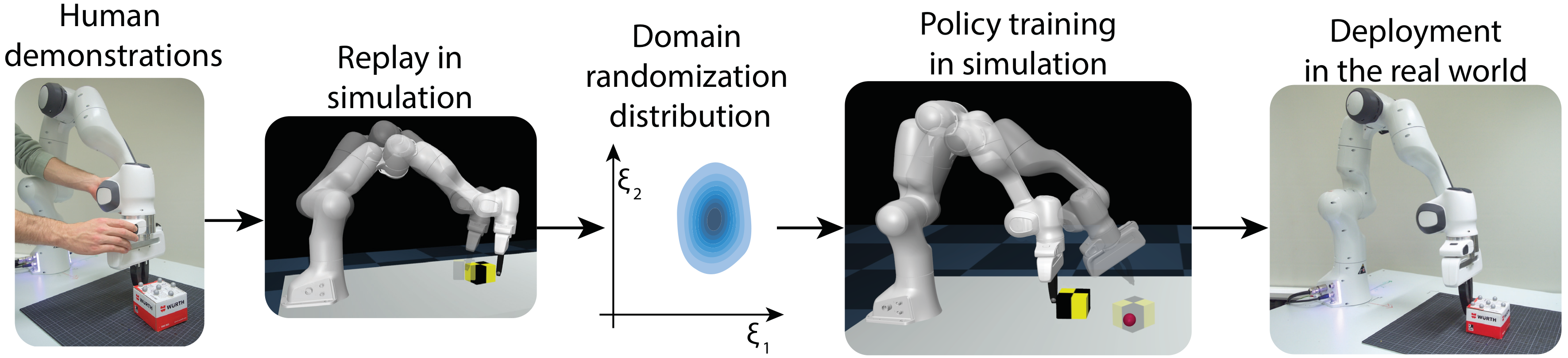
DROPO: Sim-to-Real Transfer with Offline Domain Randomization
Gabriele Tiboni, Karol Arndt, Ville Kyrki.
This repository contains the code for the paper: "DROPO: Sim-to-Real Transfer with Offline Domain Randomization" submitted to the IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RAL) Journal, in December 2021.
Abstract: In recent years, domain randomization has gained a lot of traction as a method for sim-to-real transfer of reinforcement learning policies; however, coming up with optimal randomization ranges can be difficult. In this paper, we introduce DROPO, a novel method for estimating domain randomization ranges for a safe sim-to-real transfer. Unlike prior work, DROPO only requires a precollected offline dataset of trajectories, and does not converge to point estimates. We demonstrate that DROPO is capable of recovering dynamic parameter distributions in simulation and finding a distribution capable of compensating for an unmodelled phenomenon. We also evaluate the method on two zero-shot sim-to-real transfer scenarios, showing a successful domain transfer and improved performance over prior methods.
Requirements
This repository makes use of the following external libraries:
How to launch DROPO
1. Dataset collection and formatting
Prior to running the code, an offline dataset of trajectories from the target (real) environment needs to be collected. This dataset can be generated either by rolling out any previously trained policy, or by kinesthetic guidance of the robot.
The dataset object must be formatted as follows:
n : int
state space dimensionality
a : int
action space dimensionality
t : int
number of state transitions
dataset : dict,
object containing offline-collected trajectories
dataset['observations'] : ndarray
2D array (t, n) containing the current state information for each timestep
dataset['next_observations'] : ndarray
2D array (t, n) containing the next-state information for each timestep
dataset['actions'] : ndarray
2D array (t, a) containing the action commanded to the agent at the current timestep
dataset['terminals'] : ndarray
1D array (t,) of booleans indicating whether or not the current state transition is terminal (ends the episode)
2. Add environment-specific methods
Augment the simulated environment with the following methods to allow Domain Randomization and its optimization:
-
env.set_task(*new_task)# Set new dynamics parameters -
env.get_task()# Get current dynamics parameters -
mjstate = env.get_sim_state()# Get current internal mujoco state -
env.get_initial_mjstate(state)andenv.get_full_mjstate# Get the internal mujoco state from given state -
env.set_sim_state(mjstate)# Set the simulator to a specific mujoco state -
env.set_task_search_bounds()# Set the search bound for the mean of the dynamics parameters -
(optional)
env.get_task_lower_bound(i)# Get lower bound for i-th dynamics parameter -
(optional)
env.get_task_upper_bound(i)# Get upper bound for i-th dynamics parameter
3. Run test_dropo.py
Sample file to launch DROPO.
Test DROPO on the Hopper environment
This repository contains a ready-to-use Hopper environment implementation (based on the code from OpenAI gym) and an associated offline dataset to run quick DROPO experiments on Hopper, with randomized link masses. The dataset consists of 20 trajectories collected on the ground truth hopper environment with mass values [3.53429174, 3.92699082, 2.71433605, 5.0893801].
E.g.:
-
Quick test (10 sparse transitions and 1000 obj. function evaluations only):
python3 test_dropo.py --sparse-mode -n 10 -l 1 --budget 1000 -av --epsilon 1e-5 --seed 100 --dataset datasets/hopper10000 --normalize --logstdevs
-
Advanced test (2 trajectories are considered, with 5000 obj. function evaluations, and 10 parallel workers):
python3 test_dropo.py -n 2 -l 1 --budget 5000 -av --epsilon 1e-5 --seed 100 --dataset datasets/hopper10000 --normalize --logstdevs --now 10
test_dropo.py will return the optimized domain randomization distribution, suitable for training a reinforcement learning policy on the same simulated environment.
Cite us
If you use this repository, please consider citing
@misc{tiboni2022dropo,
title={DROPO: Sim-to-Real Transfer with Offline Domain Randomization},
author={Gabriele Tiboni and Karol Arndt and Ville Kyrki},
year={2022},
eprint={2201.08434},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.RO}
}