当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to dynamic programming of leetcode learning plan day3 (198213740)
Introduction to dynamic programming of leetcode learning plan day3 (198213740)
2022-04-23 15:27:00 【Slow ploughing of stupid cattle】
Catalog
198. raid homes and plunder houses
213. raid homes and plunder houses II
Method 3 : Sort + Dynamic programming
198. raid homes and plunder houses
Problem description
You are a professional thief , Plan to steal houses along the street . There is a certain amount of cash in every room , The only restriction on your theft is that adjacent houses are equipped with interconnected anti-theft systems , If two adjacent houses are broken into by thieves on the same night , The system will automatically alarm . Given an array of non negative integers representing the storage amount of each house , Count you Without triggering the alarm , The maximum amount that can be stolen overnight .
Example 1:
Input :[1,2,3,1]
Output :4
explain : Steal 1 House No ( amount of money = 1) , And then steal 3 House No ( amount of money = 3).
Maximum amount stolen = 1 + 3 = 4 .
Example 2:
Input :[2,7,9,3,1]
Output :12
explain : Steal 1 House No ( amount of money = 2), Steal 3 House No ( amount of money = 9), Then steal 5 House No ( amount of money = 1).
Maximum amount stolen = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12 .
Tips :
1 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 400
Their thinking
Due to the restriction that adjacent houses cannot be accessed , Suppose you have visited the 1 A house , You have to skip the 2 between , Next, from page 3 I began to think about . If you skip step 1 between , You can start from 2 I began to think about .
Remember from the house k The maximum amount you can get from the beginning to the end is recorded as f(k), Then we can get the following transfer equation :
max() No 1 Item indicates access to the 1 The situation between , The first 2 Item indicates access to the 2 The situation between .
You can use recursive method or iterative method , Here we use recursion plus memoization To achieve .
Code
class Solution:
def rob(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
N = len(nums)
memo = dict()
def dp(k):
if k in memo:
return memo[k]
if k>(N-1):
return 0
ans = max(nums[k]+dp(k+2), dp(k+1))
memo[k] = ans
return ans
return dp(0)Execution time :32 ms, In all Python3 Defeated in submission 88.13% Users of
Memory consumption :15.1 MB, In all Python3 Defeated in submission 5.28% Users of
213. raid homes and plunder houses II
Problem description
You are a professional thief , Plan to steal houses along the street , There is a certain amount of cash in every room . All the houses in this place are Make a circle , This means that the first house and the last house are next to each other . meanwhile , Adjacent houses are equipped with interconnected anti-theft system , If two adjacent houses are broken into by thieves on the same night , The system will automatically alarm .
Given an array of non negative integers representing the storage amount of each house , Count you Without triggering the alarm device , The maximum amount you can steal tonight .
Example 1:
Input :nums = [2,3,2] Output :3 explain : You can't steal first 1 House No ( amount of money = 2), And then steal 3 House No ( amount of money = 2), Because they are next to each other .
Example 2:
Input :nums = [1,2,3,1] Output :4 explain : You can steal first 1 House No ( amount of money = 1), And then steal 3 House No ( amount of money = 3). Maximum amount stolen = 1 + 3 = 4 .
Example 3:
Input :nums = [1,2,3] Output :3
Tips :
1 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000
Their thinking
Because the house is in a circle , So there are a little more constraints than the previous question .
In the last question , The first 1 Both rooms and the last room are allowed , But in this question, it is not allowed ( Of course , Here is the assumption that it is cut from somewhere in the ring and arranged linearly , Otherwise , The ring itself has no second 1 Between and last 1 It's between ).
Consider the 1 Whether the house is visited or not :
- case1: Visit the house 1. The rest of the houses [2,n-2], Note that this interval is no longer constrained by the ring , Just deal with it in the same way as the basic situation of the previous question
- case2: Do not visit the house 1. The rest of the houses [1,n-1], This is not constrained by the ring , Just deal with it in the same way as the basic situation of the previous question
Encapsulate the processing of the previous question into a function rob(nums), Then the solution of this problem is And
Maximum value between .
