当前位置:网站首页>Explain TCP's three handshakes in detail
Explain TCP's three handshakes in detail
2022-04-23 14:45:00 【Luo Luo's 1024】
TCP Definition and characteristics
Definition
TCP It's connection-oriented ( Connection oriented ) Of 、 Reliable transport layer communication protocol based on byte stream .TCP Package user data into report segments , After sending, a timer will be started , Then confirm the data received at the other end 、 Reorder out of order data 、 Discard duplicate data
characteristic
- TCP Is a connection oriented transport control layer protocol
- Every one of them TCP Connections can have only two endpoints , Every one of them TCP Connections can only be point-to-point
- TCP Provide reliable delivery of services
- TCP Provide full duplex communication . Data is transmitted independently in both directions , therefore , Each end of the connection must maintain the serial number of the transmitted data in each direction .
- Byte stream oriented . For the meaning of byte stream : Although the application and TCP Interaction is a block of data at a time , But the data handed over by the application is just a series of unstructured byte streams
TCP message
Before starting three handshakes , look down TCP Data structure of message
- TCP The first one
- TCP Data section

Focus on TCP Head structure , as follows
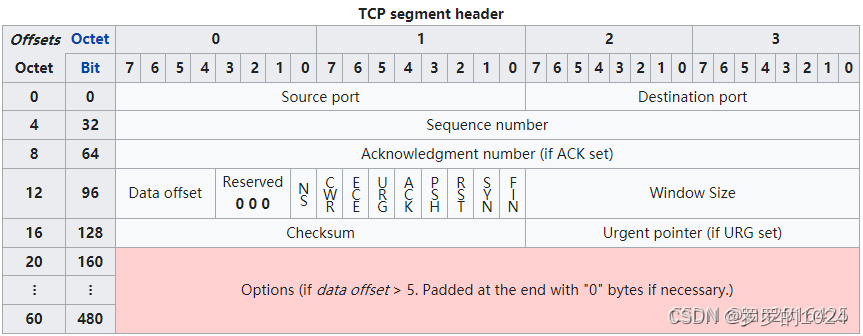
Find out what serial number and confirmation number are
- Sequence number
It means that we ( The sender ) here , This packet The first place in the data part of should be in the whole data stream The location of the .( Pay attention to the use of “ should ”. Because for transmission without data , Such as ACK, Although it has a seq, But this transmission is throughout data stream It doesn't take up a place in . So the next actual data transmission , Will still be sent from the last time ACK Of data packets seq Start )
- Acknowledge number
It means expecting the other party ( The receiving party ) Next time sequence number How much is the
Three handshakes
