当前位置:网站首页>GFS distributed file system (Theory)
GFS distributed file system (Theory)
2022-04-23 15:25:00 【C chord~】
Catalog
②、 The role of the file system
One .GFS summary
1、 file system
①、 File system composition
- File system interface (API)
- A collection of software that manages objects
- Objects and properties
②、 The role of the file system
- From a system perspective , File system is to organize and back up the space of file storage device
- A system that stores and protects and retrieves stored files
- To be specific , It's responsible for creating files for users 、 Deposit in 、 read out 、 modify 、 Dump files 、 Control the storage of files
③.GFS Professional term
- Brick( Block storage server ) The server that actually stores user data
- Volume Local file system " Partition "
- FUSE File system in user space ( Category EXT4),” This is a pseudo file system “, The switching module of the client
- VFS( Virtual ports ) Kernel virtual file system , The user is submitting a request to VFS then VFS hand FUSH, Give it back GFS client , Finally, the client gives it to the remote storage
- Glusterd( service ) Is the process that runs the re storage node ( The client is running gluster client)GFS The whole process of use GFS The exchange between is made by Gluster client and glusterd complete
④、 GFS Characteristics
- Scalability and high performance : Extensibility , Expansion nodes , Improve performance through multiple nodes
- High availability : No single point of failure , There is a backup mechanism , similar Raid The disaster recovery mechanism of
- Global unified namespace : Centralized management , analogy API The nature of / Concept , The isolation area defined according to his name in the system , It's an independent space ; Unified namespace , Interact with the client , Store the request to the block data server at the back end
- Elastic volume management : It is convenient for capacity expansion and management and maintenance of back-end storage clusters , More complicated
- Based on standard protocol : Based on standardized file usage protocol , Give Way CentOS compatible GFS
Two .GFS working principle
- When an external request passes through the mount point ,linux The system kernel passes through VFS Interface , Send a request to FUSE
- FUSE Give the data to the memory /dev/fuse, Then submit to GFS client
- GFS The client processes the data , And through the network protocol ( Such as TCP、IB etc. ), Transferred to the GFS Server side
- GFS After the server receives the data , adopt VFS Interface , Transfer the data accordingly
3、 ... and .GFS Volume type
- In order to solve the problem of distributed file data index 、 The complexity of positioning , And used HASH Algorithm to assist
- Distributed ( Average distribution ) The benefits of :
- ① When the amount of data is increasing , The amount of data relative to each storage node ( probability ) They are equal.
- ② And if you consider the single point of failure problem , When the data is stored again c Storage nodes , Regarding this GFS There will be a backup mechanism , Default 3 Backup , therefore GFS Its own mechanism will produce redundancy to the data , So as to solve the single point of failure
①. Volume type
- Distributed volumes
- Strip roll
- Copy volume
- Distributed striped volume
- Distributed replication volumes
- Strip copy volume
- Distributed striped data volume
Distributed volumes
File by HASH The algorithm is distributed to all Brick Server On , This kind of roll is GlusterFS The default volume of ; In document units according to HASH The algorithm hashes to different Brick, In fact, it just expands the disk space , If a disk is damaged , Data will also be lost , File level RAID0, No fault tolerance . In this mode , The file is not partitioned , The file is stored directly in some Server Node . Due to the direct use of the local file system for file storage , So access efficiency has not improved , On the contrary, it will be reduced due to network communication .
characteristic
- Files are distributed on different servers , No redundancy
- Expand the size of the volume more easily and cheaply
- A single point of failure can cause data loss
- Rely on the underlying data protection
Strip roll
similar RAID0, Files are divided into data blocks and distributed to multiple servers in a polling manner Brick Server On , File storage is in blocks , Support large file storage , The bigger the file , The more efficient the read is , But there is no redundancy .
characteristic
- The data is divided into smaller pieces and distributed to different stripe areas in the block server cluster
- Distribution reduces load and smaller files speed up access
- No data redundancy
Copy volume
Synchronize files to multiple Brick On , Make it have multiple copies of files , It belongs to file level RAID 1, Fault tolerance . Because the data is scattered in multiple Brick in , So the read performance has been greatly improved , But write performance drops . Replication volumes are redundant , Even if one node is damaged , It does not affect the normal use of data . But because you want to save a copy , So disk utilization is low .
characteristic
- All servers in the volume keep a complete copy
- The number of copies of a volume can be determined when the customer creates
- At least two block servers or more
- Redundancy
Distributed striped volume
Brick Server The number is the number of bands ( Block distribution Brick Number ) Multiple , It has the characteristics of distributed roll and strip roll . Mainly used for large file access processing **, Creating a distributed striped volume requires at least 4 Servers .**
Distributed replication volumes
Distributed replication volumes (Distribute Replica volume):Brick Server The number is the number of mirrors ( Number of data copies ) Multiple , Features of both distributed and replicated volumes , It is mainly used when redundancy is needed .
