当前位置:网站首页>Common interview questions of operating system:
Common interview questions of operating system:
2022-04-23 15:09:00 【White horse is not a horse·】
Catalog
- 1. Operating system foundation
- 2. Processes and threads
-
- 2.1 Difference between process and thread ?
- 2.2 What are the states of a process ?
- 2.3 State transitions between processes ?
- 2.4 Communication between processes (7 Kind of )
- 2.5 The difference between process synchronization and process asynchrony ?
- 2.6 What are the ways to synchronize threads ?
- 2.7 What are the scheduling algorithms of processes in the operating system ?
- 2.8 What is a deadlock ?
- 2.9 How to solve the deadlock problem ?
- 3. Operating system memory management foundation
-
- 3.1 What is the main memory management of the operating system ?
- 3.2 Common memory management mechanisms
- 3.3 What are fast tables and multi-level page tables ?
- 3.4 The common points and differences between paging mechanism and segmentation mechanism ?
- 3.5 Logic ( fictitious ) Difference between address and physical address ?
- 3.6 CPU Addressing understand ? Why do I need a virtual address space ?
- 4. Virtual memory
1. Operating system foundation
1.1 What is an operating system :
Definition : A program that manages computer hardware and software resources , It's the cornerstone of computers
Hardware resources : Hardware equipment management
Software resources : memory management , File system management and application management .
1.2 What is system call :
According to Program access resources Characteristics , The operation of the process in the system is divided into two states :
1) User mode : The running process can access the data of the user program
2) The system state : The process has access to all resources
3) system call : In user mode , How to access system state data ? Through system calls , Accessed by the operating system .
4) interrelation : User mode <---- Process call ----> The system state
2. Processes and threads
2.1 Difference between process and thread ?
- Process definition : Programs executed concurrently during execution , The basic unit of resource allocation . Have system resources .
- Thread definition : Is an execution unit of a process , The basic unit of processor independent scheduling . No system resources .
- Difference between process and thread :
1) address space : The process has one ; Share this process address space
2) resources : Process resources are independent ( Easy to manage and protect }; Threads share the resources of this , Not independent .( Not conducive to protection )
3) Robustness, : There is no interaction between processes ; Interaction and coupling between threads
4) Execution process : Process execution cost is high , Low thread overhead
5) Process is the basic unit of resource allocation , Threads are the basic unit of independent scheduling .
6) A process contains multiple threads
7) Processes are independent , But threads are often coupled to each other .
8) Low thread execution cost , But it is not conducive to the management and protection of resources ; Process execution cost is high , Conducive to the management and protection of resources
2.2 What are the states of a process ?
Five states of process :
- Create a state of : The process is being created , The operating system allocates resources to the process , initialization PCB
- Ready state : CPU : × Other resource requirements :
- Running state : CPU : Other resource requirements : ×
- Blocked state : CPU : × Other resource requirements : × Pausing while waiting for an event / wait for IO operation
- End state : The process is being undone from the system , The operating system will recycle the resources owned by the process , revoke PCB
2.3 State transitions between processes ?
- The ready state -> Running state : The process is scheduled
- Running state -> The ready state : It's time to , or CPU Preempted by other high priority processes .
- Running state -> Blocking state : Wait for system resource allocation or wait for an event to occur ( Take the initiative )
- Blocking state -> The ready state : Resources are allocated in place , Wait for the event to happen ( Passive behavior )
- Create state -> The ready state : The system completes the work related to the creation process
- Running state -> Termination state : End of process running , Or encountered an irreparable error in the process
2.4 Communication between processes (7 Kind of )
- Shared memory : Multiple processes can access the same memory space mutually exclusive .( Most useful , Synchronous operation can be realized through mutex lock and semaphore )
- Anonymous pipeline (Pipes) : Communication between parent-child processes or brother processes with kinship . Files that exist only in memory .
- Famous pipeline (Names Pipes) : Strictly follow the "first in, first out" principle (first in first out), Exist as a disk file .
- The signal (Signal): Notifies the receiving process that an event has occurred
- Semaphore (Semaphores: A semaphore is a counter , The intention is to synchronize between processes .
- Message queue : Deliver structured messages . The message queue is a linked list of messages , Have a specific format , Stored in memory and identified by the message queue identifier .
- Sockets: The client and server communicate through the network . It is an agreement between the two parties of communication , Use the relevant functions in the socket to complete the communication process .
- Message queue has obvious advantages :
1) It overcomes the problem that the signal carries less information
2) Pipes can only carry unformatted
3) The size of byte stream buffer is limited .
2.5 The difference between process synchronization and process asynchrony ?
- Process synchronization :
Concept : The concurrent execution of processes brings asynchrony , But the process is sometimes sequential , Solve the asynchrony problem through process synchronization . - Process synchronization method :
1) Software
(1) Single sign method : Common shaping variable record . The two processes alternately enter the critical zone . A process is accessing the critical area , Will give access to another process .
