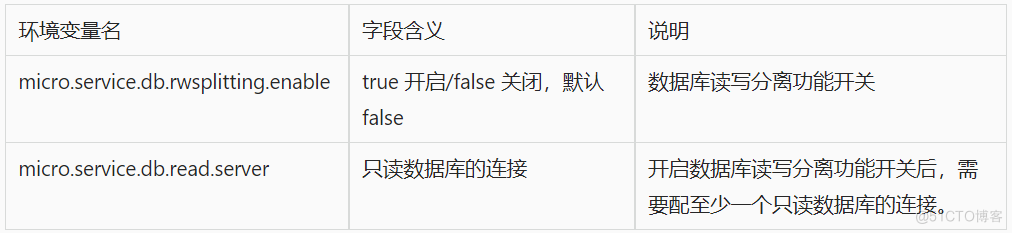
当前位置:网站首页>What is a Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) attack?How to defend?
What is a Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) attack?How to defend?
2022-08-10 03:20:00 【Front-end watermelon brother】
I am the front-end watermelon brother. Today I will learn CSRF.
CSRF, cross-site request forgery, the full English name is Cross-site request forgery.Also known as XSRF.
CSRF attacks take advantage of the user's trust in the browser.
When we successfully log in to a website, the browser actually saves the login credentials under the domain name of this website, usually through cookies.
After logging in, our request under the current domain name will bring a cookie, and the server will use it to determine which user you correspond to, allowing you to perform some operations involving personal privacy.
A mechanism of the browser: accessing a url will bring cookies corresponding to the domain name, which gives CSRF an opportunity.
Using CSRF, attackers can trick your browser into sending some requests (such as money transfers) using your account on a particular website.
Example
The attackers designed a phishing site.The website is very simple, with a form in it:
The submitted url is the address of a bank website you log in;
Use POST request (to solve the limitation that browser address bar access can only be GET request);
Pre-fill the transfer target account number, amount and other information;
Trigger submit operation directly with script;
In this way, the attacker will induce you to visit its phishing site in various ways.
Once we visit the attacker's website, simulate yourself clicking the "transfer" button on the bank's website and send the transfer request.
Of course, the premise is that you are logged in on this bank website.
But don't worry, the bank will not make such a low-level mistake, there will be a lot of defensive measures, and you may need to enter the mobile phone verification code.This is just a bad example.
Some defenses against CSRF
Check token
We can make the request carry an additional csrf_token to ensure that the request is sent through the front-end page of the website.
This csrf_token is issued by the server and should not be placed in a cookie. It should be provided to the front-end page of the website by other means. One way is to place it on the DOM.
When the front-end requests, it will find this csrf_token from the DOM, bring it as a parameter, and let the server verify it.
In order to prevent attackers from forging csrf_token, we need to ensure that csrf_token is associated with user credentials. We can consider hashing the user credentials. Attackers cannot forge without the key.
Use strict SameSite
Cookies have a SameSite attribute, which is set to strict mode (non-none value), which can make cross-domain requests from other websites without cookies.
Judging by Referer
If the request is sent in a website, the domain name in the HTTP header field Referer is the current website.If it is a request initiated by another website, the Referer is the domain name of this website.
The server can use this Referer to determine whether the request is initiated on the website page.
You can also take advantage of the Origin header field, which is usually carried in cross-origin requests.
But Referer is not completely reliable, there may be some problems in the implementation of some old browsers, and there is a possibility of loss.
No Cookies
Save the user credentials to the localStorage local cache, and manually retrieve them from the request header field when sending an Ajax request in the website.In this way, when other websites carry out CSRF attacks, the cookie carried by themselves will not have our user credentials.
It doesn't look like a big deal.There is a small problem, that is, it seems that the http-only anti-XSS attack of cookies cannot be used.
Verification
Add an SMS check, email check, Google's wicked Jiugongge, etc. to make sure that someone is trying to send the request.
All attacks can be suspended, the disadvantage is that the user experience is not very good.
End
CSRF Cross-Site Request Forgery takes advantage of people's trust in browsers (cookies are attached to websites).When you log in to website A, the attacker analyzes the request structure of website A, constructs some requests, induces users to click and then actually initiates the request to realize the attack.
To prevent CSRF, developers need to take various defensive measures during development.
I am the front-end watermelon brother, follow me and learn more front-end knowledge.
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
华为HCIE云计算之FC添加ipsan数据存储
【Kali安全渗透测试实践教程】第7章 权限提升
《GB39707-2020》PDF download
2022杭电多校联赛第七场 题解
翻译软件免费版下载-免费版翻译软件下载
Golang nil的妙用
what is eabi
【Kali安全渗透测试实践教程】第9章 无线网络渗透
控制台中查看莫格命令的详细信息
浅写一个下拉刷新组件
阿里云OSS文件上传
剑指offer专项突击版第25天
《GB39732-2020》PDF下载
Algorithm and voice dialogue direction interview question bank
实操|风控模型中常用的这三种预测方法与多分类场景的实现
Initial attempt at UI traversal
微透镜阵列后光传播的研究
web开发概述
微透镜阵列的高级模拟
[语法糖] 关于类别字符串到类别数字id的映射