Three handshakes (Three-way Handshake) In fact, it means building a TCP When the connection , Need client and server to send in total 3 A package . The main purpose of three handshakes is to confirm whether the receiving and sending capabilities of both parties are normal 、 Specify your own initialization serial number to prepare for later reliable transfer .
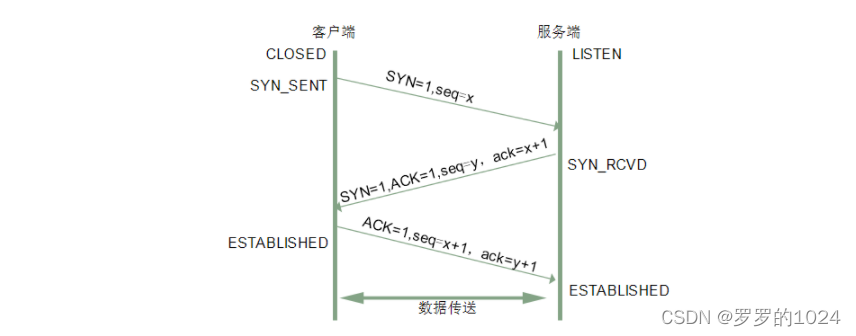
The first handshake : Sign a SYN = 1, Randomly generate a serial number seq1 = x
The second handshake : Sign a SYN ,ACK = 1, Confirmation no. ack = x + 1, Randomly generate a serial number seq2=y
The third handshake : Sign a ACK = 1, Confirmation no. ack = y + 1,seq2= x + 1
SYN/FIN Although there is no data, But the next transmission will packet seq Add a , however , about ACK The transmission of , Won't let the next transmission packet Add one , in other words , The next actual data transmission , Still sent from the last time ACK Of data packets seq Start calculating
Network packet capture analysis
