当前位置:网站首页>[ES6] promise related (event loop, macro / micro task, promise, await / await)
[ES6] promise related (event loop, macro / micro task, promise, await / await)
2022-04-23 17:15:00 【MiMenge】
List of articles
- 1 Synchronous and asynchronous
- 2 Execution stack and event queue (task queue) And the cycle of events
- 3 Macro task and micro task
- 4 Promise
-
- 4-0 Promise/A+ standard
- 4-1 Promise What is it? ?
- 4-2 Why use Promise?
- 4-3 Promise state [PromsieState] Changes
- 4-4 Promise Basic workflow
- 4-5 Promise Apis
- 4-6 Promise Some of the key questions
-
- 4-6-1 How to change Promise The state of ?
- 4-6-2 One promise More than one success was specified / Failed callback function , Are they called ?
- 4-6-3 change promise Status and who comes first after the specified callback function ?
- 4-6-4 promise.then() Return to new promise What determines the result state ?
- 4-6-5 promise How to concatenate multiple operation tasks ?
- 4-6-6 promise extraordinary transmission ?
- 4-6-7 interrupt promise chain ?
- 5 Async and Await
1 Synchronous and asynchronous
1-1 Sync
It can be understood that when the program is executing , Each code task can only be executed after the execution of the previous code task ( In analogy, the person behind the queue must wait until the person in front has finished buying the ticket ).
console.log(' The first to perform the task ');
console.log(' The second execution task ');
console.log(' The third execution task ');
/*
1
2
3
*/
1-2 asynchronous
It can be understood as : To cook by yourself, you need to buy vegetables 【 Sync 】, Buy kitchen utensils , Buy gas , Buying by yourself means you need to wait for a single thing ( Such as buying vegetables ) The next purchase can only be made after completion , And when buying with a mobile phone 【 asynchronous 】, You just need to tell the merchant , However, merchant distribution , In this process, you don't have to wait until the previous thing is completed before notifying the next business , Just receive the goods when they arrive .
because js The code is Single thread Executive , So there is no asynchrony in itself , however JavaScript There is a special function in , Callback function , Through callback function (callback Function)js Asynchronous is realized .
console.log('1');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('2');
});
console.log('3');
/* 1 3 2 */
2 Execution stack and event queue (task queue) And the cycle of events
1, stay javascript During code execution, different variables will be stored in different locations in memory : Pile up :(head) and Stack (stack) To distinguish . In the heap are some object , Some stored in the stack Variables of base type And the pointer to the object .
2, When I call a method ,JavaScript An execution environment will be generated (context), Also known as Execution context , There is a private scope for this method in this execution environment , The upper Scope The direction of , Method parameters , The variables defined in this scope and the this object . And when a series of methods are called in turn , because js It's single threaded , Only one method can be executed at a time , So these methods are queued up in a separate place . This place is called __ Execution stack __.
3, When the code is first executed ,js The engine will parse the code , And add the synchronization code into the execution stack according to the execution sequence , Then start from the beginning . If a method is currently executing , that js The execution environment of this method will be added to the execution stack , Then enter the execution environment to continue to execute the code . When the code in this execution environment After execution and return the result ,js Will exit the execution environment and destroy it , Go back to the execution environment of the previous method .. The process goes on and on , Until all the code in the execution stack is executed .
4,js The engine does not wait for an asynchronous event to return results , It will suspend the event , Continue to perform other tasks in the execution stack . When an asynchronous event returns a result ,js This event will be added to a different queue than the current execution stack , We call it Event queue . Being put into the event queue does not immediately execute its callback , Instead, wait for all tasks in the current execution stack to finish , When the main thread is idle , The main thread will look up whether the event queue has tasks . If there is , Then the main thread will take out the events in the first place , And put the callback corresponding to this event into the execution stack , Then execute the synchronization code …, So again and again , This creates an infinite cycle . This is the process called “ The event loop (Event Loop)” Why .