Code
class Solution:
def rob_linear(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
N = len(nums)
memo = dict()
def dp(k):
if k in memo:
return memo[k]
if k>(N-1):
return 0
ans = max(nums[k]+dp(k+2), dp(k+1))
memo[k] = ans
return ans
return dp(0)
def rob(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
return max(nums[0]+self.rob_linear(nums[2:-1]), self.rob_linear(nums[1:]))
Execution time :40 ms, In all Python3 Defeated in submission 41.06% Users of
Memory consumption :15.3 MB, In all Python3 Defeated in submission 5.19% Users of
740. Delete and get points
Problem description
Give you an array of integers nums , You can do something with it .
In every operation , Choose any one nums[i] , Delete it and get nums[i] Number of points . after , You have to delete it all be equal to nums[i] - 1 and nums[i] + 1 The elements of .
At first you have 0 Points . Return the maximum number of points you can get through these operations .
Example 1:
Input :nums = [3,4,2] Output :6 explain : Delete 4 get 4 Points , therefore 3 Also deleted . after , Delete 2 get 2 Points . All in all 6 Points .
Example 2:
Input :nums = [2,2,3,3,3,4] Output :9 explain : Delete 3 get 3 Points , And then we're going to delete two 2 and 4 . after , Delete again 3 get 3 Points , Delete again 3 get 3 Points . All in all 9 Points .
Tips :
1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 10^41 <= nums[i] <= 10^4
Method 1
Ideas
Because elements with the same number of points are either retained or deleted at the same time , So you can first merge elements with the same value ( Add up its value ), Build a hash table ,key Is its original value ,value Is the value of the merged node .
Next, the question seems to turn into a 0/1 knapsack problem , But more than basic 0/1 The knapsack problem is more complicated .
Consider a pair of {key, value} The choice of .
- If you keep this key Words , You need to key-1 and key+1 from keys Delete... From the collection ;
- If you delete this key Words , Sure ( But not necessarily , This also depends on other key The choice of ) Retain key-1 and key+1
So we can get the equation of state transition , But in fact, it is difficult to express it in the form of mathematical equations .
Code
from typing import List
class Solution:
def deleteAndEarn(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
d = dict()
for k,num in enumerate(nums):
if num in d:
d[num] = d[num] + num
else:
d[num] = num
memo = dict()
def dp(d0):
if len(d0)==0:
return 0
if len(d0)==1:
return d0.popitem()[1]
if tuple(d0.keys()) in memo:
return memo[tuple(d0.keys())]
# print(d0)
d1 = d0.copy()
d2 = d0.copy()
k0,v0 = d1.popitem()
# Don't take this key
# print(k0,v0,d1)
v1 = dp(d1)
# Take this key, and hence remove k0+/-1
neibourKey = []
d2.pop(k0)
for key2 in d2:
if key2 == k0+1 or key2 == k0-1:
neibourKey.append(key2)
for key in neibourKey:
# print(key)
d2.pop(key)
# print(d2)
v2 = v0 + dp(d2)
ans = max(v1,v2)
memo[tuple(d0.keys())] = ans
return ans
return dp(d)
if __name__ == "__main__":
sln = Solution()
nums = [3,1]
print(sln.deleteAndEarn(nums))
nums = [3,4,2]
print(sln.deleteAndEarn(nums))
nums = [2,2,3,3,3,4]
print(sln.deleteAndEarn(nums))It's overtime ...
Method 2
Ideas
The way of thinking is the same .
however , It is not expressed by hash table nums The element values in and their corresponding sums , Instead, we use an array to represent . The original array corresponds to nums The original element value , The stored content is its corresponding sum . The advantage of doing so is , You don't have to pass the entire hash table keys As memo Of key.
After counting in this way , The problem is to program the trade-offs for each element from this array , Under constraints, two adjacent elements that are not indexed cannot be taken at the same time . That is, turn into 198 The same question .