The specific connection process is given above , But partial theory , Let's have a real fight , Analysis through packet capture
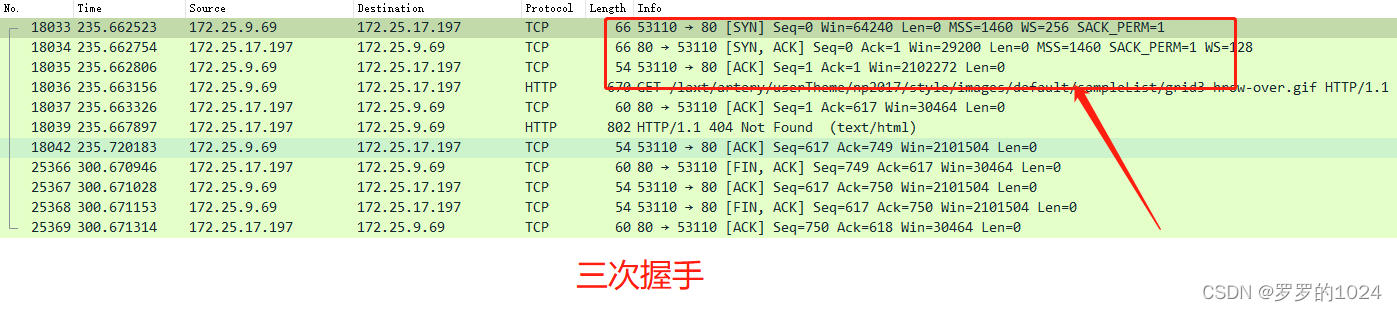
See what you do with each handshake ( It mainly depends on the serial number , Confirmation no. )
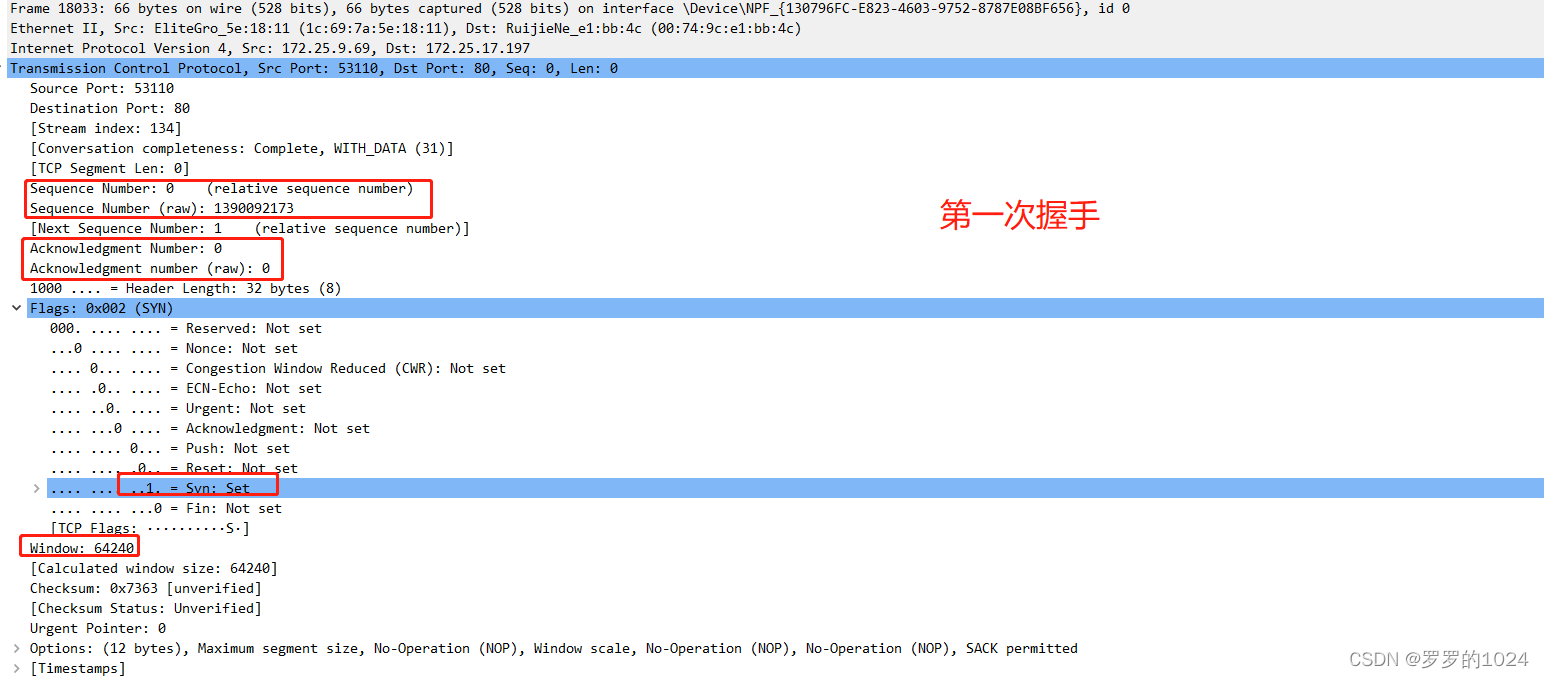
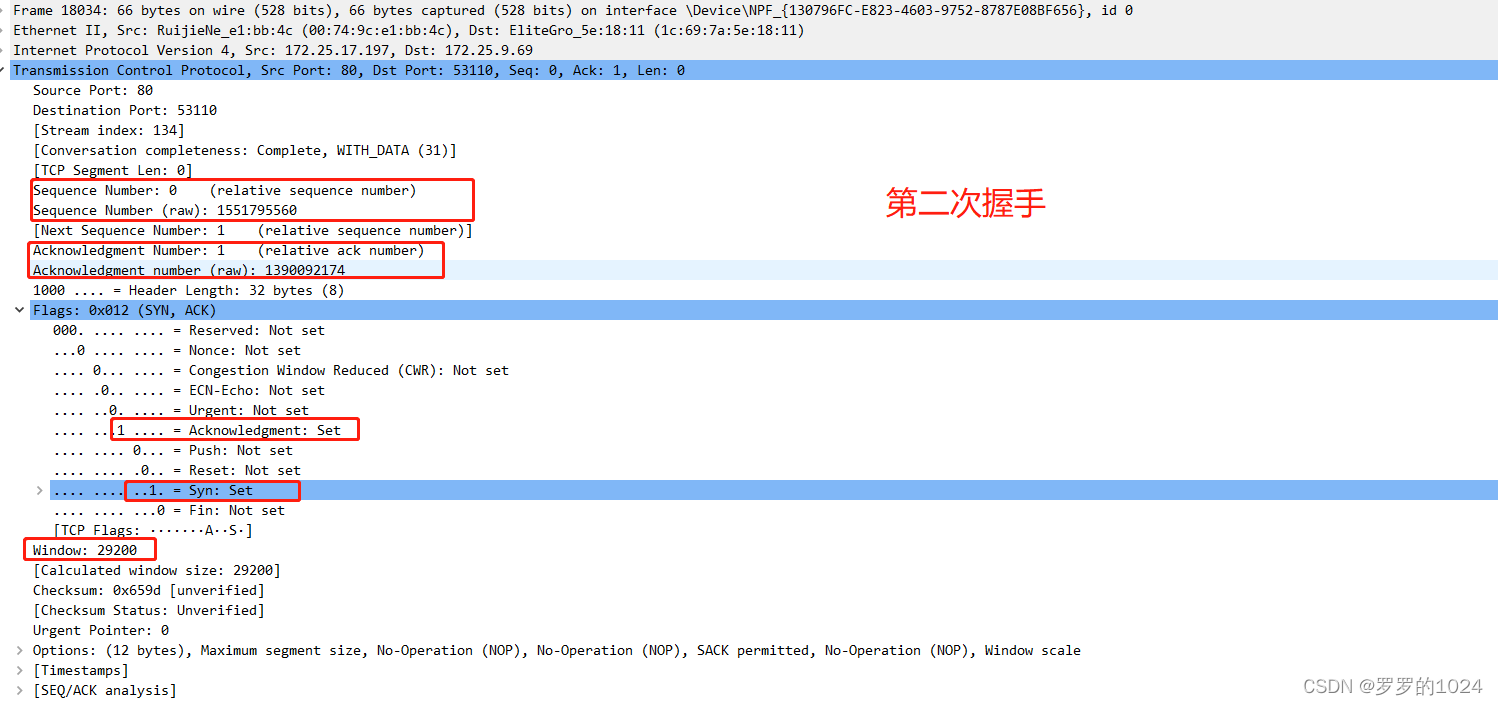
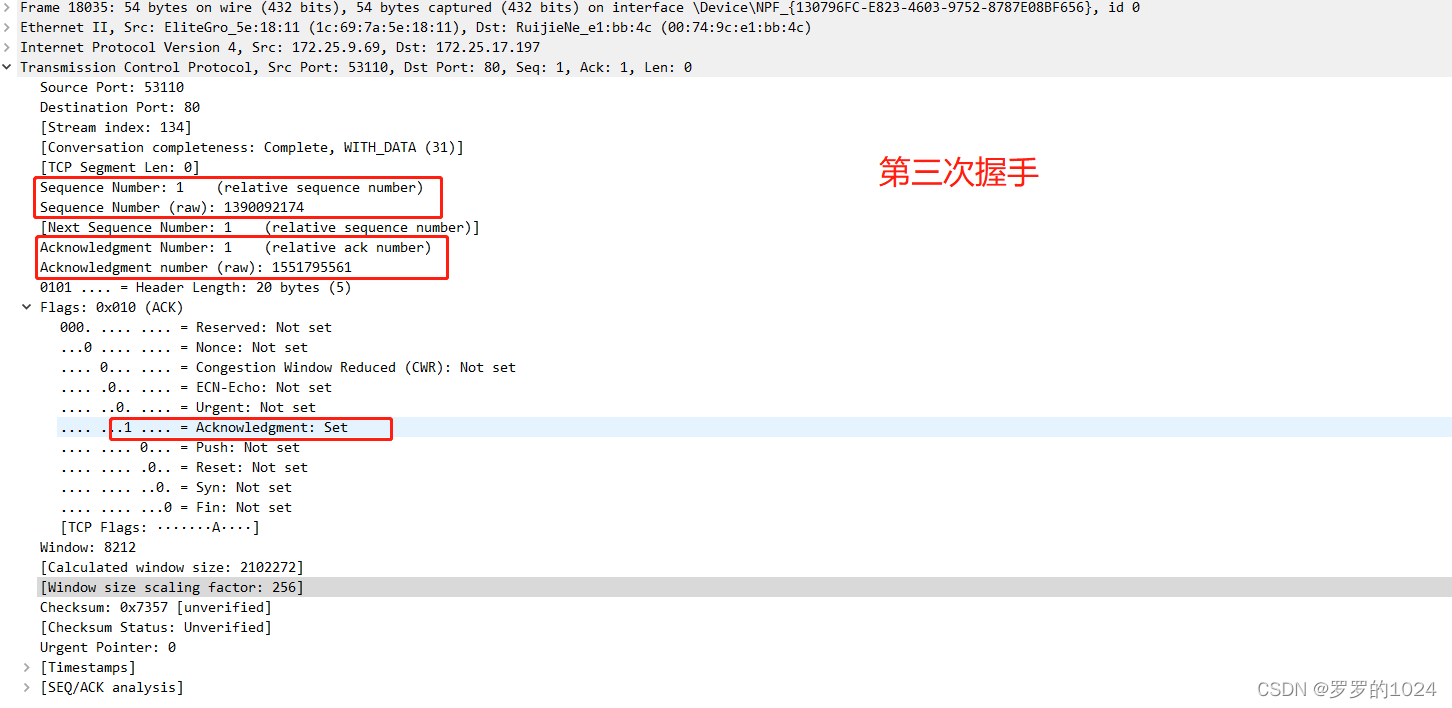
There's a picture, there's a truth , I'm not afraid you don't believe it
Reference link :https://www.jianshu.com/p/15754b4e9458
common problem
Question 1 : Why not two handshakes , It's three handshakes
In the first two handshakes, the client can confirm that the reception and transmission of the server are normal ( One back and forth ), However, the server does not know whether the sending ability of the client is normal , that TCP It's impossible to talk about the reliability of , So we need a third handshake to confirm the sending and receiving ability of both sides , In order to ensure that TCP Reliability of connection .