3 Macro task and micro task
What we know about asynchronous code is setTimeout and setInterval, ajax request , promies object then(),async/await, dom event , Although they are asynchronous events , But they are still very different ,
3-1 Macro task , Differences between micro tasks
-
Macro tasks include
Timer Functions,Dom event,ajax request -
Micro tasks include
Promise.resolve().then(),async\await -
Execution timing , Micro tasks are executed earlier than macro tasks , When the code in the main execution stack is executed , The main execution stack will first look for micro tasks in the event queue and put them into the execution stack for execution , Then find the macro task and put it into the execution stack for execution
-
Micro tasks are Dom You can perform... Before rendering , Macro tasks are Dom After rendering, you can perform
3-2 perform
- In a cycle of events , The asynchronous event will be put into a task queue after the result is returned . However , According to the type of asynchronous event , This event will actually be sent to the corresponding macro task queue or micro task queue . And when the current execution stack is empty , The main thread will Check whether there are events in the micro task queue . If it doesn't exist , Then go to the macro task queue to get an event and add the corresponding back to the current execution stack ; If there is , Then the callback corresponding to the event in the queue will be executed successively , Until the micro task queue is empty , Then go to the macro task queue to get the first event , Add the corresponding callback to the current execution stack … So again and again , Into the loop .
- stay js When the code starts executing ,script The tag will enter the macro task queue , There are no micro queues before this macro task queue , So the script It will enter the call stack and execute the synchronization code , Then press the micro task into the micro task queue , Press macro task into macro task queue , When the execution in the call stack is completed, the micro task queue code will be executed first , After the execution, in Execute the first macro task in the macro task queue , The macro task and micro task will be pushed into the corresponding queue , When each macro task is fully executed , Will clear the corresponding micro task queue code . To and fro
In short : When the current execution stack finishes executing, it will immediately process all the events in the micro task queue , Then go to the macro task queue to get an event ( first ). In the same event cycle , Micro tasks always execute before macro tasks .
4 Promise
4-0 Promise/A+ standard
ES6 New pair Pormise/A+ The perfection of the specification supports , namely Promise type , It has become the dominant asynchronous programming mechanism .
ES6 New reference type Promise, Can pass new Operator to instantiate . When creating a new appointment, you need to pass in the actuator (exector) Function as argument only
// establish Promise
// Receive a parameter function
// The parameter function receives two parameters
// resolve , reject
let p = new Promise((res , rej)=>{
});
4-1 Promise What is it? ?
- 1 Abstract expression
- Promise yes es6 A new technology .
- Promise yes js A new solution for asynchronous programming in ( The old is to simply use callback functions )
- Specific expression :
- Syntactically speaking, it is a constructor
- Functionally, it is used to encapsulate an asynchronous operation and obtain its success / The result value of failure
4-2 Why use Promise?
4-2-1 Specifying callback functions is more flexible
1 old : You must specify... Before starting an asynchronous task
2 promise: Start asynchronous task => return Promise object => to Promise Object binding callback function ( Even specify multiple... After the asynchronous task ends )
4-2-2 Support chain calls , Can solve the problem of callback to hell
-
What is the problem of callback hell ?
We need to perform a lot of asynchronous tasks , And the result should have the output of synchronous rules ( When the result of the previous callback is used as the condition of the next asynchronous function callback ), We will nest a large number of callbacks , At this time, the overall readability of the code is very poor , There is a phenomenon of callback to hell
-
The characteristics of callback hell ?
Not easy to read
Not convenient for exception handling
-
Solution
promise call chaining
fs.readFile('./a.txt', function (err, date) {
if (err) {
return console.log(' Read error ');
}
console.log(date.toString());
fs.readFile('./b.txt', function (err, date) {
if (err) {
return console.log(' Read error ');
}
console.log(date.toString());
fs.readFile('./ introduce .html', function (err, date) {
if (err) {
return console.log(' Read error ');
}
return console.log(date.toString());
});
});
});
// The problem can be solved at this time , However, if there are too many businesses, it will be difficult to maintain ---------- Back to hell ---- Code presentation '>' type
4-3 Promise state [PromsieState] Changes
4-3-1 Contractual status
When we create an appointment instance , This instance may be in three states
- undetermined pendding
- cash fulfilled ( Also known as solving , resolved)
- Refuse rejected
Undetermined is the initial state of the contract . In pending status , The contract can be converted to cash status , Or switch to reject status .
The pending status can be changed to cash status or reject status , However, the rejected or cashed status cannot be changed to pending status , And there is no transition between cash status and reject status
The state of the covenant is private , adopt js The appointment status of the instance cannot be accessed . The main purpose is to avoid reading the expiration status , Process the state in a synchronous manner

When printing an appointment instance
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(' The timer is over ');
})
});
console.log(promise);
// Promise {<pending>}
At this point, the instance is in the pending state ( pendding ).
