当前位置:网站首页>Redis "8" implements distributed current limiting and delay queues
Redis "8" implements distributed current limiting and delay queues
2022-04-23 16:14:00 【Samson_ bu】
Form writing habits together ! This is my participation 「 Nuggets day new plan · 4 Yuegengwen challenge 」 Of the 8 God , Click to see the event details .
01- Distributed current limitation
01.1-Redis In the implementation of Lua Script
Redis Natural support Lua Script , In addition to being used as a distributed cache , It can also realize other functions , For example, distributed current limiting .
stay Redis 7 Before ,Lua Scripts can only pass through EVAL Command execution .
// key [key ...] Can be in Lua The script passes table KEYS visit , for example KEYS[1] Represents the first key
// arg [arg ...] Can be in Lua The script passes table ARGV visit , for example ARGV[1] Represents the first arg
EVAL script numkeys key [key ...] arg [arg ...]
Copy code About Lua You can refer to lua.org/user-manual. More about EVAL For information about the command, refer to redis.io.
01.2- Distributed current limiter implementation
The main idea of current limiter is to Redis Maintain a counter in , If the counter exceeds the limit, conduct current limiting . Current limiter Lua The script is as follows :
-- filter.lua
local c
-- see Redis Whether the counter in exceeds the limit , The counter for KEYS[1] , The threshold for ARGV[1]
c = redis.call('incr', KEYS[1])
-- Transfinite
if c and tonumber(c) > tonumber(ARGV[1]) then
return c;
end
-- If current limiting is called for the first time , Set the expiration time of the counter , The expiration date is from ARGV[2] Appoint
if tonumber(c) == 1 then
redis.call('expire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2])
end
return c;
Copy code 01.3- stay Spring-data-redis Call in Lua Script
Spring-data-redis in ,Lua The script is abstracted as RedisScript object .
@Bean(name = "filter_lua")
public RedisScript<Long> filterLuaScript() {
return RedisScript.of(new ClassPathResource("lua/filter.lua"), Long.class);
}
Copy code In need of execution Lua In the object of the script , Just get... From the container RedisScript object , And then use RedisTemplate Execution can be .
// this.filterLua It's the one above RedisScript object
// key by Redis The key corresponding to the counter in
// threshold ttl yes filter.lua Parameters required in , The duration counter and the threshold counter represent the duration, respectively
long count = (Long) this.redisTemplate.execute(this.filterLua,
singletonList(key),
threshold, ttl);
if (count > threshold) {
// It means the limit is exceeded
} else {
// No overrun
}
Copy code 01.4- stay Redisson Call in Lua Script
Redisson Execution is also provided in Lua Script interface . And Spring-data-redis The difference is ,Redisson It defines RScript To express Lua Script .
// redisson yes RedissonClient object
long count = (Long) redisson.getScript(StringCodec.INSTANCE).eval(
RScript.Mode.READ_WRITE,
script, // lua Script
RScript.ReturnType.INTEGER,
singletonList(key),
threshold, "30");
Copy code It should be noted that ,script Is a string . And Sping-data-redis Read from file Lua Compared with the way of script , stay Java Splicing code Lua Scripts are obviously more cumbersome , And less easy to maintain .
About the complete code of the above two methods , You can refer to my gitee.
02- Delay queue
Redis Sometimes it is also used to implement the delay queue function . The data structure related to the delay queue function is zset, The relevant commands are as follows :
- zadd key score member [score memeber ...], Add elements and fractions to an ordered set
- zrange key min max [withscores], Query by subscript [min, max] Elements in scope
- zrem key member [member ...], Remove elements from ordered collection
The idea of realizing delay queue is as follows :
- Producers will need delayed messages id Add to zset in , Its score is set to “ current time + Time to delay ”
- Consumers constantly rotate the size of the first element in the ordered set and the current time , If it exceeds the current time , It is considered that the delay has been met , Consume the news .