Question two :TCP Can all three handshakes carry data ? If not , So which handshake can carry data , Why can't others carry data ?
Suppose the first handshake, the client carries data to the server , The server parses and stores the connection information , If you have a lot of data , The server should allocate enough memory for storage , If there are hackers while(1000000000) To create a new connection , The result is predictable , The server will take up a lot of memory .
The third handshake , At this point, for the client , Connection established , There is no problem for the client to carry data
Question 3 : In transit , What if the message is lost
- The first handshake message is lost
The client sends SYN message , And then into SYN_SENT state .
The client fails to receive the information from the server SYN-ACK message , It will trigger the timeout retransmission mechanism of the client .
stay Linux in , Client's SYN The maximum number of retransmissions of the message is determined by /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_syn_retries Kernel parameter control , This parameter can be customized , The default value is usually 5. Each timeout is the last time 2 times . When the fifth timeout retransmission , Will continue to wait 32 second , If the server still does not respond ACK, The client will no longer send SYN package , Then disconnect TCP Connect .
- The second handshake message is lost
The second handshake , The server will enter SYN_RCVD state
Client angle : The message sent by the client's first handshake did not get a reply , Then the client will feel its own SYN Message lost , Then the client will trigger the timeout retransmission mechanism , Retransmission SYN message .
Server angle : send out SYN_ACK A timer will be started after the message , If the message is not answered , The timeout retransmission mechanism will be triggered , Retransmission SYN-ACK message , The number of retransmissions is determined by /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_synack_retries control , The default is 5 Time .
- The third handshake message is lost
Server angle : send out SYN_ACK A timer will be started after the message , If the time set by the timer is exceeded, the client does not receive ACK, It will be reissued SYN_ACK package . from /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_synack_retries control , The default is 5 Time .
Client angle : Wound up , Now I am ACK message , Have unique permissions , So I won't repeat it
Question 4 : When the message fails or is discarded
- The semi connection queue of the server (syns quene) Full of , The client has been timeout retransmission SYN message , Until the maximum number of retransmissions is reached
- The connection queue of the server (accept quene) Full of
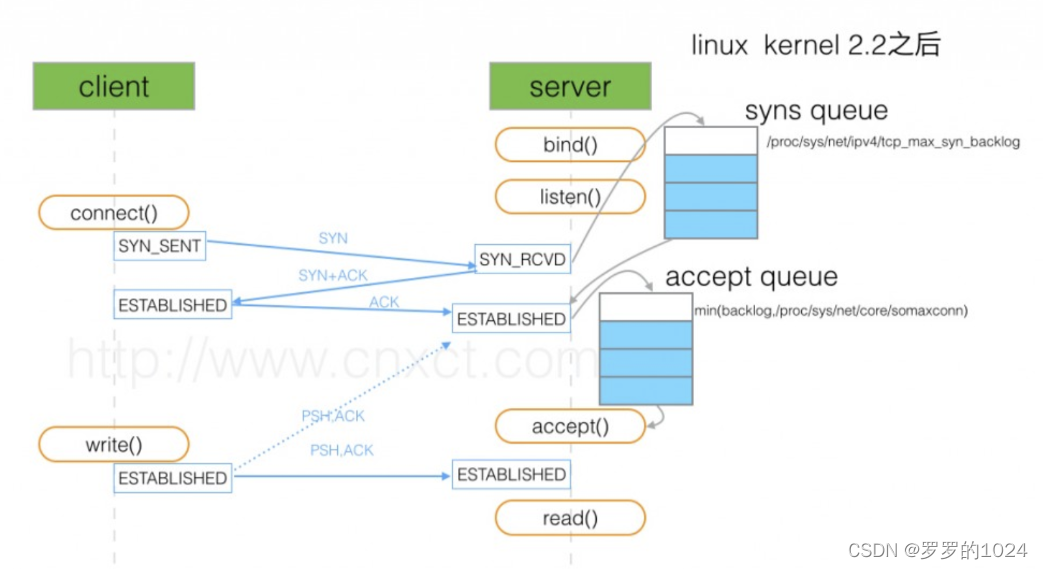
TCP Full connection and semi connection queues
When called by the server listen() When the function listens to the port , The kernel will listen for each socket Create two queues
- Semi connected queues (syn queue): The client sends SYN package , The server will reply after receiving it SYN+ACK after , Server access SYN_RCVD state , At this time socket Will be placed in the semi connected queue .
