当前位置:网站首页>Merge k sorted linked lists
Merge k sorted linked lists
2022-08-10 22:31:00 【dry rice white】

ojbk...At first I thought there was no memory requirement for this question,So use a very simple method to merge.Create a third linked list,As a result, some cases failed.
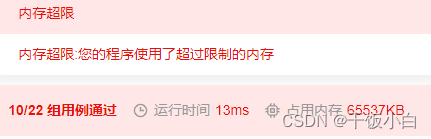
这个代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergetK(ListNode *A,ListNode *B)
{
ListNode *C = nullptr;
ListNode *ans = nullptr;
while(A != nullptr && B != nullptr)
{
ListNode *s = new ListNode(0);
if(A->val > B->val)
{
s->val = B->val;
s->next = nullptr;
B = B->next;
}
else
{
s->val = A->val;
s->next = nullptr;
A = A->next;
}
if(C == nullptr)
{
C = s;
ans = C;
}
else
{
C->next = s;
C = C->next;
}
}
while(A != nullptr)
{
ListNode *s = new ListNode(0);
s->val = A->val;
s->next = nullptr;
if(C == nullptr)
{
C = s;
ans = C;
}
else
{
C->next = s;
C = C->next;
}
A = A->next;
}
while(B != nullptr)
{
ListNode *s = new ListNode(0);
s->val = B->val;
s->next = nullptr;
if(C == nullptr)
{
C = s;
ans = C;
}
else
{
C->next = s;
C = C->next;
}
B = B->next;
}
return ans;
}
ListNode *mergeKLists(vector<ListNode *> &lists) {
if(lists.empty())
{
return nullptr;
}
ListNode *ans;
ans = lists[0];
for(int i=1;i<lists.size();i++)
{
ans = mergetK(ans,lists[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};好吧,It appears that new nodes cannot be created,Only auxiliary pointers can be used.....(This problem is to merge two sorted linked lists,水题)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergetK(ListNode *A,ListNode *B)
{
ListNode *pA = A;
ListNode *pB = B;
ListNode *ans = nullptr;
ListNode *head = nullptr;
while(A != nullptr && B != nullptr)
{
if(A->val <= B->val)
{
if(ans == nullptr)
{
ans = A;
head = A;
}
else
{
head->next = A;
head = head->next;
}
//pA = A;
A = A->next;
}
else
{
if(ans == nullptr)
{
ans = B;
head = B;
}
else
{
head->next = B;
head = head->next;
}
//pB = B;
B = B->next;
}
}
if(A != nullptr)
{
head->next = A;
}
if(B != nullptr)
{
head->next = B;
}
return ans;
}
ListNode *mergeKLists(vector<ListNode *> &lists) {
if(lists.empty())
{
return nullptr;
}
ListNode *ans;
ans = lists[0];
for(int i=1;i<lists.size();i++)
{
if(lists[i] == nullptr)
{
continue;
}
ans = mergetK(ans,lists[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};我去,超时.....
![]()
It seems that this question is not as simple as I thought....
Analyze the time complexity of the code,,,,
遍历 litsts O(n)
内部:It's like traversing it once 链表 O(n+m)
这么算:O(n^2)
It depends on the time complexity O(nlogk)
kis the number of linked lists:说明只能从 遍历 litsts开了....
根据经验,The time complexity of merging two sorted linked lists is optimal O(n+m) 再一次说明 只能从 遍历 litsts优化了
等等,logK对数时间,The first reaction should be two points.我去,说不定可以解决
二分的前提:保证有序,nice,The conditions of the question are just in order(Because array subscripts are incremented)
优化后:
我操,终于过了.....感动,落泪.An hour woohoo....
两个链表的合并:(The previous code is a bit smallbug,There is one situation that requires special handling)
When a linked list is empty at the end:(Merging should not be required at this point)
[{-9},{},{-10,-8,-2,-1,2},{-10,-9,-7,-6,-5,-2,-2,1,4},{-7,-7,-1,0,4},{},{-4,0},{-9,-6,-5,-5,-2,2,3,3}]
更改:Make a special judgment,The merging of two ordered linked lists will not be mentioned,As long as you are serious, you can write it.
