当前位置:网站首页>Have you learned the basic operation of circular queue?
Have you learned the basic operation of circular queue?
2022-04-23 15:03:00 【White folding fan y】
Newcomer Xiaobai's first blog
️ I hope you will pay more attention
It will be updated frequently in the future ~️ Personal home page : Collection and attention , Never get lost ~ ️
Preface
Tips: It's a little long , Little Lord, be patient ~
Programming to achieve the basic operation of circular queue : Build a queue , Take the team leader element , The team , Out of the team
One 、 What is a circular queue ?
1️⃣ Let's first introduce the linear table : The data structure is divided into linear structure and nonlinear structure , Queues and linear tables are linear structures . The linear table is written by n A finite sequence of data elements , The sequence has a unique “ first ” And unique “ the last one ” data elements ; except “ first ” and “ the last one ” outside , Each data element in the queue has only one direct precursor and one direct successor . The insertion and deletion of a linear table can be performed anywhere in the table .
2️⃣ Let's talk about the queue : A queue is a special kind of linear table , What's special about this is that it's only allowed at the front of the table (front) Delete operation , And at the back end of the table (rear) Insert operation . Like the stack , A queue is a linear table with restricted operations . The end of the insertion operation is called the tail of the queue , The end of the delete operation is called the queue head . When there are no elements in the queue , Called an empty queue .
3️⃣ Related concepts of queue : The data elements of a queue are called queue elements . Inserting a queue element into a queue is called queuing , Deleting a queue element from a queue is called out of queue . Because queues can only be inserted at one end , Delete... At the other end , So only the first elements to enter the queue can be deleted from the queue first , So the queue is also called first in, first out (FIFO—first in first out) The linear table .
4️⃣ Why do you have a circular queue : In order to make full use of vector space , Overcome " False spillover " The method of phenomenon is : Think of a vector space as a ring with its head and tail connected , And call this vector a cyclic vector . The queues stored in it are called circular queues (Circular Queue). A circular queue is a sequential queue connected end to end , Look at the table that stores the queue elements logically as a ring , It's called a circular queue .
5️⃣ Related characteristics of circular queue : In the circular queue structure , When the last position of the storage space has been used and it is necessary to enter the queue operation , Only the first location of the storage space is free , You can add the element to the first position , The first location of the storage space will be used as the tail of the team . Circular queues can more easily prevent pseudo overflow , But the queue size is fixed .
Two 、 Defined function
1. Define the storage structure
// Storage structure of circular queue
#define MAXQSIZE 100 // Maximum queue length
typedef struct
{
QElemType *base; // Used to dynamically allocate storage space
int front; // Team leader index
int rear; // End of team index
} SqQueue;
2. initialization
// initialization
void InitQueue (SqQueue &Q)
{
// Construct an empty queue
Q.base =new QElemType[MAXQSIZE];
Q.front=Q.rear=0;
}
3. Destroy queue
// Destroy queue
void DestroyQueue(SqQueue &Q)
{
if(Q.base)
free(Q.base);
Q.base = NULL;
Q.front = Q.rear = 0;
}
4. Clear queue
// Clear queue
void ClearQueue(SqQueue &Q)
{
Q.front=Q.rear=0;
}
5. Find the length
// Find the length
int QueueLength (SqQueue Q)
{
return (Q.rear-Q.front+MAXQSIZE)%MAXQSIZE;
}
6. Sentenced to empty
// Sentenced to empty
bool QueueEmpty (SqQueue Q)
{
return (Q.front==Q.rear);
}
7. Find the team head element
// Find the team head element
Status GetHead (SqQueue Q, QElemType &e)
{
if(Q.front==Q.rear) return ERROR;
e=Q.base[Q.front];
return OK;
}
8. Loop queue in
// Loop queue in
Status EnQueue(SqQueue &Q,QElemType e)
