当前位置:网站首页>Golang 对分片 append 是否会共享数据
Golang 对分片 append 是否会共享数据
2022-04-23 14:11:00 【Mrpre】
Golang 对分片 append 是否会共享数据
Golang 官方对 slice 的说明见文章:https://blog.golang.org/slices-intro 大部分特别是前半部分,写的非常详细,但是最后关于append相关部分,就让人感觉浅尝辄止了。
首先,先写结论:append 返回的slice对象,有可能会共享入参slice的底层(意味着对返回对象slice的赋值会影响入参slice)也可能不共享入参slice的底层。
先给几个例子
例1:
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
s := make([]int, 3)
s[1] = 1000
fmt.Println(len(s), cap(s), s)
}
打印出的结果就是3 3 [0 1000 0],这个毫无争议。
例2:
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
s1 := make([]int, 3)
s2 := append(s1, 1000)//s1 追加 值1000,返回值是s2
fmt.Println("s2", len(s2), cap(s2), s2)
fmt.Println("s1", len(s1), cap(s1), s1)
fmt.Println("After modify s2")
s2[1] = 999//对s2赋值,看看是否对s1有影响
fmt.Println("s2", len(s2), cap(s2), s2)
fmt.Println("s1", len(s1), cap(s1), s1)
}
打印结果
s2 4 6 [0 0 0 1000]
s1 3 3 [0 0 0]
After modify s2
s2 4 6 [0 999 0 1000]
s1 3 3 [0 0 0]
似乎,我们对s2的赋值(s2[1] = 999)没有影响s1,所以,append返回的对象,就和是s1没任何关系了?NO,我们来看例3
例3:
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
s1 := make([]int, 3)
s_slice := s[1:2]
s2 := append(s_slice, 1000)
fmt.Println("s2", len(s2), cap(s2), s2)
fmt.Println("s1", len(s1), cap(s1), s1)
fmt.Println("After modify s2")
s2[1] = 999
fmt.Println("s2", len(s2), cap(s2), s2)
fmt.Println("s1", len(s1), cap(s1), s1)
}
s2 2 2 [0 1000]
s1 3 3 [0 0 1000]
After modify s2
s2 2 2 [0 999]
s1 3 3 [0 0 999]
从结果来看,你看s1被同步修改了。例3 和 例2的唯一区别在于append的入参,s_slice和s1,这里 我们就要反过头来看看文章前面提到的官方文档:https://blog.golang.org/slices-intro 分片的属性包含3个(数组指针、cap、len),而例3中,s_slice和s1的区别就在于 他两 cap len不同(相关知识可以搜索其他文章或者直接看上面给的链接)。
所以,可以猜到,append的操作肯定是判断了 cap 或者len了。 cap 表示 了 slice的存储最大能力,len表示当前元素个数。
len(s1), cap(s1),都是3,表示 s1 容量是3,元素个数是3,即表示 s1满了,你在s1上操作append,那么必然需要新创建数组指针,即例2中,s2->数组指针 和 s1->数组指针 完全是独立的。这也就是为什么 append 入参 是 s1 时,对返回的s2的操作,根本不会影响s1。
回到 例3,入参 s_slice 的 cap 是 2,len 是1(因为s_slice 衍生自s1,s1容量是3,len是3,s_slice取[1:2],cap还空了一个),所以此时 s_slice 是有容量的。
对于有容量的slice,append操作,是在当前 指针数组后面插入值即可。这也就意味着,s2使用了s1的指针数组,修改s1会同步修改s1。
append实现的伪代码可以理解为
append(src, other) {
ret = src
//超过容量,就申请新的内存,否则返回对象的byte还是src的byte
if len(other) + src->len > src->cap {
byte = new(...);
copy(byte, src->byte)
ret->byte = byte//replaced by new buffer
} //else ret->byte == src->byte
copy(src->byte + src->len, other)
}
append居然还有两副面孔。
版权声明
本文为[Mrpre]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://wonderful.blog.csdn.net/article/details/107486979
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Some experience of using dialogfragment and anti stepping pit experience (getactivity and getdialog are empty, cancelable is invalid, etc.)
uni-app消息推送
Operation instructions of star boundary automatic text translator (advanced version)
Operation instructions of star boundary text automatic translator

什么是云迁移?云迁移的四种模式分别是?