Merge two ordered linked list codes:
struct ListNode
{
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
ListNode* merge(ListNode *A,ListNode *B)
{
//特判 (A=nullptr && B=nullptr) 或者
// (A=nullptr && B!=nullptr) 或者 (A!=nullptr && B=nullptr)
if(A == nullptr || B == nullptr)
{
return A==nullptr ? B:A;
}
ListNode *head = nullptr;
ListNode *ans = nullptr;
while(A != nullptr && B != nullptr)
{
if(A->val <= B->val)
{
if(ans == nullptr)
{
ans = A;
head = A;
}
else
{
head->next = A;
head = head->next;
}
A = A->next;
}
else
{
if(ans == nullptr)
{
ans = B;
head = B;
}
else
{
head->next = B;
head = head->next;
}
B = B->next;
}
}
if(A != nullptr)
{
head->next = A;
}
if(B != nullptr)
{
head->next = B;
}
retrun ans;
}
Dichotomous ideas and codes:
There are two methods for bisection:递归(推荐使用) 非递归
Usually we just use recursion,好分析,好写代码
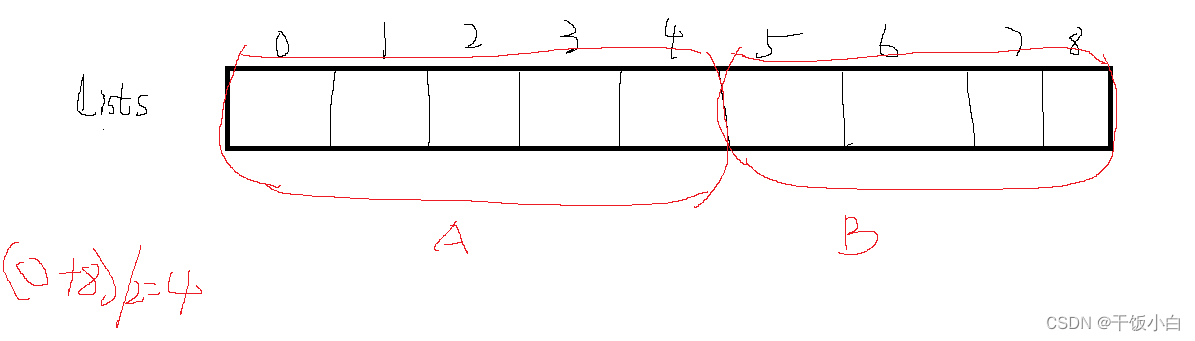
Let's look at an example to analyze:
Divide in half first: A和BThe process must be the same(Or divide a whole into two subproblems that are the same as the whole)
假设将A和Binto the smallest sub-problem,What should we do now????
Of course, the linked list is merged....
OK, let's merge,又看,A和BIt has not been divided to the minimum.(Recursion is a top-down process)
Why am I here to sayA和BConsider it the smallest sub-problem??This is the author's special understanding of recursion,If the solution space is drawn,Recursion does not require backtracking,Does it need to be merged when we go back to this level A和B.
ok....For ease of understanding, we might as well treat each state as a minimal problem,What is the solution to the minimum problem,We'll just do what we do,And the number is divided into the same problem as the sub-problem,It's just a scale traversal.