(2) Double sign check first : Check the object status first , Then put your own logo .
(3) Double sign post check : Put your own logo first , Check the object status again . Disadvantages of the double marker method : It is possible to access and not access at the same time , Because modification and judgment cannot be completed at the same time .
(4) Pearson algorithm : Combination of single sign and double sign post inspection , Avoid waiting indefinitely .
2) Hardware
(1)TestAndSet Use instructions for atomic operations
Interrupt mask - Asynchronous process : Multiple processes cannot access critical resources at the same time , Mutual exclusive access required , At the same time , There is a visit .
2.6 What are the ways to synchronize threads ?
-
Why do you need synchronization between threads ?
Because threads share the resources of this process , If multiple threads execute concurrently , It is necessary to avoid the use conflict of key shared resource variables . -
How to synchronize threads :
1) A critical region : Only one thread is allowed to access shared resource variables at any time , If more than one thread attempts to access a common resource , Latecomers will be suspended .
2) The mutex (Mutex): Adopt mutually exclusive object mechanism , Only threads with mutexes have access to public resources .( There is only one mutex ). Example : such as Java Medium synchronized Key words and all kinds of Lock It's all this mechanism . A lock is its mutually exclusive object .
3) Semaphore (Semphares): Allow multiple threads to access the same resource at the same time , Control the maximum number of threads accessing this resource at the same time .
4) event (Event): Keep multi-threaded synchronization through notification operations .
2.7 What are the scheduling algorithms of processes in the operating system ?
-
First come, first serve (FCFS) Scheduling algorithm ( Unfriendly to short processes ) :
First come first serve , Until the operation ends or is blocked , Like a bank party . -
Short job preferred (SJF) Scheduling algorithm of ( Take care of the short process , Ignore the long process , Will be hungry ):
Select a process from the ready queue with the shortest estimated run time to allocate resources to it , Until the operation ends or is blocked . -
Highest response ratio :
Response ratio = response time / Service time -
Priority scheduling :
Schedule according to the priority of the process , Until the scheduling is finished . -
Time slice rotation scheduling algorithm :
Each process runs the time slice , Perform traversal and execute . -
Multilevel feedback queue scheduling algorithm :
Recognized as the best scheduling algorithm : It can make high priority jobs respond , It can also make short homework complete quickly .
Multi level priority alignment , High priority low time slice , Then the high priority consumption time slice is processed first , Then process the sub priority time slice .
2.8 What is a deadlock ?
- A deadlock describes one of the following situations :
The processes wait for each other's resources , Cause the process to jam , Unable to move forward .
The allocation of inalienable resources is unreasonable , May cause deadlock . - Deadlock , What's the difference between hunger and death cycle ?
1) Deadlock : At least two processes are blocked at the same time — Operating system solution
2) hunger : Only one process can be blocked ----- Operating system solution
3) Dead cycle : There may be only one . ------ appear bug, Programmers solve - Necessary conditions for deadlock :
1) Mutually exclusive : Resources must be unshared , Only one process can use... At a time .
2) non-preemptive : Resources cannot be preempted
3) Take possession and wait : The process occupies at least one resource , And wait for another resource
4) Loop waiting for : Resource waiting forms a closed loop
5) Four conditions are met at the same time , Before a deadlock can occur .
2.9 How to solve the deadlock problem ?
Four methods to solve deadlock problem :
- The prevention of : No deadlock allowed ; static state : Deadlock prevention ; Four necessary conditions for breaking deadlock
- avoid : No deadlock allowed ; dynamic : Avoid deadlock ; Prevent the system from entering an unsafe state ( Banker Algorithm )
- testing : Allow deadlock to occur ; When a deadlock occurs , Accurately detect the location and related resources of deadlock
- relieve : Allow deadlock to occur ; Cooperate with detection , Release the process from deadlock
- Prevention is to avoid four conditions , Avoidance is the use of four conditions , Find the most reasonable ;
- Prevention and avoidance are deadlocks that don't happen ; Detection and release are operations after deadlock occurs .
- Avoid the banker's algorithm in : Allocate resources for the process by probing , Judge whether the system is in a safe state after allocation through the security algorithm .
3. Operating system memory management foundation
3.1 What is the main memory management of the operating system ?
Mainly completed Memory allocation and recycling ; Address translation ; Memory space expand and Storage protection .
- Memory allocation , Recycling :malloc function , Application memory ;free function , Free memory
- address translation : Convert logical address to physical address .
- Expansion of memory space : Virtual storage technology or automatic coverage technology
- Storage protection : Each job runs in its own storage space , Mutual interference .