Strip copy volume
- Strip copy volume (Stripe Replica volume) similar RAID 1 0, It has the characteristics of striped volume and replicated volume at the same time .
- Distributed striped replication volumes (Distribute Stripe Replicavolume) Composite volume of three basic volumes , Usually used for classes Map Reduce application
版权声明
本文为[C chord~]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231406063645.html
边栏推荐
- Crawling fragment of a button style on a website
- TLS / SSL protocol details (30) RSA, DHE, ecdhe and ecdh processes and differences in SSL
- asp. Net method of sending mail using mailmessage
- Share 3 tools, edit 5 works at home and earn more than 400
- Three uses of kprobe
- kubernetes之常用Pod控制器的使用
- MySQL query library size
- About UDP receiving ICMP port unreachable
- Mysql连接查询详解
- 函数(第一部分)
猜你喜欢
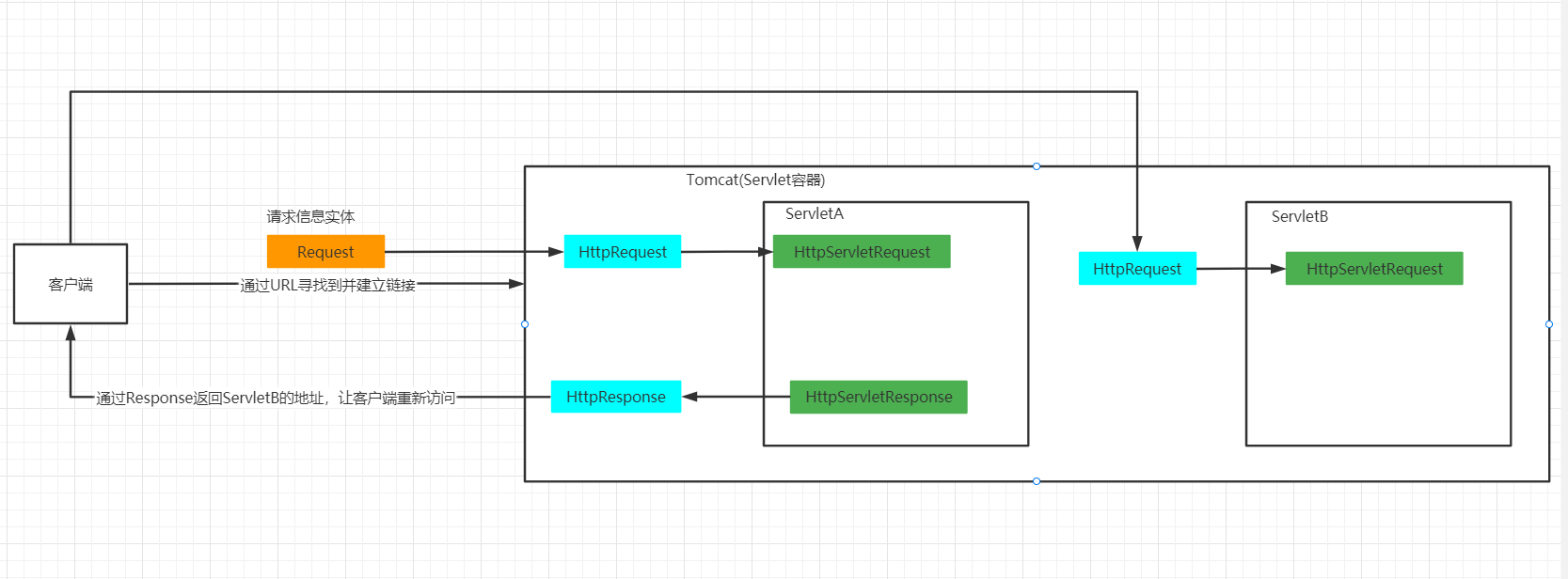
Detailed explanation of redirection and request forwarding
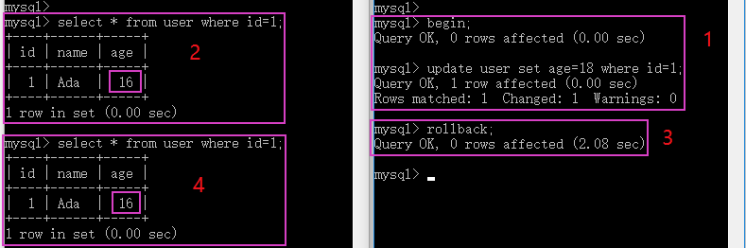
MySQL InnoDB transaction
![Detailed explanation of C language knowledge points -- first understanding of C language [1] - vs2022 debugging skills and code practice [1]](/img/07/c534238c2b5405bbe4655e51cfee51.png)
Detailed explanation of C language knowledge points -- first understanding of C language [1] - vs2022 debugging skills and code practice [1]

如何设计一个良好的API接口?