{
if((Q.rear+1)%MAXQSIZE==Q.front) return ERROR;
Q.base[Q.rear]=e;
Q.rear = (Q.rear+1) % MAXQSIZE;
return OK;
}
9. Loop queue out
// Loop queue out
Status DeQueue (SqQueue &Q,QElemType &e)
{
if(Q.front==Q.rear) return ERROR;
e=Q.base[Q.front];
Q.front=(Q.front+1) % MAXQSIZE;
return OK;
}
10. Traversal causes the queue to display
// Traversal causes the queue to display
void DisplayQueue(SqQueue Q)
{
int i=Q.front;
while(Q.front!=Q.rear && (i+MAXQSIZE) % MAXQSIZE != Q.rear)
{
cout<<Q.base[i]<<endl;
i++;
}
}
3、 ... and 、 Define small menus
You can use a small menu to make the interface more beautiful ~
void show_help()
{
cout<<"******* Data Structure ******"<<endl;
cout<<"1---- Empty the circular queue "<<endl;
cout<<"2---- Determine whether the circular queue is empty "<<endl;
cout<<"3---- Find the length of the loop queue "<<endl;
cout<<"4---- Take the team leader element "<<endl;
cout<<"5---- The team "<<endl;
cout<<"6---- Out of the team "<<endl;
cout<<"7---- Show queue "<<endl;
cout<<" sign out , Input 0"<<endl;
}
Four 、 Complete code
️️️
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define ERROR -1
#define OK 1
typedef int QElemType;
typedef int Status;
// Storage structure of circular queue
#define MAXQSIZE 100 // Maximum queue length
typedef struct
{
QElemType *base; // Used to dynamically allocate storage space
int front; // Team leader index
int rear; // End of team index
} SqQueue;
// initialization
void InitQueue (SqQueue &Q)
{
// Construct an empty queue
Q.base =new QElemType[MAXQSIZE];
Q.front=Q.rear=0;
}
// Destroy queue
void DestroyQueue(SqQueue &Q)
{
if(Q.base)
free(Q.base);
Q.base = NULL;
Q.front = Q.rear = 0;
}
// Clear queue
void ClearQueue(SqQueue &Q)
{
Q.front=Q.rear=0;
}
// Find the length
int QueueLength (SqQueue Q)
{
return (Q.rear-Q.front+MAXQSIZE)%MAXQSIZE;
}
// Sentenced to empty
bool QueueEmpty (SqQueue Q)
{
return (Q.front==Q.rear);
}
// Find the team head element
Status GetHead (SqQueue Q, QElemType &e)
{
if(Q.front==Q.rear) return ERROR;
e=Q.base[Q.front];
return OK;
}
// Loop queue in
Status EnQueue(SqQueue &Q,QElemType e)
{
if((Q.rear+1)%MAXQSIZE==Q.front) return ERROR;
Q.base[Q.rear]=e;
Q.rear = (Q.rear+1) % MAXQSIZE;
return OK;
}
// Loop queue out
Status DeQueue (SqQueue &Q,QElemType &e)
{
if(Q.front==Q.rear) return ERROR;
e=Q.base[Q.front];
Q.front=(Q.front+1) % MAXQSIZE;
return OK;
}
// Traversal causes the queue to display
void DisplayQueue(SqQueue Q)
{
int i=Q.front;
while(Q.front!=Q.rear && (i+MAXQSIZE) % MAXQSIZE != Q.rear)
{
cout<<Q.base[i]<<endl;
i++;
}
}
void show_help()
{
cout<<"******* Data Structure ******"<<endl;
cout<<"1---- Empty the circular queue "<<endl;
cout<<"2---- Determine whether the circular queue is empty "<<endl;
cout<<"3---- Find the length of the loop queue "<<endl;
cout<<"4---- Take the team leader element "<<endl;
cout<<"5---- The team "<<endl;
cout<<"6---- Out of the team "<<endl;
cout<<"7---- Show queue "<<endl;
cout<<" sign out , Input 0"<<endl;
}
int main()
{
char operate_code;
show_help();
SqQueue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
QElemType e;
int i;
while(1)
{
cout<<" Please enter the operation code :";
cin>>operate_code;
if(operate_code=='1')
{
cout<<"The queue has been cleared."<<endl;
ClearQueue(Q);
}
else if (operate_code=='2')
{
if(QueueEmpty(Q))
cout<<"The queue is empty."<<endl;
else
cout<<"The queue is not empty."<<endl;
}
else if (operate_code=='3')
{
cout<<"The length of queue is:"<<QueueLength(Q)<<endl;
}
else if (operate_code=='4')
{
cout<<" The team leader element is :"<<endl;
if(GetHead(Q,e) == 1) cout<<e<<endl;
else cout <<"error"<<endl;
}
else if (operate_code=='5')
{
cout<<" Please enter the number of you want to join the team :"<<endl;
cin>>e;
EnQueue(Q,e);
}
else if (operate_code=='6')
{
cout<<" The outgoing element is :"<<endl;
if(DeQueue(Q,e)) cout<<e<<endl;
}
else if (operate_code=='7')
{
cout<<"The contents of the queue are:"<<endl;
DisplayQueue(Q);
}
else if (operate_code=='0')
{
break;
}
else
{
cout<<"\n Opcode error !!!"<<endl;
show_help();
}
}
// Call the destroy stack function
DestroyQueue(Q);
return 0;
}
5、 ... and 、 Running results
️️️