我们继续划分
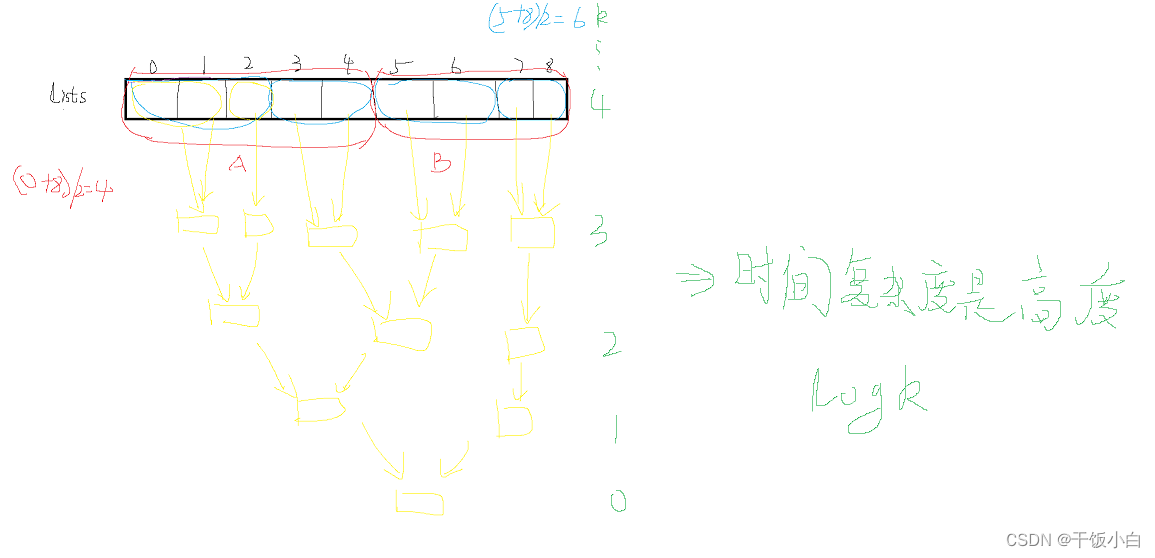
Let's write code(二分代码)
//The return value looks at the picture I drew above
ListNode* binary_lists(vector<ListNode *> &lists,int l,int r)
{
//先写边界条件(出口)
if(l == r)
{
return lists[l];
}
if(l > r)
{
return nullptr;
}
int mid = (l+r)/2;
//合并 A和B Because backtracking to this point requires mergingA和B
return merge(binary_lists(lists,l,mid),binary_lists(lists,mid+1,r));
}okk...
Let's put all the code together
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *ans1;
ListNode* merget(ListNode *A,ListNode *B)
{
if(A == nullptr || B == nullptr)
{
return A == nullptr ? B:A;
}
ListNode *pA = A;
ListNode *pB = B;
ListNode *ans = nullptr;
ListNode *head = nullptr;
while(A != nullptr && B != nullptr)
{
if(A->val <= B->val)
{
if(ans == nullptr)
{
ans = A;
head = A;
}
else
{
head->next = A;
head = head->next;
}
//pA = A;
A = A->next;
}
else
{
if(ans == nullptr)
{
ans = B;
head = B;
}
else
{
head->next = B;
head = head->next;
}
//pB = B;
B = B->next;
}
}
if(A != nullptr)
{
head->next = A;
}
if(B != nullptr)
{
head->next = B;
}
return ans;
}
ListNode* merList(vector<ListNode *> &lists,int l,int r)
{
if(l == r) //只有一条
{
return lists[l];
}
if( l > r)
{
return nullptr;
}
int mid = (l + r)/2;
return merget(merList(lists,l,mid),merList(lists,mid+1,r));
}
ListNode *mergeKLists(vector<ListNode *> &lists) {
if(lists.empty())
{
return nullptr;
}
// ans = lists[0];
// for(int i=1;i<lists.size();i++)
// {
// if(lists[i] == nullptr)
// {
// continue;
// }
// ans = mergetK(ans,lists[i]);
// }
return merList(lists,0,lists.size()-1);
}
};
小结:创作不易,Click to support it
如果有喜欢C++The students can view the author's other columns,全套C++都在更新(从C++基础到Linux系 system programming、网络编程 Data programming, etc... And there is a completeC++项目)
边栏推荐
- Use Cloudreve to build a private cloud disk
- LeetCode Daily Question (1573. Number of Ways to Split a String)
- 这款可视化工具神器,更直观易用!太爱了
- VLAN huawei 三种模式
- The Thread State,
- 今日睡眠质量记录75分
- 接口测试的概念、目的、流程、测试方法有哪些?