4-3-2 Promise Value in object
Another property in the instance object [PromiseResult]
Namely object [ success / Failure ] Result
There are only two ways to change this value
- resolve
- reject
4-4 Promise Basic workflow
!!!
1> new Promise Create a Promise Instance object , And create an asynchronous task inside it
2> Perform asynchronous operations in it , If the asynchronous operation is successful , Call resolve(); This function , change Promise Example of [PromiseState] The status of is __resolved__( success )
3> Called on success then() Method change Promise Value [PromiseResult] Value , And execute a successful callback , Back to a new Promise object __( The core of chain call )__
4 > If the asynchronous operation fails , Call reject(); This function ,Promise Example of [PromiseState] The status of is __rejected__( Failure ),
5> Call... On failure then() Method change Promise Value [PromiseResult] Value , And execute the failed callback , Back to a new Promise object __( The core of chain call )__.
The illustration :

Use :- demand : To call the import... In order ,a,b Three files
// General solutions ----- Callback
// fs.readFile('./a.txt', function (err, date) {
// if (err) {
// return console.log(' Read error ');
// }
// console.log(date.toString());
// fs.readFile('./b.txt', function (err, date) {
// if (err) {
// return console.log(' Read error ');
// }
// console.log(date.toString());
// fs.readFile('./ introduce .html', function (err, date) {
// if (err) {
// return console.log(' Read error ');
// }
// return console.log(date.toString());
// });
// });
// });
The problem can be solved at this time , However, if there are too many businesses, it will be difficult to maintain ---------- Back to hell
-
es6 Of promise Method ------------ promise api
function rand(url) { // Encapsulate a method of reading files ( Have the ability to process asynchrony into synchronization ) // Create a promise Containers // promise Once the container is created, it will execute the code inside let p = new Promise(function (reslove, reject) { // At first, the code in the container has a status of pending( Have in hand ) fs.readFile(url, function (err, date) { // Read the file if (err) { // Read failed // At this point, change the execution status of the code in the container to failed // And pass this state through reject To pass it on reject(err); } // Read successful // At this time, the execution status in the container is changed to successful // And pass this state through reslove To pass it on reslove(date); }); }); return p; }; rand('./a.txt')// Call the method and pass in the path // then() Methods there are two ways to deal with .then((date) => { // success console.log(date.toString()); return rand('./b.txt');// Return to one promise Object to the next then----- Only when this then The next... Cannot be output until the execution is completed then Results received }, (err) => { // Failure return console.log(err);// In case of failure, the next... Will not be executed then() }) .then((date) => { console.log(date.toString()); return rand('./ introduce .html'); }, (err) => { return console.log(err); }).then((date) => { console.log(date.toString()); }, (err) => { return console.log(err); });
4-5 Promise Apis
4-5-1 Promise Constructors :Promise(exctor){}
- executor function : actuator (resolve,reject) => {}
executor Function parameters passed in when creating an instance , It takes two parameters
- resolve function : The function we call when the internal definition succeeds value => {}
- reject function : The function we call when the internal definition fails reason =>{}
explain :executor Will be in Promise Internal immediate synchronization call , Asynchronous operations are performed in the actuator
4-5-2 Promise.prototype.then Method :(onResolved,onRejected)=> {}
-
onResolved function : Successful callback function (value) => {}
then The first parameter received by the function
-
onRejected function : Failed callback function (reason) => {}
then The second parameter received by the function
explain : Specified for success value The successful callback of and used to get the failure reason The failure callback of , Back to a new Promise object
4-5-3 Promise.prototype.catch Method : (onRejected) => {}
- onReject function : Failed callback function (reason) => {}
When the function chain call fails, the failed object will enter this function
4-5-4 Promise The method in
Promise.resolve();Method :(value) => {}
value : Successful data or Promise object
Be careful : This method returns a success or failure Promise object
let p2 = Promise.resolve('123');
console.log(p2);
//Promise { '123' }
// stay Promise.resolve If the parameter passed in the method parameter is non Promise The object of ,
// A successful... Is returned Promise object
// If the incoming is Promise Object instances , The value returned is based on the value in the parameter promise Depending on the result of the object ---- Dolls
Promise.resolve(new Promise(
(resolve, reject) => {
let falg = false;
if (falg) {
resolve(' Success value ');
} else {
reject(' Failure value ');
}
}
)).then(
(value) =>{
