当前位置:网站首页>剑指offer专项突击版第26天
剑指offer专项突击版第26天
2022-08-11 07:40:00 【_hys】
直接完成所有元素的排序。
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
sort(nums.rbegin(),nums.rend());
return nums[k-1];
}
};
通过快排思想,无需完成所有元素的排序获得第k大。(算法过程与二分很类似)
- 快排总是根据基准值将数据分成两堆:一堆大于基准值,一堆小于基准值。
- 所以第 k k k 大肯定在其中一堆,另外一堆就可以忽略了。
- 获得第 k k k 大在当前堆中的相对第几大,传到下一次递归中,直到找到第 k k k 大。
class Solution {
public:
int topk(int l,int r, int k, vector<int> &nums) {
//k表示相对位置
if(l >= r) return nums[l];
int i = l-1, j = r+1;
int mid = nums[i+j>>1];
while(i < j) {
do i++; while(nums[i] > mid);
do j--; while(nums[j] < mid);
if(i < j) swap(nums[i],nums[j]);
}
if(k <= j-l) return topk(l, j, k, nums); //注意这里应该是k <= j-l而不是j
else return topk(j+1, r, k-(j-l+1), nums); //j-l+1是l到j的总长
}
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
return topk(0, nums.size()-1, k-1, nums);
}
};
所有排序中归并排序是最适合链表的
1、链表归并自顶向下(递归),空间复杂度 O ( l o g N ) O(logN) O(logN) (多消耗了 l o g N logN logN 个函数栈),这里比较特别的是链表的 m i d mid mid 结点采用快慢指针获取。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* get_mid(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head; //空结点或单结点
ListNode *slow = head, *quick = head;
while(quick->next) {
if(quick->next->next) quick = quick->next->next;
else break;
slow = slow->next;
}
auto mid = slow->next; //相当于/2上取整
slow->next = nullptr; //必须断开
return mid;
}
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
return merge_sort(head, get_mid(head));
}
ListNode* merge_sort(ListNode* l, ListNode *r) {
if(l == r) return l;
ListNode *head = new ListNode(), *tmp = head;
ListNode *i = merge_sort(l,get_mid(l)), *j = merge_sort(r,get_mid(r));
while(i != nullptr && j != nullptr) {
if(i->val < j->val) {
tmp->next = i;
i = i->next;
} else {
tmp->next = j;
j = j->next;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
if(i) tmp->next = i;
if(j) tmp->next = j;
return head->next;
}
};
2、链表归并自底向上(迭代),空间复杂度 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr) {
return head;
}
int length = 0;
ListNode* node = head;
while (node != nullptr) {
length++;
node = node->next;
}
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
for (int subLength = 1; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1) {
ListNode* prev = dummyHead, *curr = dummyHead->next;
while (curr != nullptr) {
ListNode* head1 = curr;
//移动subLength长度
for (int i = 1; i < subLength && curr->next != nullptr; i++) {
curr = curr->next;
}
ListNode* head2 = curr->next;
curr->next = nullptr;
curr = head2;
//移动subLength长度
for (int i = 1; i < subLength && curr != nullptr && curr->next != nullptr; i++) {
curr = curr->next;
}
ListNode* next = nullptr; //下一个需要归并的子序列开始位置
if (curr != nullptr) {
next = curr->next;
curr->next = nullptr;
}
ListNode* merged = merge(head1, head2); //返回有序的链表头
prev->next = merged;
while (prev->next != nullptr) {
//接上有序链表
prev = prev->next;
}
curr = next; //curr移动到下一个需要归并的子序列开始位置
}
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2) {
//无递归
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* temp = dummyHead, *temp1 = head1, *temp2 = head2;
while (temp1 != nullptr && temp2 != nullptr) {
if (temp1->val <= temp2->val) {
temp->next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1->next;
} else {
temp->next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2->next;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
if (temp1 != nullptr) {
temp->next = temp1;
} else if (temp2 != nullptr) {
temp->next = temp2;
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
};
就类似归并排序中的操作,按顺序一个一个合并需要 N N N 次。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
ListNode *res = nullptr;
for(int i = 0; i < lists.size(); i++) {
res = merge(res,lists[i]);
}
return res;
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode* h1, ListNode *h2) {
if(!h1) return h2;
ListNode *res = new ListNode(), *tmp = res;
while(h1 && h2) {
if(h1->val < h2->val) {
tmp->next = h1;
tmp = tmp->next;
h1 = h1->next;
} else {
tmp->next = h2;
tmp = tmp->next;
h2 = h2->next;
}
}
if(h1) tmp->next = h1;
if(h2) tmp->next = h2;
return res->next;
}
};
分治合并,只需要 l o g N logN logN 次合并即可。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* merge_list(ListNode* h1, ListNode *h2) {
if(!h1) return h2;
ListNode *res = new ListNode(), *tmp = res;
while(h1 && h2) {
if(h1->val < h2->val) {
tmp->next = h1;
tmp = tmp->next;
h1 = h1->next;
} else {
tmp->next = h2;
tmp = tmp->next;
h2 = h2->next;
}
}
if(h1) tmp->next = h1;
if(h2) tmp->next = h2;
return res->next;
}
ListNode* merge(vector <ListNode*> &lists, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) return lists[l];
if (l > r) return nullptr;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
return merge_list(merge(lists, l, mid), merge(lists, mid + 1, r));
}
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
return merge(lists, 0, lists.size() - 1);
}
};
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
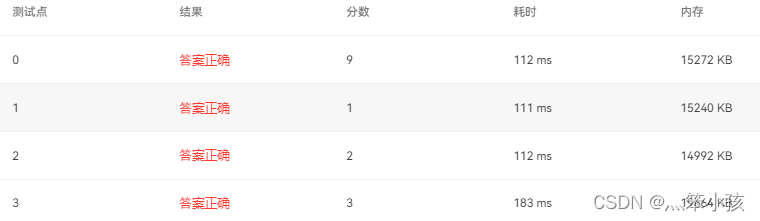
1061 True or False (15 points)