3.2 Common memory management mechanisms
Memory management falls into two broad categories , Four sub categories :
1) Continuous distribution management scheme : Single continuous , Fixed partition and dynamic partition
2) Discontinuous distribution management scheme : Basic paging management ; Basic segment management and segment page management ;
- Block management : Divide the memory into fixed blocks , process / Job continuous storage ;
- Basic paging management : Divide the memory into several blocks , The process is also divided into blocks of corresponding size . Improve memory utilization ; Page table for logical address and physical address
- Basic segment management : Paging management , Each page has no specific meaning , Segmented management gives each paragraph specific meaning ( Main program section , Subroutine segments, etc ), Corresponding logical address and physical address through segment table .
- Basic segment page management : Segment main memory first , Page again , Combine the advantages of both
3.3 What are fast tables and multi-level page tables ?
3.4 The common points and differences between paging mechanism and segmentation mechanism ?
3.5 Logic ( fictitious ) Difference between address and physical address ?
3.6 CPU Addressing understand ? Why do I need a virtual address space ?
4. Virtual memory
4.1 What is virtual memory ?
4.2 What is the principle of locality
4.3 What is virtual storage
4.4 Implementation technology of virtual memory
4.5 Page replacement algorithm
版权声明
本文为[White horse is not a horse·]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231407524717.html
边栏推荐
- Redis master-slave synchronization
- 如何设计一个良好的API接口?
- My raspberry PI zero 2W tossing notes record some problems encountered and solutions
- Leetcode151 - invert words in string - String - simulation
- [NLP] HMM hidden Markov + Viterbi word segmentation