console.log(value);
// Success value
},
(reason) => {
console.log(reason);
// Failure value
}
)
-
Promise.reject();Method :(reason) => {} reason : The reason for the failure
Be careful : What is returned is a failed Promise object
let p2 = Promise.reject('123');
// console.log(p2);
//Promise { <rejected> '123' }
// stay Promise.reject The method returns the failed parameter Promise object ( Always return failed )
Promise.reject(new Promise(
(resolve, reject) => {
let falg = true;
if (falg) {
resolve('success');
} else {
reject('fuile');
}
}
)).catch
(
(reason) => {
console.log(reason);
// Failure value
}
)
Promise {
'success' }
(node:14092) UnhandledPromiseRejectionWarning: 123
(Use `node --trace-warnings ...` to show where the warning was created)
(node:14092) UnhandledPromiseRejectionWarning: Unhandled promise rejection. This error originated either by throwing inside of an async function without a catch block, or by rejecting a promise which was not handled with .catch(). To terminate the node process on unhandled promise rejection, use the CLI flag `--unhandled-rejections=strict` (see https://nodejs.org/api/cli.html#cli_unhandled_rejections_mode). (rejection id: 1)
(node:14092) [DEP0018] DeprecationWarning: Unhandled promise rejections are deprecated. In the future, promise rejections that are not handled will terminate the Node.js process with a non-zero exit code.
-
Promise.all() Method :(Promise) => {}
Among them Promise Parameters : Contains multiple Promise An array of objects
explain : Back to a new Promise, When all in the array Promise The result is complete , The final result is completion
// - 3 Promise.all() Method
let p3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(' The first success value ');
});
let p4 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(' This is the second success value ');
});
let p5 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(' This is the first 3 A success value ');
});
Promise.all([p3, p4, p5]).then((value)=>{
console.log(value);
});
let p6 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(' The first success value ');
});
let p7 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(' This is the second failure ');
});
let p8 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(' This is the first 3 A success value ');
});
Promise.all([p6, p7, p8]).then((value)=>{
console.log(value);
});
// (node:7824) UnhandledPromiseRejectionWarning: This is the second failure
-
Promise.race() Method :(Promise) => {}
Among them Promise Parameters : Contains multiple Promise An array of objects
explain : Back to a new Promise, The first to finish Promise The state of is the final state , The final result is completion
let a1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(' This is the first failure value ');
});
let a2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(' This is the second success value ');
});
let a3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(' This is the third failure value ');
})
Promise.race([a1, a2, a3]).then((value) => {
console.log(value)
}, (reason) => {
throw new Error(reason)
});
//Error: This is the first failure value
4-6 Promise Some of the key questions
4-6-1 How to change Promise The state of ?
1> resolve(value): If it is currently pending It will become resolved
2> reject(reason): If it is currently rending It will become rejected
3> Throw an exception : If it is currently pending It will become rejected
4-6-2 One promise More than one success was specified / Failed callback function , Are they called ?
When Promise It is called when it changes to the corresponding state
4-6-3 change promise Status and who comes first after the specified callback function ?
1> It's possible , Under normal circumstances, the callback is specified first, and then the state is changed , But you can also change the state first and specify the callback
2> How to change the state first and then specify the callback ?
- Call directly in the actuator resolve() / reject()
- Call after a longer delay then()
It involves the execution sequence of micro tasks and macro tasks
3> When can I get the data ?
- If you specify a callback first , When the state changes , The callback function will call , Get data
- If you change the state first , When a callback is specified , The callback function will call , Get data
4-6-4 promise.then() Return to new promise What determines the result state ?
1> Simple expression : from then() The result of the specified callback function execution determines
2> Detailed information expression :
-
If an exception is thrown , new promise Turn into rejected,reason Exception thrown for
let b1 = new Promise((res, rej) => { rej(' success '); }) b1.then( value => { console.log(value); }, reason => { console.log(reason) throw ' Something went wrong '; } ); /* (node:15316) UnhandledPromiseRejectionWarning: Something went wrong */ -
If yes or no is returned promise value , new promise Value to resolved,value For the returned value
-
If you return another new promise, this promise The result will be new promise Result
4-6-5 promise How to concatenate multiple operation tasks ?