- Full connection queue (accept queue): When the server receives the ACK after ,socket It will be moved from the semi connected queue to the full connected queue . When calling accpet Function , The available... Is returned from the head of the full connection queue socket Give the user process .
stay 4.3 Kernel before version ,SYN The maximum size of the queue used to be
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlogTo configure the , But it's no longer used .
Now usenet.core.somaxconnTo represent at the same time SYN Queue and Accept The maximum size of the queue
View a port ( That is, a service ) The connection condition of
ss command
ss yes Socket Statistics Abbreviation . seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function ,ss Commands can be used to get socket Statistics , It can show and netstat Similar content .ss The advantage is that it can show more details about TCP And connection status information , And ratio netstat Faster and more efficient .
# ss
Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
tcp ESTAB 0 0 10.0.2.10:ssh 10.0.2.2:52316
Recv-Q: Semi connected queues
Send-Q: Full connection queue
版权声明
本文为[Luo Luo's 1024]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231426114313.html
边栏推荐
- Swift: entry of program, swift calls OC@_ silgen_ Name, OC calls swift, dynamic, string, substring
- 基于TLC5615的多路可调数控直流稳压电源,51单片机,含Proteus仿真和C代码等
- MySQL error packet out of order
- Matlab Simulink modeling and design of single-phase AC-AC frequency converter, with MATLAB simulation, PPT and papers
- 面试官:说一下类加载的过程以及类加载的机制(双亲委派机制)
- 51 Single Chip Microcomputer Design of traffic light system (with Proteus simulation, C program, schematic diagram, PCB, thesis and other complete data)
- 解决computed属性与input的blur事件冲突问题
- 全连接层的作用是什么?
- Sword finger offer II 019 Delete at most one character to get palindrome (simple)
- Contraction mapping theorem
猜你喜欢
8.5 循环神经网络简洁实现
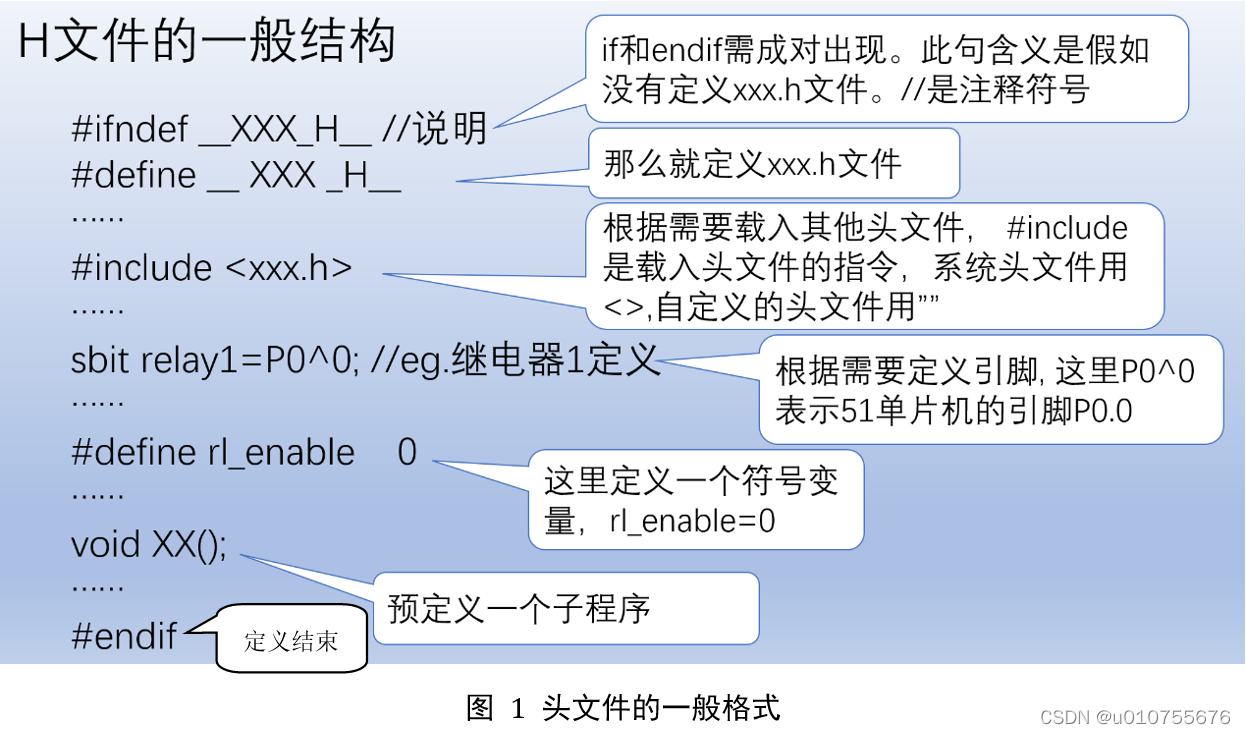
Provided by Chengdu control panel design_ It's detailed_ Introduction to the definition, compilation and quotation of single chip microcomputer program header file
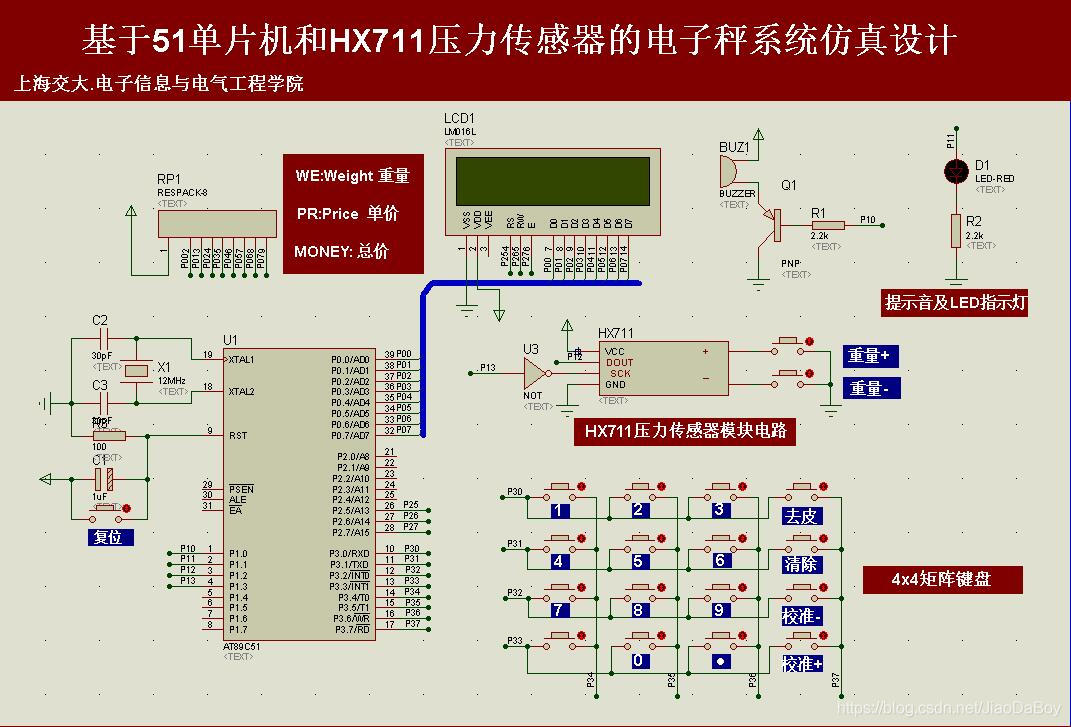
电子秤称重系统设计,HX711压力传感器,51单片机(Proteus仿真、C程序、原理图、论文等全套资料)

Swift:Entry of program、Swift调用OC、@_silgen_name 、 OC 调用Swift、dynamic、String、Substring
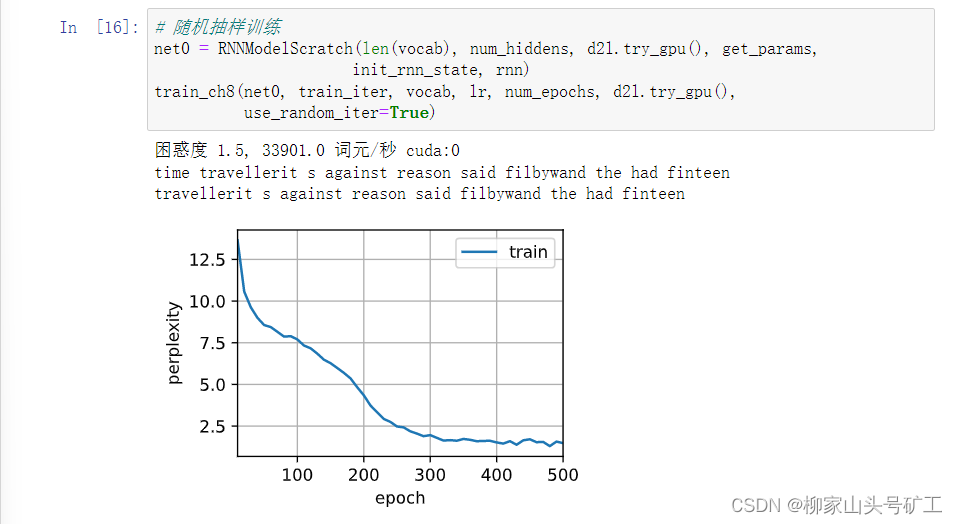
8.4 循环神经网络从零实现

DS1302的电子万年历_51单片机,年月日、星期、时分秒、农历和温度,带闹钟,全套资料

Detailed explanation of SAR command