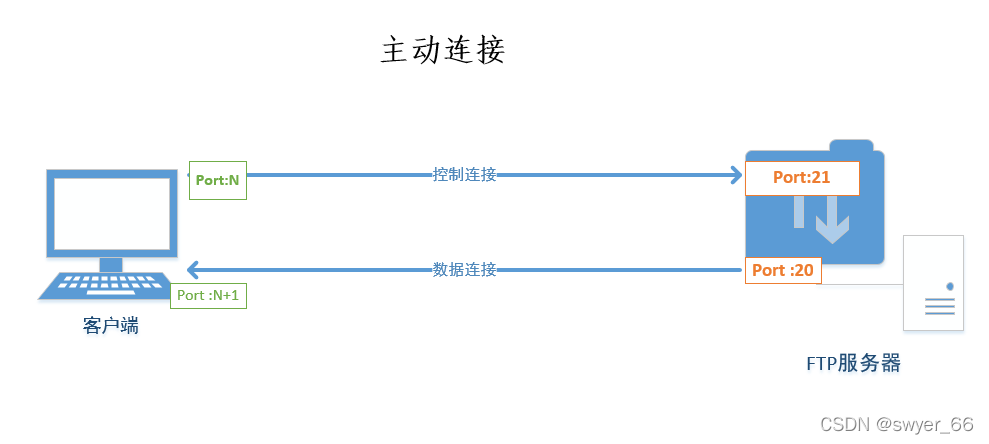
常见存储类型和FTP主被动模式解析

HyperMotion云迁移助力中国联通,青云完成某央企上云项目,加速该集团核心业务系统上云进程
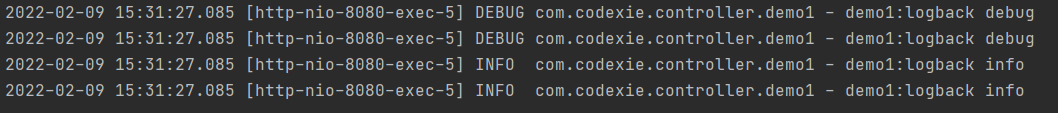
Logback logger and root
倒计时1天~2022云容灾产品线上发布会即将开始
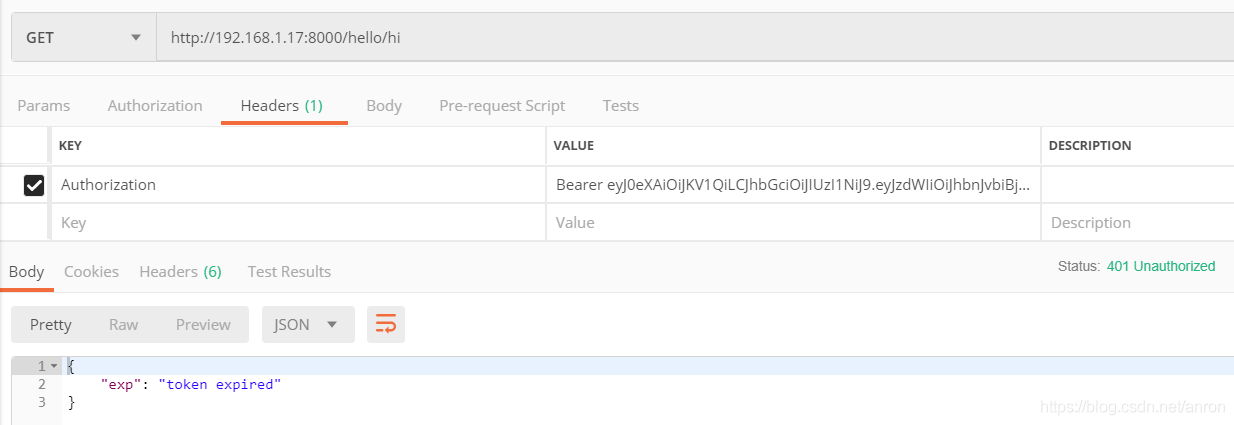
API Gateway/API 网关(四) - Kong的使用 - 集成Jwt和熔断插件
随机推荐
修改Firebase Emulators的默认侦听IP
在电视屏幕上进行debug调试
On the problem of cliff growth of loss function in the process of training
返回数组排序后下标
A table splitting implementation scheme of MySQL and InnoDB, MyISAM and MRG_ Introduction to MyISAM and other engine application scenarios
如何轻松做好一个项目
Operation instructions of star boundary text automatic translator
js 格式化时间
Tongxin UOS uninstall php7 2.24, install php7 4.27 ; Uninstall and then install PHP 7.2.34
微信小程序将原生请求通过es6的promise来进行优化
MySQL数据库讲解(九)
关于UDP接收icmp端口不可达(port unreachable)
HyperMotion云迁移完成阿里云专有云产品生态集成认证
MySQL-InnoDB-事务
Introduction to the use of countdownlatch and cyclicbarrier for inter thread control
Five ways of using synchronized to remove clouds and fog are introduced
JS parabola motion packaging method
JumpServer
json date时间日期格式化
快速搞懂线程实现的三种方式