summary
This paper is used to introduce the code implementation process and running result example of circular queue in data structure . The initialization of the circular queue is displayed in menu style 、 Empty 、 The destruction 、 Find the length , Find the team head element 、 Sentenced to empty 、 The team , Out of the team , And traversing the queue to make it display .

版权声明
本文为[White folding fan y]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231410400560.html
边栏推荐
- Introduction to Arduino for esp8266 serial port function
- 8.3 language model and data set
- Share 20 tips for ES6 that should not be missed
- Redis主从同步
- 你还不知道责任链模式的使用场景吗?
- 小红书 timestamp2 (2022/04/22)
- QT Detailed explanation of pro file
- Pnpm installation and use
- For 22 years, you didn't know the file contained vulnerabilities?
- Progress in the treatment of depression
猜你喜欢

Leetcode exercise - 396 Rotation function
22年了你还不知道文件包含漏洞?
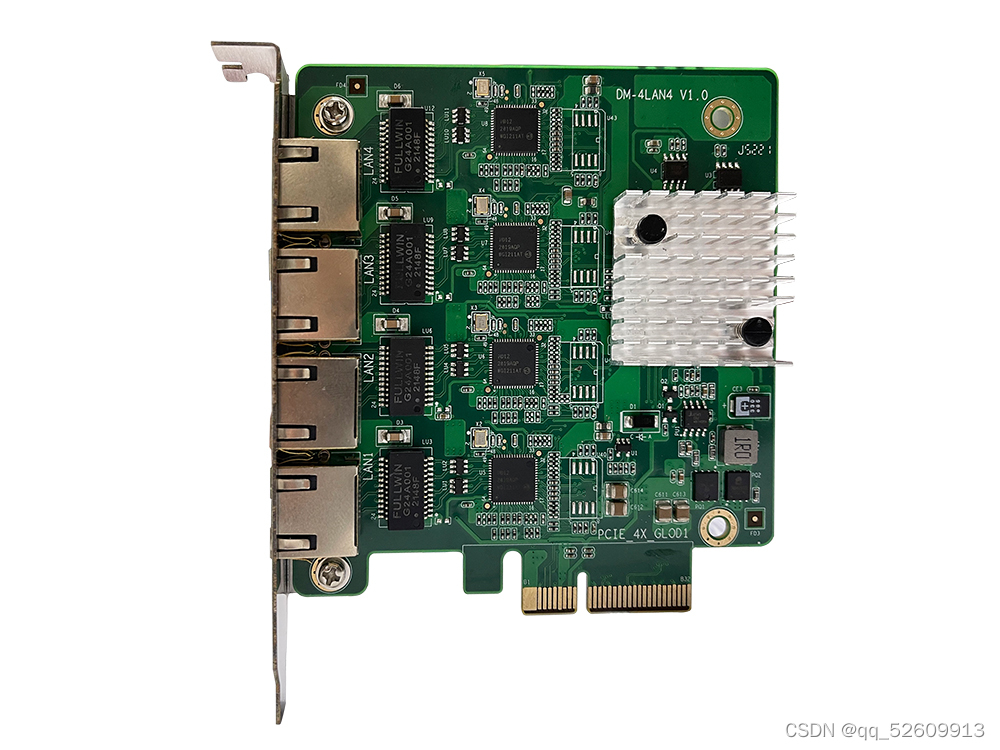

What is the main purpose of PCIe X1 slot?

LeetCode165-比较版本号-双指针-字符串
分享 20 个不容错过的 ES6 的技巧
eolink 如何助力遠程辦公
win10 任务栏通知区图标不见了
Nuxt project: Global get process Env information

For 22 years, you didn't know the file contained vulnerabilities?
Set onedrive or Google drive as a drawing bed in upic for free
随机推荐
C语言超全学习路线(收藏让你少走弯路)
Unity_ Code mode add binding button click event
博睿数据携手F5共同构建金融科技从代码到用户的全数据链DNA
do(Local scope)、初始化器、内存冲突、Swift指针、inout、unsafepointer、unsafeBitCast、successor、
解决computed属性与input的blur事件冲突问题
剑指 Offer II 019. 最多删除一个字符得到回文(简单)
Select receives both normal data and out of band data
Nuxt project: Global get process Env information
How do I open the win10 startup folder?
Borui data and F5 jointly build the full data chain DNA of financial technology from code to user
Provided by Chengdu control panel design_ It's detailed_ Introduction to the definition, compilation and quotation of single chip microcomputer program header file
Svn detailed use tutorial
8.5 concise implementation of cyclic neural network
js——實現點擊複制功能
Using MATLAB programming to realize the steepest descent method to solve unconstrained optimization problems
How to write the keywords in the cover and title? As we media, why is there no video playback
分享3个使用工具,在家剪辑5个作品挣了400多
Realization of four data flow modes of grpc based on Multilingual Communication
What is the role of the full connection layer?
Explain TCP's three handshakes in detail