1> promise Of then() Back to a new promise, It can be done then() Chain call of
2> adopt then A chain call concatenates multiple synchronizations / Asynchronous task
4-6-6 promise extraordinary transmission ?
1 > When using promise Of then Chain call , Failed callbacks can be specified at the end
2 > Any previous operations handle exceptions , Will be passed to the last failed callback for processing
4-6-7 interrupt promise chain ?
1 > When using promise When the chain call of , Interrupt in the middle , The subsequent callback function is no longer called
2> Way : Returns a pending State of promise object
5 Async and Await
5-1 Async
0 Used to mark the formation of functions async function
1 The return value of the function is promise object
2 promise The result of the object is determined by async The return value of the function execution determines
-
1 Returns a non promise value
let d1 = async function done_one() { return 521; } console.log(d1()); //Promise { 521 } // As long as the result returned is yes or no promise object , Then the return will always be a successful promise object -
2 return promise object
let d2 = async function done_two() { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { if (true) { resolve(' success '); } else { reject(' Failure '); } }); } console.log(d2()); //Promise { <pending> } // The result is promise object , Then getting is corresponding to success / The failure of the promise object -
3 Throw an error
let d3 = async function done_three() { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { throw ' Throw out ' }); } console.log(d3()); //Promise { <pending> } // The result returned is an exception , Then getting is a failure promise object
5-2 await
-
1 await The expression on the right is usually promise object , But it can also be other values
-
2 If the expression is promise object ,await The return is promise The value of success
async function two() { let d2 = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => { resolve(' success 123'); // reject(' Failure 456'); }) return d2; } console.log(two()); //Promise {<pending>} // [[Prototype]]: Promise // [[PromiseState]]: "fulfilled" // [[PromiseResult]]: " success 123" // or // Promise {<pending>} // [[Prototype]]: Promise // [[PromiseState]]: "rejected" // [[PromiseResult]]: " Failure 456" -