Openfaas practice 4: template operation
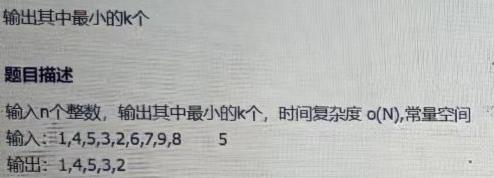
Byte interview programming question: the minimum number of K
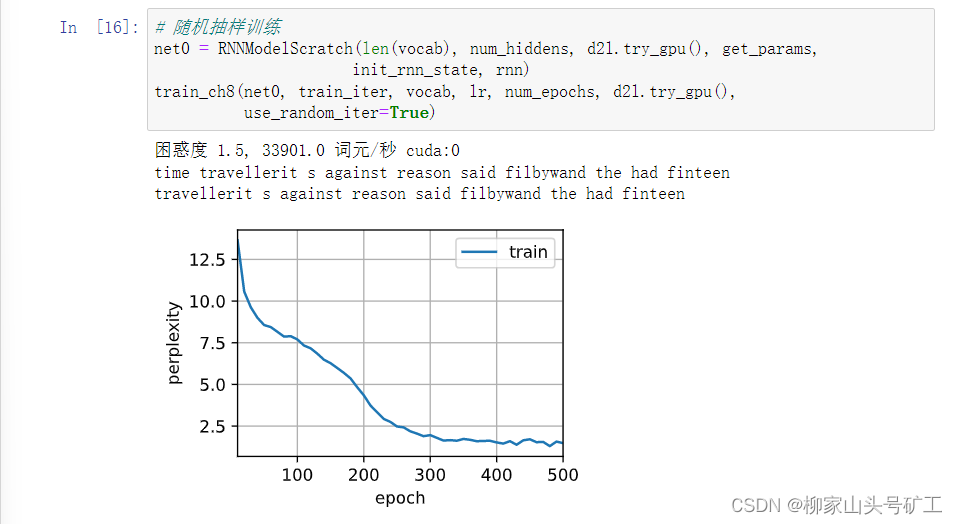
8.4 realization of recurrent neural network from zero
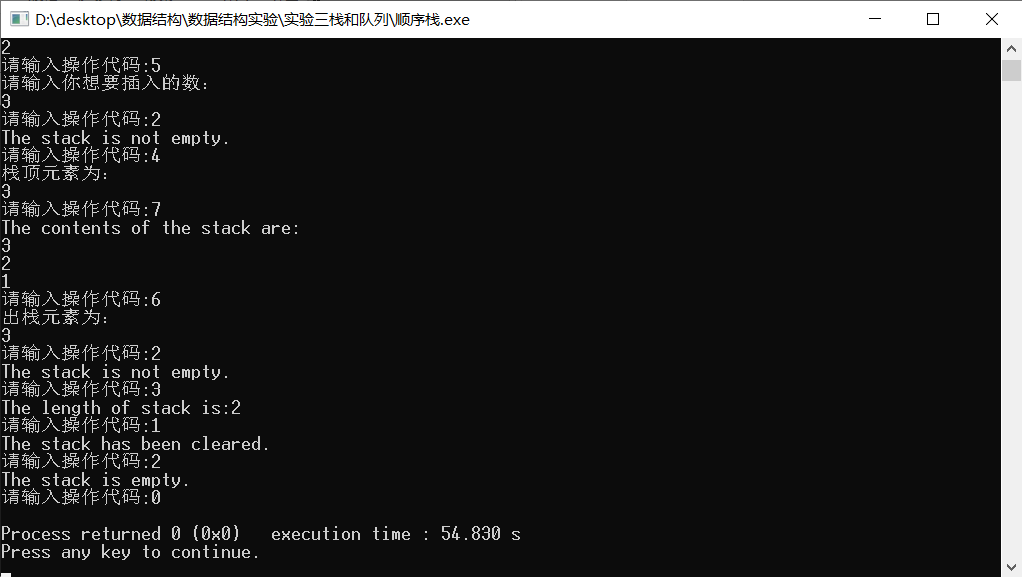
Basic operation of sequential stack
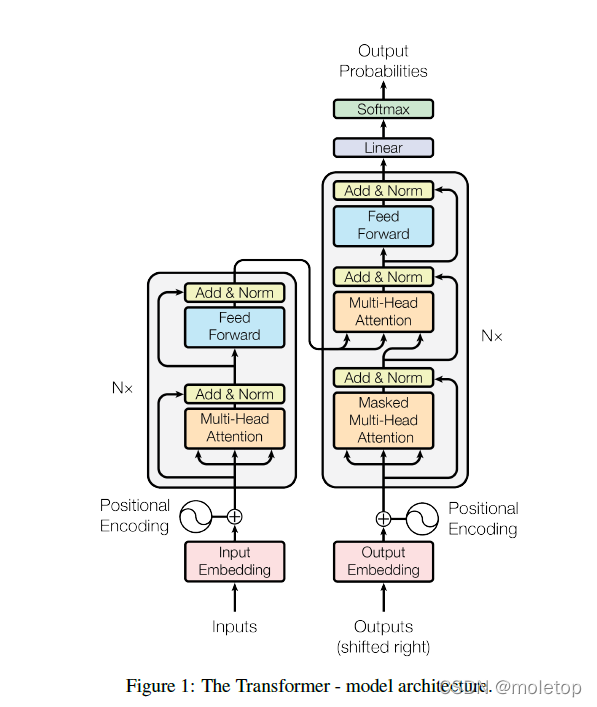
字节面试 transformer相关问题 整理复盘
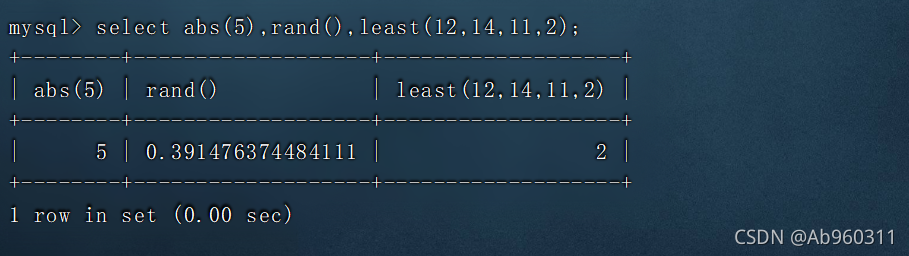
Mysql database explanation (IX)
随机推荐
C语言超全学习路线(收藏让你少走弯路)
C language super complete learning route (collection allows you to avoid detours)
Design of digital temperature monitoring and alarm system based on DS18B20 single chip microcomputer [LCD1602 display + Proteus simulation + C program + paper + key setting, etc.]
木木一路走好呀
C语言超全学习路线(收藏让你少走弯路)
Collation of errors encountered in the use of redis shake
JUC learning record (2022.4.22)
Detailed explanation of kubernetes (IX) -- actual combat of creating pod with resource allocation list
调度系统使用注意事项
API gateway / API gateway (III) - use of Kong - current limiting rate limiting (redis)
Introduction to dirty reading, unrepeatable reading and phantom reading
Async void caused the program to crash
Thinkphp5 + data large screen display effect
Async keyword
ffmpeg安装遇错:nasm/yasm not found or too old. Use --disable-x86asm for a crippled build.
Common interview questions of operating system:
Tencent has written a few words, Ali has written them all for a month
Leetcode学习计划之动态规划入门day3(198,213,740)
Detailed explanation of kubernetes (XI) -- label and label selector
T2 iCloud日历无法同步