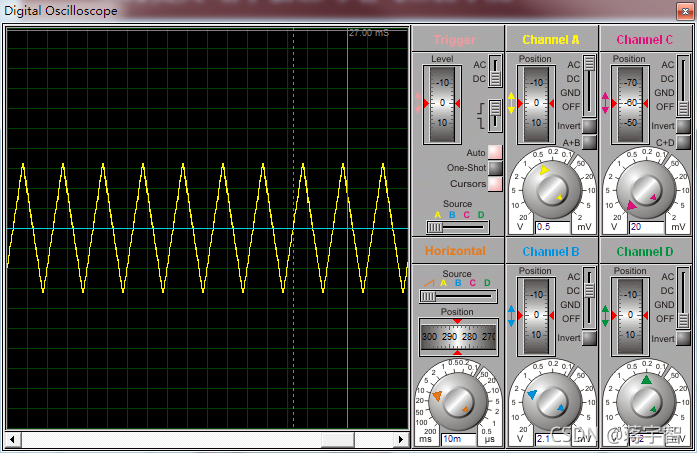
MCU function signal generator, output four kinds of waveforms, adjustable frequency, schematic diagram, simulation and C program

数组模拟队列进阶版本——环形队列(真正意义上的排队)
MQ-2和DS18B20的火灾温度-烟雾报警系统设计,51单片机,附仿真、C代码、原理图和PCB等
随机推荐
QT interface optimization: double click effect
自动化的艺术
Solve the problem of SSH configuration file optimization and slow connection
TLC5615 based multi-channel adjustable CNC DC regulated power supply, 51 single chip microcomputer, including proteus simulation and C code
单相交交变频器的Matlab Simulink建模设计,附Matlab仿真、PPT和论文等资料
Select receives both normal data and out of band data
Branch statement of process control
Model location setting in GIS data processing -cesium
Frame synchronization implementation
你還不知道責任鏈模式的使用場景嗎?
Find daffodils - for loop practice
OC 转 Swift 条件编译、标记、宏、 Log、 版本检测、过期提示
Swift:Entry of program、Swift调用OC、@_silgen_name 、 OC 调用Swift、dynamic、String、Substring
拼接hql时,新增字段没有出现在构造方法中
四层和八层电梯控制系统Proteus仿真设计,51单片机,附仿真和Keil C代码
[servlet] detailed explanation of servlet (use + principle)
8.4 循环神经网络从零实现
2-GO variable operation
1 minute to understand the execution process and permanently master the for cycle (with for cycle cases)
QT actual combat: Yunxi calendar