当前位置:网站首页>Operators in C language
Operators in C language
2022-04-23 17:55:00 【Chshyz】
C Language operators
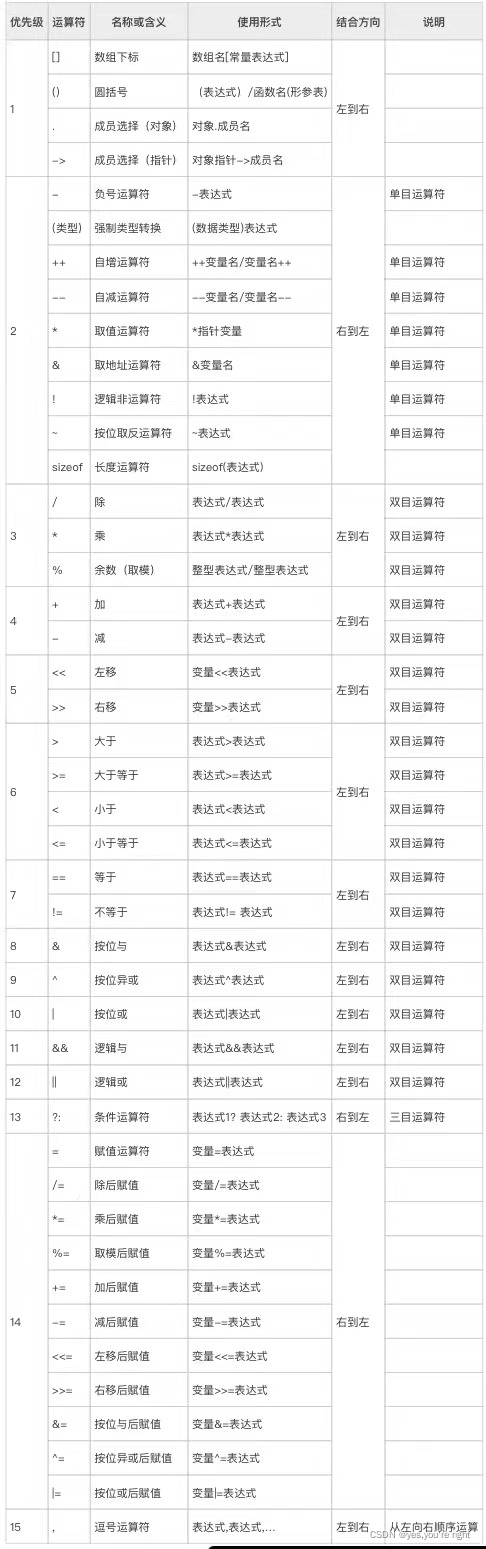
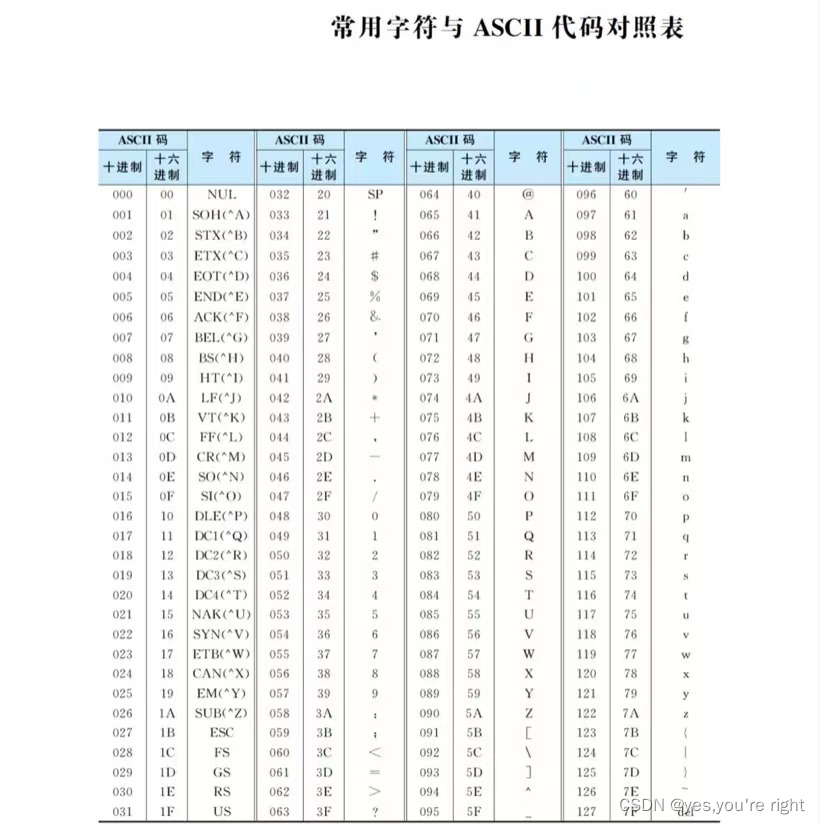
The precedence table of operators and ASCII surface
One 、 Arithmetic operator
- Add (+) reduce (—) ride (*) except (/)
- model ( more than ) Operator (%): Floating point is not allowed , The remainder depends on the divisor
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i, b, a, c;
i= 4, b=3;
a= i+b;
c= i*a;
float p, k;
p= i/b;
k= i%a;
printf("a=%d,c=%d,p=%f,k=%f\n",a,c,p,k);
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# ./o
a=7,c=28,p=1.000000,k=4.000000
- Self increasing (++i,–i;i++,i–)
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i;
i= 4;
printf("%d\n",++i);
return 0;
}
[[email protected]shuyi c]# ./o
5
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i;
i= 4;
printf("%d\n",i--);
//printf("%d\n",i); The output is
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# ./o
4
Two 、 Relational operator
- Greater than (>) Less than (<) be equal to (==)
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b, max;
printf ("please enter a and b\n");
scanf ("%d %d",&a, &b);
if (a>b) max=a;
if (a<b) max=b;
if (a==b) max=a;
printf ("max=%d\n",max);
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# ./o
please enter a and b
55 66
max=66
[[email protected] c]# ./o
please enter a and b
44 44
max=44
- Less than or equal to (<=) Greater than or equal to (>=) It's not equal to (!=) assignment (-=、+=、*=);
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int a = 10;
a +=a *=a -=20;
printf("%d\n",a);
}
[[email protected] c]# ./ass
200
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b, max;
printf ("please enter a and b\n");
scanf ("%d %d",&a, &b);
if (a>=b) max=a;
if (a<=b) max=b;
printf ("max=%d\n",max);
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# ./o
please enter a and b
55 66
max=66
[[email protected] c]# ./o
please enter a and b
77 77
max=77
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b, max;
printf ("please enter a and b\n");
scanf ("%d %d",&a, &b);
if (a!=b);
if (a>b) max=a;
if (a<b) max=b;
printf ("max=%d\n",max);
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# ./o
please enter a and b
44 44
max=0
[[email protected] c]# ./o
please enter a and b
44 55
max=55
3、 ... and 、 Logical operators ( also 、 perhaps 、 Unless )
PS: Priority from top to bottom
- Logic is not (! NOT)
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num = 0;
printf ("Please enter num value: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
if (num != 69) {
printf ("num %d is not equal to 69.\n", num);
}
return 0;
}
~
[[email protected] c]# ./o
Please enter num value: 69
[[email protected] c]# ./o
Please enter num value: 1
num 1 is not equal to 69.
- Logic and (&& AND)
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b, x, y;
printf ("please enter a and b,x and y\n");
scanf ("a=%d,b=%d,x=%d,y=%d",&a, &b, &x, &y);
if (a==b && x==y){
printf ("a=b,x=y\n");
}
else
printf ("sorry,I donot konw.\n");
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# ./o
please enter a and b,x and y
a=1,b=2,x=1,y=1
sorry,I donot konw.
[[email protected] c]# ./o
please enter a and b,x and y
a=1,b=1,x=2,y=2
a=b,x=y
- Logic or (|| OR)
Four 、 An operator
- Move right (>>) Move left (<<)
- Bitwise AND (&)
- Press bit or (|)
- Bitwise XOR (^)
- Take the opposite (~)
5、 ... and 、 Assignment operator
- Equal sign (=)
- Extended assignment operators
+= Add the assignment (a += 3 Equivalent to a = a + 3)
-= Assignment reduction
*= Take the assignment
/= In addition to the assignment
%= Complementary valuation
&= Bitwise and assignment
| = By bit or by assignment
^= Assign values by bitwise exclusive or
<<= Left shift assignment (>>= Right shift assignment )
<> When the right operand is another assignment expression , Form multiple assignment expressions
6、 ... and 、 Conditional operator
PS: Conditional operators take precedence over assignment 、 The comma operator , Lower than other operators .
- Relationship expression ? expression 1 : expression 2
Ternary operator : Conditions ? result 1 : result 2
Example :
Judge a Less than or greater than b, Output Max max