Code
class Solution:
def deleteAndEarn(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
total = (max(nums)+1) * [0]
for num in nums:
total[num] = total[num] + num
N = len(total)
memo = dict()
def dp(k):
if k in memo:
return memo[k]
if k>(N-1):
return 0
ans = max(total[k]+dp(k+2), dp(k+1))
memo[k] = ans
return ans
return dp(0)Execution time :56 ms, In all Python3 Defeated in submission 24.32% Users of
Memory consumption :22.1 MB, In all Python3 Defeated in submission 5.01% Users of
Method 3 : Sort + Dynamic programming
The official solution also gives a solution of dynamic programming by sorting first and then zoning , Ideas as follows ( The code is slightly ):
Note that if nums There is no element in the x, Then select any less than x The element of does not affect more than x Selection of elements . So we can nums After ordering , Divide it into several continuous sub arrays , The difference between any adjacent elements in the subarray does not exceed 1. For each subarray, the result is calculated according to the dynamic programming process of method 2 , Adding up all the results is the answer .
Go back to the general catalogue : Slow ploughing by stupid cattle Leetcode General catalogue of daily questions ( Dynamic update ...)
版权声明
本文为[Slow ploughing of stupid cattle]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231523111345.html
边栏推荐
- Detailed explanation of kubernetes (IX) -- actual combat of creating pod with resource allocation list
- Redis cluster principle
- TLS / SSL protocol details (28) differences between TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2
