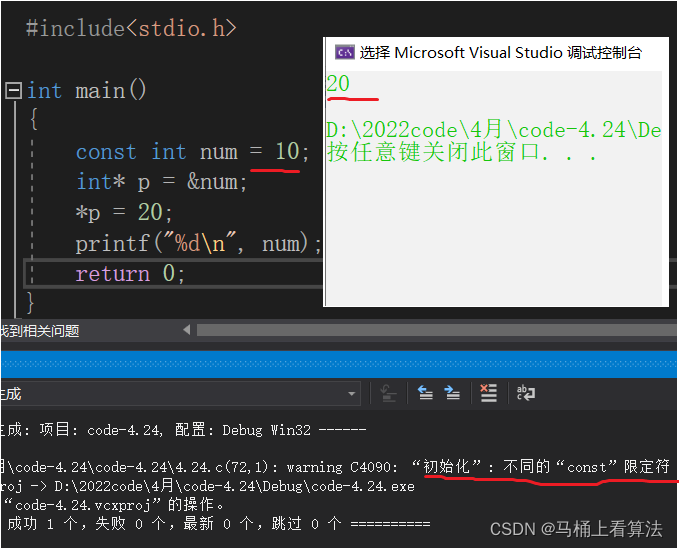
Join in const My original intention is not to change num Value , But now it has changed . although num By const modification ,num The value of cannot be changed , but num He gave his address to p. Through to p Dereference will still num The value of is changed . For example, we have to enter the classroom , Normally, you can only enter through the door , But now the door is locked , We can also go in through the window .

We add const The purpose of this is very clear , That is to make num The value of cannot be changed . You can still access the address here num The value of the change , It seems very clever , But it doesn't meet our requirements . Then what can I do to lock the window ?
terms of settlement : take p Add one to the left of const
That's what it says :
const int* p = #Run the code and you'll find , The program will report an error . It's equivalent to locking the windows here .

The code is as follows :
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
const int num = 10;
const int* p = #
//const When modifying the pointer
//const If you put it in * Left side , Modification is *p, Indicates what the pointer points to , It can't be changed by pointer
*p = 20;
printf("%d\n", num);
return 0;
}️
Be careful : although const Modification is *p, But for my pointer variable p No impact
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
const int num = 10;
const int* p = #
//const When modifying the pointer
//const If you put it in * Left side , Modification is *p, Indicates what the pointer points to , It can't be changed by pointer
//*p = 20;
// But the pointer variable itself can be modified
int n = 100;
p = &n;// Revised p Variable itself
printf("%d\n", num);
return 0;
}The current code run result is : 10

️ 4. Cool skin boy Online
The above situation is const Put it in * On the left , So let's talk about const Put it in * On the right .

For example, now there is a girl and a boy 1, They are boyfriend and girlfriend . The boy has ten dollars , The girl wants to eat cold skin , Let the boy buy her cold skin , And a bowl of cold skin costs ten yuan , What happens at this time is *p = 0, It's equivalent to the boy spending ten yuan .

In fact, the boy is very stingy , He was thinking that I only had ten dollars , Please eat , I have no money , Then I won't treat you to . So he thought of a way , Is in the * Add a to the left of const. modification *p, This is the time *p = 0 This action can't be completed .

The girl is angry , You can't give up ten dollars , I think the boy 2 Also very handsome , Break up ! I'll be a boy 2 My girlfriend . What happens at this time is p = &n.

This time the boy 1 panic , You're breaking up with me , That won't work , So the boy thought of a way , That is in * Add... To the right of const.

one day , The boy came up with a bad idea . That's going to be * Add... On both sides of the const


版权声明
本文为[Toilet look algorithm]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231654019726.html
边栏推荐
- How does flash cache data in memory?
- VLAN高级技术,VLAN聚合,超级Super VLAN ,Sub VLAN
- Paging the list collection
- Camtasia2022软件新增功能介绍
- 手写事件发布订阅框架
- Copy constructor shallow copy and deep copy
- 自定义my_strcpy与库strcpy【模拟实现字符串相关函数】
- Talk about browser cache control
- Encapsulating the logging module
- VLAN advanced technology, VLAN aggregation, super VLAN, sub VLAN
猜你喜欢
ByteVCharts可视化图表库,你想要的我都有

批量制造测试数据的思路,附源码
Derivation of Σ GL perspective projection matrix
Use case execution of robot framework
STM32__ 03 - beginner timer

【PIMF】OpenHarmony啃论文俱乐部—在ACM Survey闲逛是什么体验
![[pimf] openharmony paper Club - what is the experience of wandering in ACM survey](/img/b6/3df53baafb9aad3024d10cf9b56230.png)
[pimf] openharmony paper Club - what is the experience of wandering in ACM survey
How vscode compares the similarities and differences between two files
Take according to the actual situation, classify and summarize once every three levels, and see the figure to know the demand
Mock test
随机推荐
Calculate pie chart percentage
Linux MySQL data timing dump
Idea of batch manufacturing test data, with source code
Sub database and sub table & shardingsphere
伪分布安装spark
Decimal format decimal / datetime conversion processing
Creation of RAID disk array and RAID5
[pimf] openharmony paper Club - what is the experience of wandering in ACM survey
NVIDIA graphics card driver error
PyMySQL
ACL 2022 | DialogVED:用于对话回复生成的预训练隐变量编码-解码模型
文件操作详解(2)
Blue Bridge Cup provincial road 06 -- the second game of the 12th provincial competition
Nodejs reads the local JSON file through require. Unexpected token / in JSON at position appears
Node access to Alipay open platform sandbox to achieve payment function
Deeply understand the relevant knowledge of 3D model (modeling, material mapping, UV, normal), and the difference between displacement mapping, bump mapping and normal mapping
Talk about browser cache control
vscode如何比较两个文件的异同
MySQL restores data through binlog file
Path environment variable