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int a, b, max;
scanf("a=%d,b=%d",&a,&b);
max=a>b?a:b;
printf("max=%d\n",max);
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# gcc -o swap swap.c
[[email protected] c]# ./swap
a=2,b=3
max=3
7、 ... and 、 The comma operator (,)
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int i = 1;
int a = (i+100,i++,i);
printf("%d\n",a);
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# ./comma
2
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int i = 1;
int a = (i=i+100,i++,i);
printf("%d\n",a);
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# ./comma
102
8、 ... and 、 Pointer operator
- Pointer to the variable (*)
Definition : Base type * Pointer variable name ;
Example 1: Access integer variables through pointer variables
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b; # Define two int Variable
int * pointer_1, * pointer_2; # Define two pointer variables , Point to int Variable
a = 100; b = 10;
pointer_1 = &a; # Put variables a To the pointer pointer_1
pointer_2 = &b;
printf ("a = %d, b = %d \n", a, b);
printf (" * pointer_1 = %d, * pointer_2 = %d \n", * pointer_1, * pointer_2); # The value of the integer variable pointed to by the output pointer variable
return 0;
}
~
[[email protected] c]# gcc -o pointer1 pointer1.c
[[email protected] c]# ./pointer1
a = 100, b = 10
* pointer_1 = 100, * pointer_2 = 10
[[email protected] c]# vi pointer1.c
Example 2: Than the size
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
int * p1, * p2, * p, a, b;
scanf ("%d, %d", &a, &b);
p1 = &a; p2 = &b;
if (a < b) {
p = p1; p1 = p2; p2 = p;
}
printf ("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
printf ("max = %d, min = %d\n", * p1, * p2);
return 0;
}
r
[[email protected] c]# ./pointer2
4,6
a = 4, b = 6
max = 6, min = 4
Example 3: The arithmetic
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
int maxsum = 123;
double temp = 888.8889922111111;
temp += (float)maxsum;
printf ("%7.3f, %d\n", (float)temp, (int)temp);
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# gcc -o compulsion compulsion.c
[[email protected] c]# ./compulsion
1011.889, 1011
Nine 、 Find byte operator (sizeof)
- When sizeof( And data types ( Such as int,float,char … etc. ) When used together , Returns the amount of memory allocated to the data type .
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d\n",sizeof(char));
printf("%d\n",sizeof(int));
printf("%d\n",sizeof(float));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(double));
return 0;
}
- When sizeof When used with expressions , Returns the size of the expression .
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 1, b = 3;
printf ("%d\n", sizeof ( a + b ));
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# gcc -o sizeof1 sizeof1.c
[[email protected] c]# ./sizeof1
4
Ten 、 Cast operators
example 1: Decimal to integer
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
float f = 8.88;
int i;
i = (int) f;
printf ("f = %f, i = %d \n", f, i);
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# gcc -o compulsion compulsion.c
[[email protected] c]# ./compulsion
f = 8.880000, i = 8
example 2: Integer to decimal
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
int maxsum = 123;
printf ("%lf\n", (double) maxsum);
return 0;
}
[[email protected] c]# gcc -o compulsion compulsion.c
[[email protected] c]# ./compulsion
123.000000
11、 ... and 、 member operator
- member operator (.)
- Indirect member operator (–>)
Twelve 、 Subscript operator ([ ])
PS: Precedence and associativity of operators
版权声明
本文为[Chshyz]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230547413924.html
边栏推荐
- Dry goods | how to extract thumbnails quickly?
- The JS timestamp of wechat applet is converted to / 1000 seconds. After six hours and one day, this Friday option calculates the time
- 394. String decoding - auxiliary stack
- Summary of common server error codes
- 209. Minimum length subarray - sliding window
- .104History
- JS parsing and execution process
- 587. 安装栅栏 / 剑指 Offer II 014. 字符串中的变位词
- On the method of outputting the complete name of typeID from GCC
- Submit local warehouse and synchronize code cloud warehouse
猜你喜欢
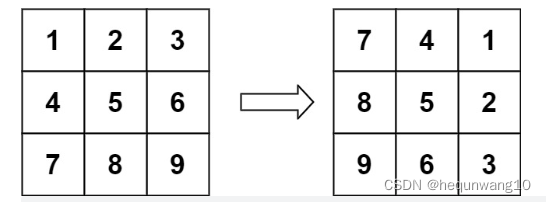
48. 旋转图像