- TLS / SSL protocol details (30) RSA, DHE, ecdhe and ecdh processes and differences in SSL
- setcontext getcontext makecontext swapcontext
- YML references other variables
- Precautions for use of dispatching system
- Adobe Illustrator menu in Chinese and English
- Explanation 2 of redis database (redis high availability, persistence and performance management)
- Five data types of redis
猜你喜欢
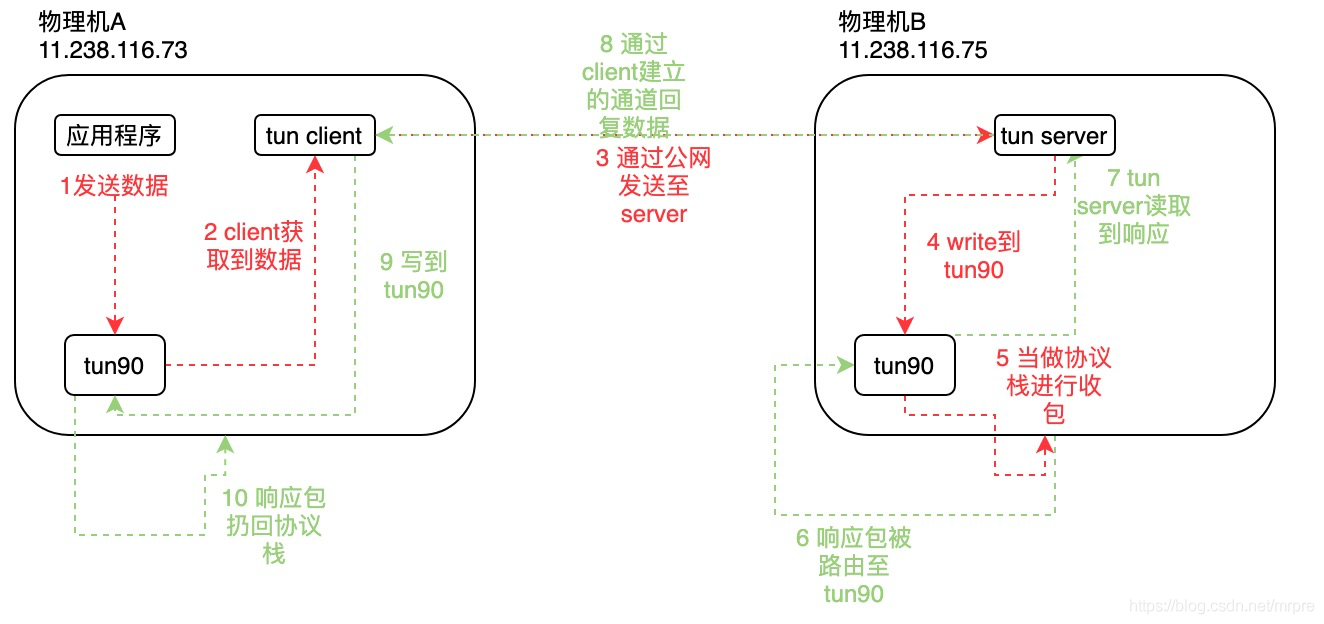
Tun equipment principle

深度学习——超参数设置
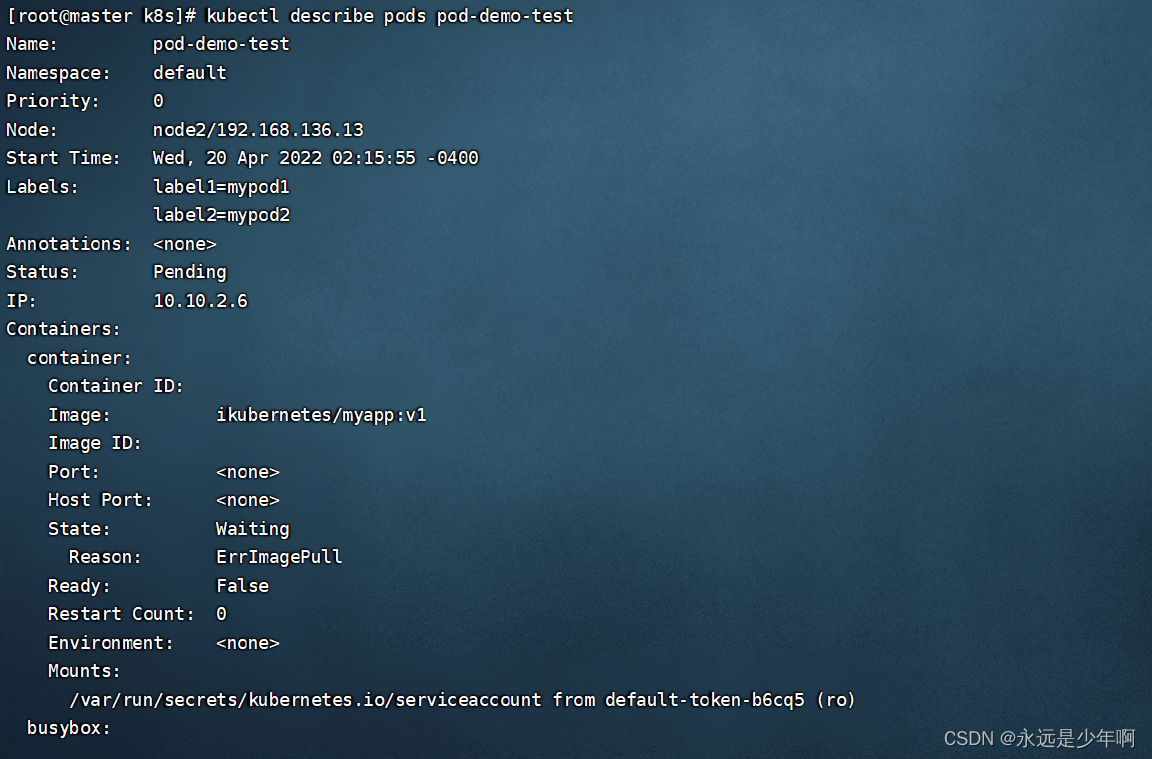
Detailed explanation of kubernetes (IX) -- actual combat of creating pod with resource allocation list
T2 icloud calendar cannot be synchronized
Tun model of flannel principle
Basic operation of circular queue (Experiment)
Special analysis of China's digital technology in 2022
For 22 years, you didn't know the file contained vulnerabilities?
服务器中毒了怎么办?服务器怎么防止病毒入侵?
Mysql database explanation (10)
随机推荐
A series of problems about the best time to buy and sell stocks
SSH connects to the remote host through the springboard machine
今日睡眠质量记录76分
How to use OCR in 5 minutes
Analysis of common storage types and FTP active and passive modes
Reptile exercises (1)
Detailed explanation of kubernetes (XI) -- label and label selector
函数(第一部分)
自动化测试框架常见类型▏自动化测试就交给软件测评机构
软件性能测试报告起着什么作用?第三方测试报告如何收费?
kubernetes之常用Pod控制器的使用
Tun equipment principle
[thymeleaf] handle null values and use safe operators
Rsync + inotify remote synchronization
Wechat applet customer service access to send and receive messages
Squid agent
Set onedrive or Google drive as a drawing bed in upic for free
C语言超全学习路线(收藏让你少走弯路)
Will golang share data with fragment append
Leetcode学习计划之动态规划入门day3(198,213,740)