3 If the expression is another value , Take this value directly as await The return value of
async function one(){ let d1 = await 123; return d1; } console.log(one()); //Promise {<pending>} // [[Prototype]]: Promise // [[PromiseState]]: "fulfilled" // [[PromiseResult]]: 123
5-3 Be careful
-
await Must be written in async Function , however async Function can have no await
-
If await Of promise failed , Will throw an exception , Need to pass through
try......catch....Capture processingasync function two() { try { let d2 = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => { resolve(' success 123'); // reject(' Failure 456'); }) console.log(d2);// success 123 return d2; } catch (e) { throw new Error(e);//Error: Failure 456 } } two();
5-4 async and await Use a combination of
class Time1 {
fn1(num, timeout) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(` I'm a file ${
num}`)
}, timeout);
});
};
};
const s1 = new Time1();
const s2 = new Time1();
const s3 = new Time1();
// Use async Function can handle promise Back to promise object
// Among them await amount to then The role of
async function asc() {
// When each execution reaches await when , The program will wait until the last time promise Only when there is a return value can the following code be executed
let data1 = await s1.fn1(1, 3000);
console.log('------------------------');
console.log(data1);
let data2 = await s2.fn1(2, 1000);
console.log('------------------------');
console.log(data2);
let data3 = await s3.fn1(3, 2000);
console.log('------------------------');
console.log(data3);
let data = [data1, data2, data3];
return data;
};
asc().then((data) => {
// After the execution of data Receive is async The success return value of (promise)
console.log(' completion of enforcement ', data);
}).catch((err) => {
// When a problem occurs in one of the three execution steps, the process will no longer go on and throw an error
console.log(err);
})
版权声明