Compilation principle first set follow set select set prediction analysis table to judge whether the symbol string conforms to the grammar definition (with source code!!!)
![[appium] write scripts by designing Keyword Driven files](/img/05/536701f39dcf8474e90e58738f2094.png)
[appium] write scripts by designing Keyword Driven files

2022江西储能技术展会,中国电池展,动力电池展,燃料电池展

C#的随机数生成

Hcip fifth experiment

Go language JSON package usage

云原生虚拟化:基于 Kubevirt 构建边缘计算实例
Applet learning notes (I)

In JS, t, = > Analysis of
随机推荐
239. Maximum value of sliding window (difficult) - one-way queue, large top heap - byte skipping high frequency problem
C#字节数组(byte[])和字符串相互转换
Use of list - addition, deletion, modification and query
Fashion classification case based on keras
Remember using Ali Font Icon Library for the first time
Future usage details
ros常用的函数——ros::ok(),ros::Rate,ros::spin()和ros::spinOnce()
Logic regression principle and code implementation
Go语言JSON包使用
Anchor location - how to set the distance between the anchor and the top of the page. The anchor is located and offset from the top
undefined reference to `Nabo::NearestNeighbourSearch
.105Location
Open source key component multi_ Button use, including test engineering
[binary number] maximum depth of binary tree + maximum depth of n-ary tree
On the method of outputting the complete name of typeID from GCC
纳米技术+AI赋能蛋白质组学|珞米生命科技完成近千万美元融资
MySQL 中的字符串函数
Element calculation distance and event object
2022年茶艺师(初级)考试模拟100题及模拟考试
Notes on common basic usage of eigen Library