- January 1, 1990 is Monday. Define the function date_ to_ Week (year, month, day), which realizes the function of returning the day of the week after inputting the year, month and day, such as date_ to
- Leetcode exercise - 396 Rotation function
- Detailed comparison between asemi three-phase rectifier bridge and single-phase rectifier bridge
- win10 任务栏通知区图标不见了
- Have you learned the basic operation of circular queue?
猜你喜欢

TLS / SSL protocol details (30) RSA, DHE, ecdhe and ecdh processes and differences in SSL

Is asemi ultrafast recovery diode interchangeable with Schottky diode
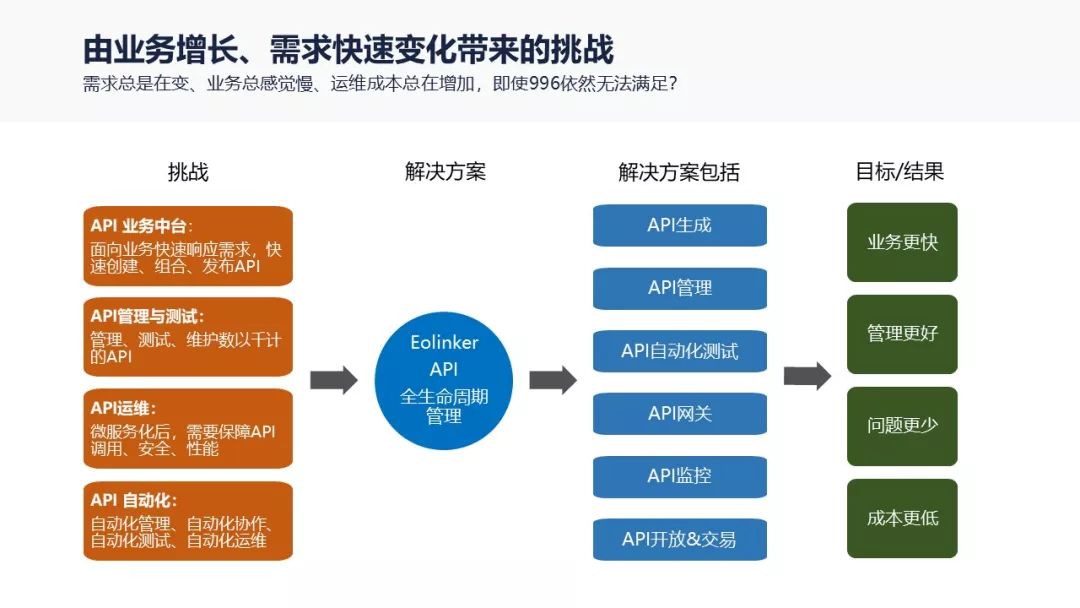
eolink 如何助力遠程辦公

每日一题-LeetCode396-旋转函数-递推

eolink 如何助力远程办公
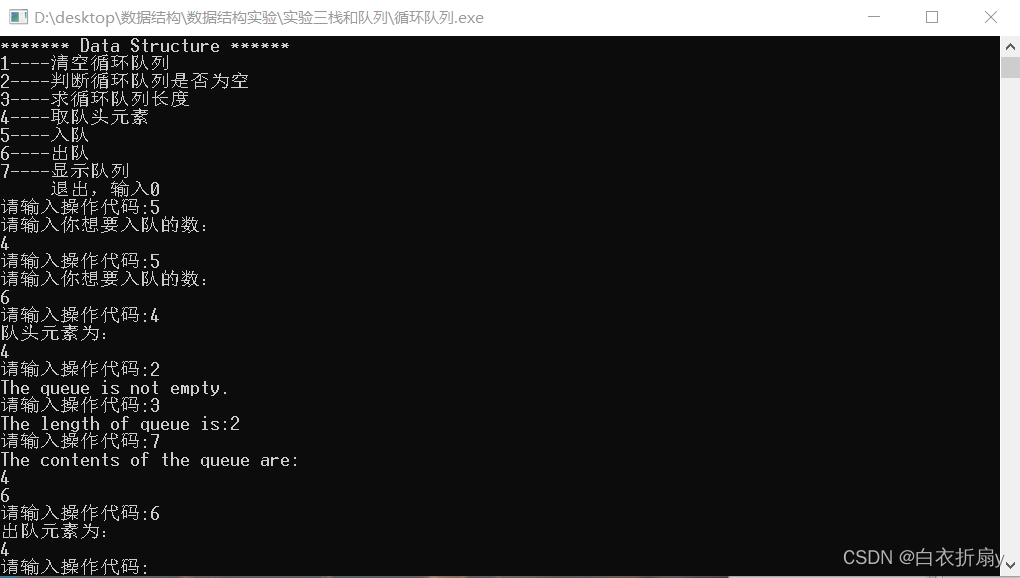
Basic operation of circular queue (Experiment)

Leetcode151 - invert words in string - String - simulation
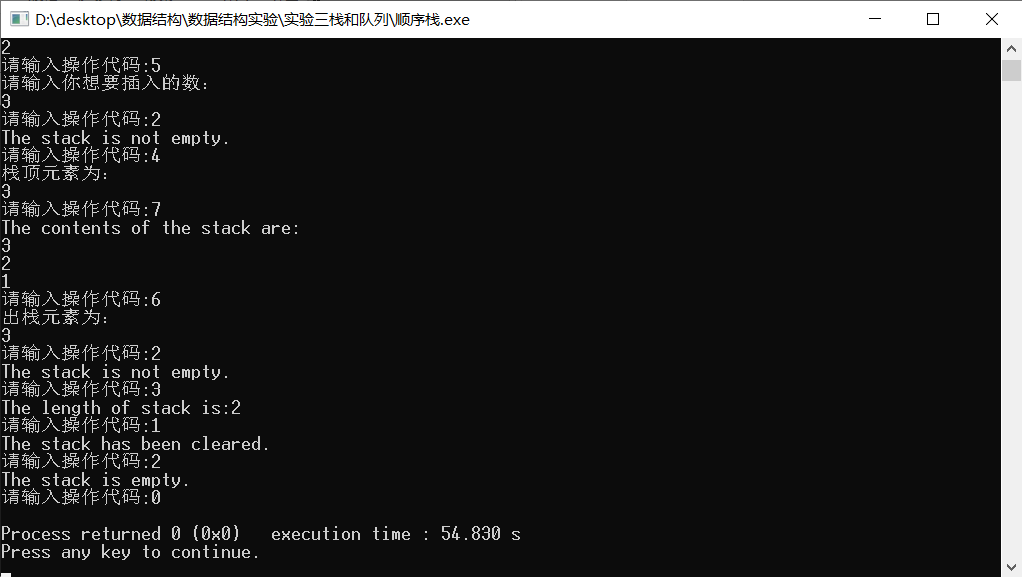
Basic operation of sequential stack
中富金石财富班29800效果如何?与专业投资者同行让投资更简单

Role of asemi rectifier module mdq100-16 in intelligent switching power supply
随机推荐
Basic operation of sequential stack
Redis主从同步
分享3个使用工具,在家剪辑5个作品挣了400多
Introduction to dirty reading, unrepeatable reading and phantom reading
Fill in the next right node pointer II of each node [classical hierarchy traversal | regarded as linked list]
Comment eolink facilite le télétravail
Detailed analysis of SQL combat of Niuke database (26-30)
8.4 realization of recurrent neural network from zero
Swift protocol Association object resource name management multithreading GCD delay once
Have you really learned the operation of sequence table?
SQL中HAVING和WHERE的区别
nuxt项目:全局获取process.env信息
每日一题-LeetCode396-旋转函数-递推
Mds55-16-asemi rectifier module mds55-16
Share 20 tips for ES6 that should not be missed
Async void caused the program to crash
eolink 如何助力远程办公
setcontext getcontext makecontext swapcontext
What is the effect of Zhongfu Jinshi wealth class 29800? Walk with professional investors to make investment easier
ffmpeg安装遇错:nasm/yasm not found or too old. Use --disable-x86asm for a crippled build.