- Shell 编程--Sed
- xshell (sed command)
- Black cats take you learn Makefile article 13: a Makefile collection compile problem
猜你喜欢

Conditional Statements of Shell Programming (2)
C#【必备技能篇】Hex文件转bin文件的代码实现
链表中的节点每k个一组翻转

C # Hex file transfer skills necessary article 】 【 bin file code implementation
c语言之 练习题1 大贤者福尔:魔法数,神奇的等式
Service - DNS forward and reverse domain name resolution service
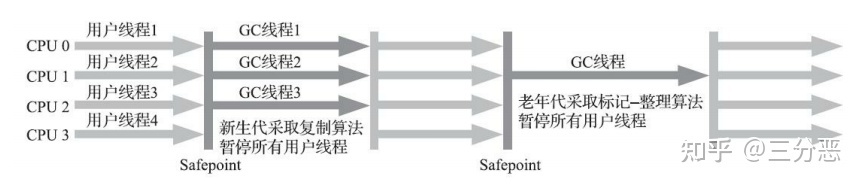
这些不可不知的JVM知识,我都用思维导图整理好了
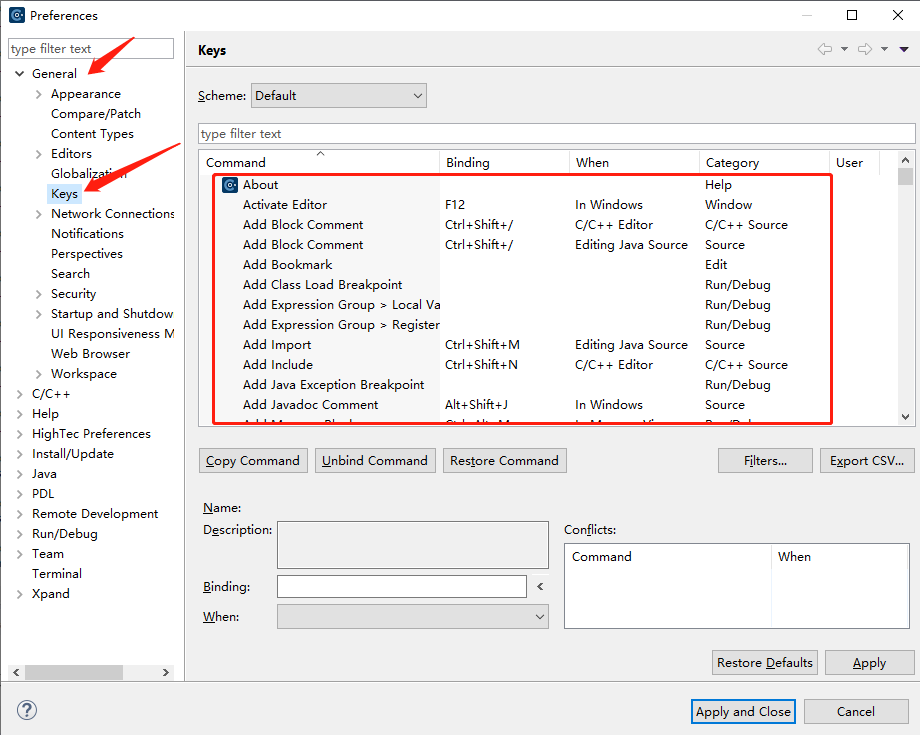
HighTec快捷键(Keys)设置位置
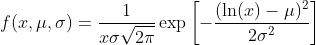
配电网络扩展规划:考虑使用概率性能源生产和消费概况的决策(Matlab代码实现)
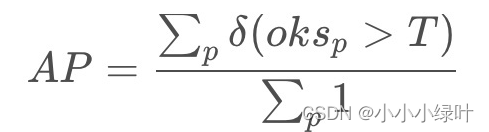
mmpose关键点(一):评价指标(PCK,OKS,mAP)
随机推荐
camera预览流程 --- 从HAL到OEM
美味的佳肴
LeetCode-36-Binary search tree and doubly linked list
JVM classic fifty questions, now the interview is stable
商家招募电商主播要考虑哪些内容
LeetCode Daily 2 Questions 01: Reverse Strings (both 1200) Method: Double Pointer
Live Classroom System 08 Supplement - Tencent Cloud Object Storage and Course Classification Management
“数据引擎”开启前装规模量产新赛道,「智协慧同」崭露头角
美味的石井饭
Service - DNS forward and reverse domain name resolution service
LeetCode-402 - Remove K digits
服务——DHCP原理与配置
从斐波那契 - 谈及动态规划 - 优化
Shell编程之条件语句(二)
SDP
Redis Performance Impact - Asynchronous Mechanisms and Response Latency
关于 DataFrame: 处理时间
华为HCIE云计算之Fusion Access桌面云
xshell (sed 命令)
2022年8月10日:使用 ASP.NET Core 为初学者构建 Web 应用程序--使用 ASP.NET Core 创建 Web UI(没看懂需要再看一遍)