Redis source code: how to view the Redis source code, the order of viewing the Redis source code, the sequence of the source code from the external data structure of Redis to the internal data structu
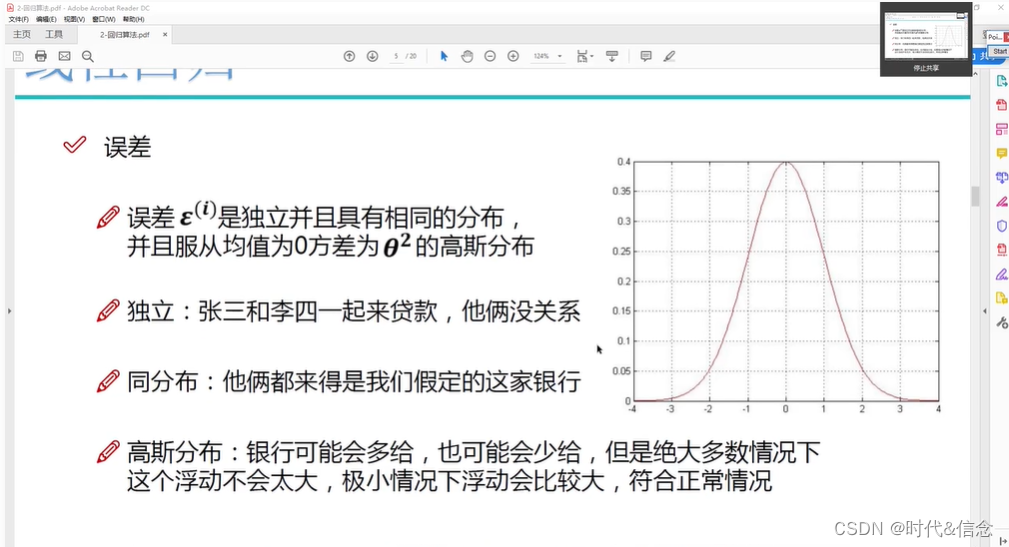
机器学习总结(二)
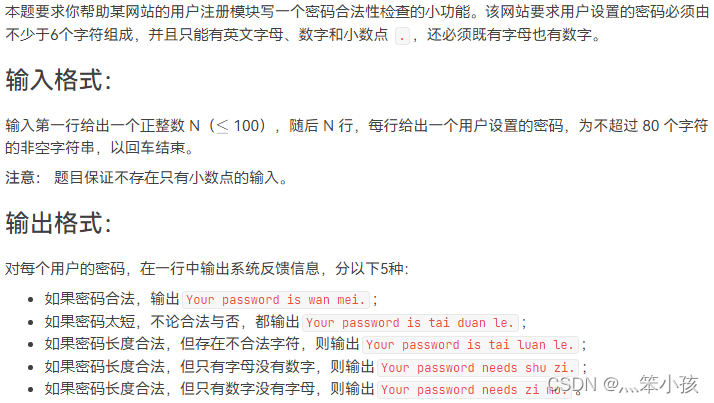
1081 Check Password (15 points)
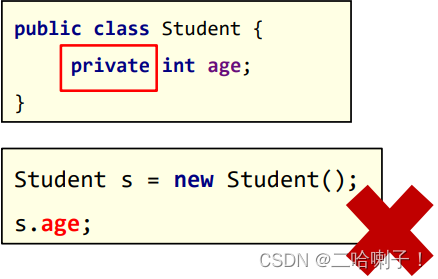
CSDN21天学习挑战赛——封装(06)
1106 2019 Sequence (15 points)

JRS303-Data Verification
租房小程序

求职简历这样写,轻松搞定面试官
关于#sql#的问题:怎么将下面的数据按逗号分隔成多行,以列的形式展示出来
随机推荐
Use tf.argmax in Tensorflow to return the index of the maximum value of the tensor along the specified dimension
Kaldi语音识别工具编译问题记录(踩坑记录)
Dynamic Agent Learning
经典论文-MobileNet V1论文及实践
The softmax function is used in TF;
Activity的四种状态
1046 划拳 (15 分)
1036 跟奥巴马一起编程 (15 分)
1101 How many times B is A (15 points)
Decrement operation in tf; tf.assign_sub()
klayout--导出版图为gds文件
为什么会没有内存了呢
Active users of mobile banking grew rapidly in June, hitting a half-year high
The easiest trick to support quick renaming of various files
Serverless + domain name can also build a personal blog? Really, and soon
Test cases are hard?Just have a hand
关于Excel实现分组求和最全文档
动态代理学习
matrix multiplication in tf
基于微信小程序的租房小程序