本文为[MiMenge]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230553027146.html
边栏推荐
- Nacos + aspnetcore + Ocelot actual combat code
- El date picker limits the selection range from the current time to two months ago
- Shell - introduction, variables, and basic syntax
- C# Task. Delay and thread The difference between sleep
- JS failed to change all variables and changed to the return method. Finally, the problem was solved
- 2. Electron's HelloWorld
- Variable length parameter__ VA_ ARGS__ Macro definitions for and logging
- ClickHouse-SQL 操作
- [C] thoroughly understand the deep copy
- Multithreaded @ async thread pool
猜你喜欢
![[logical fallacy in life] Scarecrow fallacy and inability to refute are not proof](/img/71/14a17128dbe0f02edb4db3da479ef2.jpg)
[logical fallacy in life] Scarecrow fallacy and inability to refute are not proof
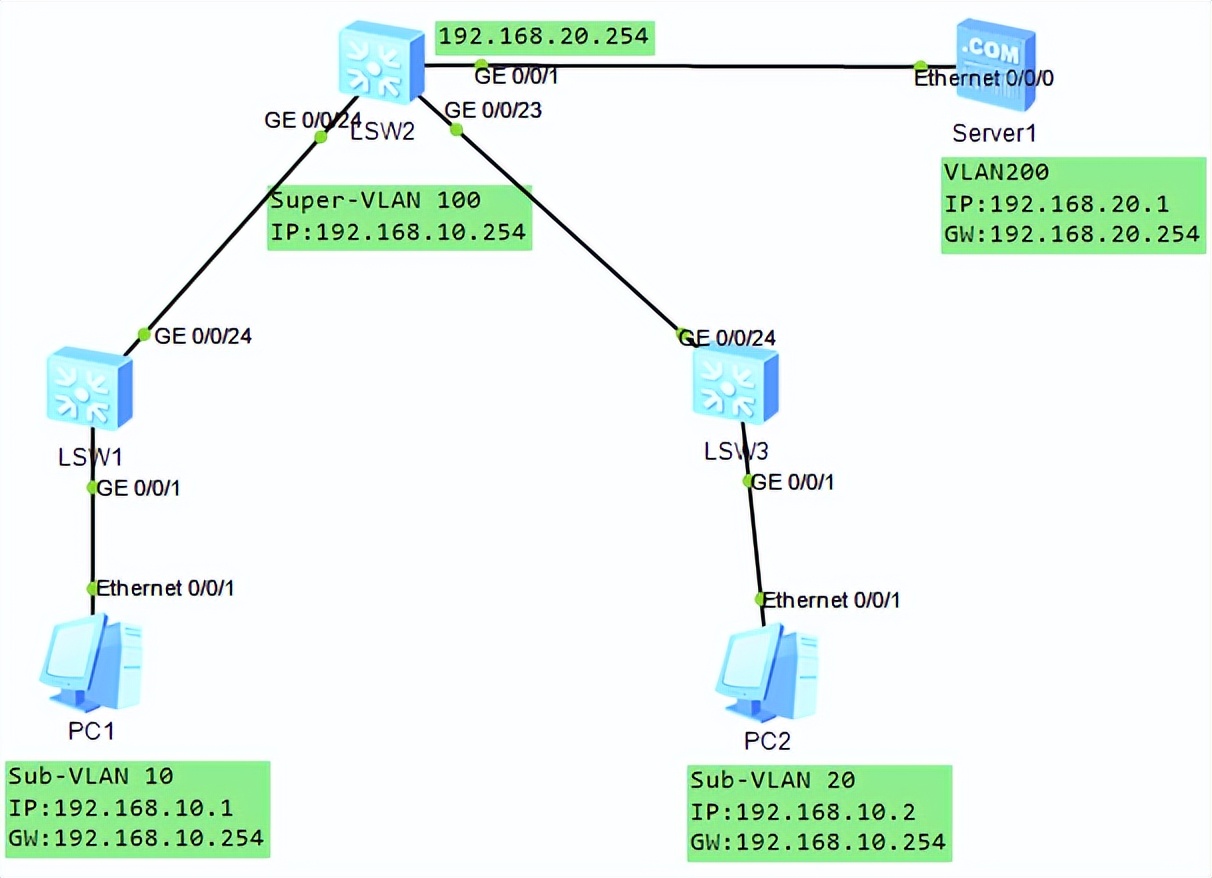
VLAN advanced technology, VLAN aggregation, super VLAN, sub VLAN
1-4 configuration executable script of nodejs installation

Perception of linear algebra 2
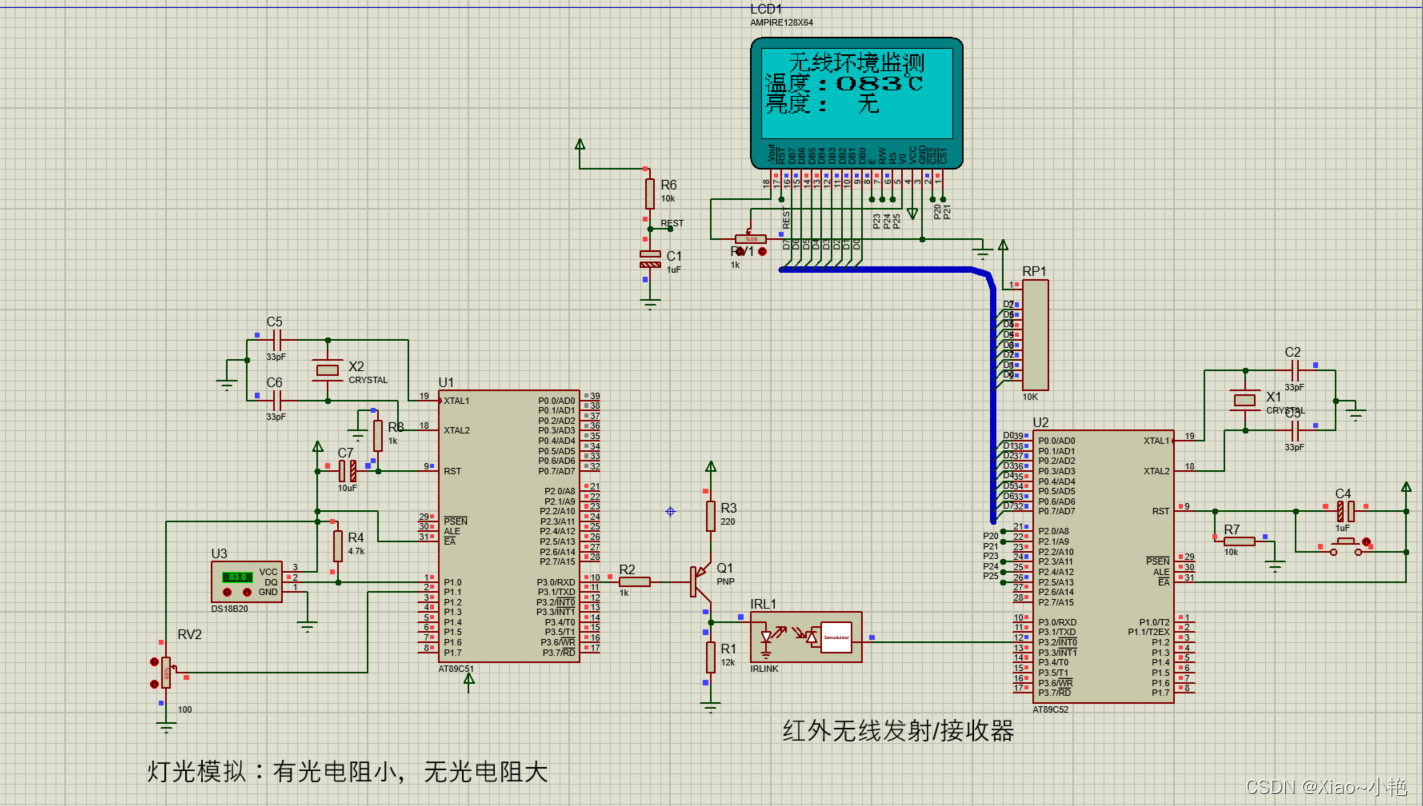
基于51单片机红外无线通讯仿真
Bottom processing of stack memory in browser

Document operation II (5000 word summary)

Scope and scope chain in JS
Deep understanding of control inversion and dependency injection
![[WPF binding 3] listview basic binding and data template binding](/img/2e/fbdb4175297bb4964a8ccfd0b909ae.png)
[WPF binding 3] listview basic binding and data template binding
随机推荐
Redis docker installation
Nacos + aspnetcore + Ocelot actual combat code
On lambda powertools typescript
Collection of common SQL statements
2.Electron之HelloWorld
Come out after a thousand calls
1-1 NodeJS
Shell-入门、变量、以及基本的语法
Generate random numbers with high quality and Gaussian distribution
手写事件发布订阅框架
freeCodeCamp----shape_ Calculator exercise
Shell-sort命令的使用
[problem solving] [show2012] random tree
VLAN advanced technology, VLAN aggregation, super VLAN, sub VLAN
PostgreSQL column storage and row storage
Shell-sed命令的使用
Your brain expands and shrinks over time — these charts show how
Go language, array, string, slice
Decimal format decimal / datetime conversion processing
[C#] 彻底搞明白深拷贝