be based on Redisson The implementation code of is as follows :
// Producer thread , Responsible for adding messages to the delay queue
// obtain zset
String key = "example:delay:queue";
RScoredSortedSet<String> delayQueue = this.redisson.getScoredSortedSet(key);
// Each direction zset Add 5 Bar message , The message is a random UUID,score For the current time + Time delay
int d = Integer.parseInt(delay);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
String member = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
long score = System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000 + d;
boolean result = delayQueue.add(score, member);
if (result) {
LOGGER.info(" Insert a message :[{}]({})", member, score);
} else {
LOGGER.warn(" Failed to insert message :[{}]({})", member, score);
}
}
Copy code // Consumer thread
while (true) {
// obtain zset
RScoredSortedSet<String> delayQueue = this.redisson.getScoredSortedSet(key);
// If Redis There is no delay queue in the , Or there are no messages in the delay queue , Then rotate and wait
if (delayQueue == null || delayQueue.isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
// a. Check whether the element score of the queue header meets the delay
long score = delayQueue.firstScore().longValue();
if (score <= (System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000)) {
// b. News consumption
String message = delayQueue.pollFirst();
LOGGER.info("{} ms Consumed a message , news ID {}, Threads ID {}", System.currentTimeMillis(), message, Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
Copy code The code in the consumer is non thread safe in the case of multithreading , Some threads will be in b. Get null, The main reason is that steps a. and b. It's non atomic . Solution : Or lock it , Either through Lua The script makes the above two steps called atomic . Locking reduces concurrency performance , Here we mainly through Lua Script to solve non atomic problems .
To check and consume a message from a delay queue Lua The script is as follows :
-- consume.lua
local entry = redis.call('zrange', KEYS[1], 0, 0, 'WITHSCORES')
if entry then
if entry[2] and tonumber(entry[2]) <= tonumber(ARGV[1]) then
redis.call('zrem', KEYS[1], entry[1])
return entry[1]
end
end
return nil;
Copy code The producer thread does not need to change , The usage in the consumer thread is changed to :
while (true) {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000;
final String message = this.redisTemplate.execute(this.consumeScriptLua, Collections.singletonList(key), now + "");
if (null != message) {
LOGGER.info("{} ms Consumed a message , news ID {}, Threads ID {}", System.currentTimeMillis(), message, Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {}
}
Copy code For complete sample code, please refer to my gitee .
Let's analyze the disadvantages of this way of implementing delay queue :
- First , Use rotation training , It's definitely a waste CPU Resources
- secondly , Not very accurate , There is a certain error .
Article history
Redis 「7」 Implement distributed locks
Redis 「6」 Implement message queuing
Redis 「5」 Event handling model and key expiration policy
Redis 「4」Redis Application in second kill system
版权声明
本文为[Samson_ bu]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https:https://yzsam.com/html/MzcuRx.html
边栏推荐
- PHP 零基础入门笔记(13):数组相关函数
- MySQL - MySQL查询语句的执行过程
- PS add texture to picture
- Filter usage of spark operator
- 撿起MATLAB的第(9)天
- Force buckle - 198 raid homes and plunder houses
- 捡起MATLAB的第(2)天
- 捡起MATLAB的第(4)天
- You need to know about cloud disaster recovery
- Best practice of cloud migration in education industry: Haiyun Jiexun uses hypermotion cloud migration products to implement progressive migration for a university in Beijing, with a success rate of 1
猜你喜欢
Day 10 abnormal mechanism
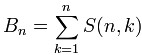
C, calculation method and source program of bell number
捡起MATLAB的第(8)天
Ice -- source code analysis

Research and Practice on business system migration of a government cloud project
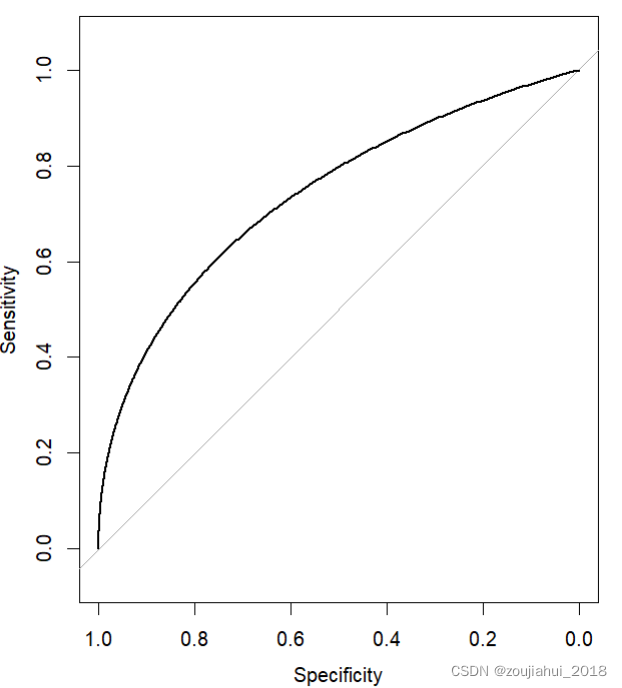
Method 2 of drawing ROC curve in R language: proc package
撿起MATLAB的第(9)天
How important is the operation and maintenance process? I heard it can save 2 million a year?

The solution of not displaying a whole line when the total value needs to be set to 0 in sail software
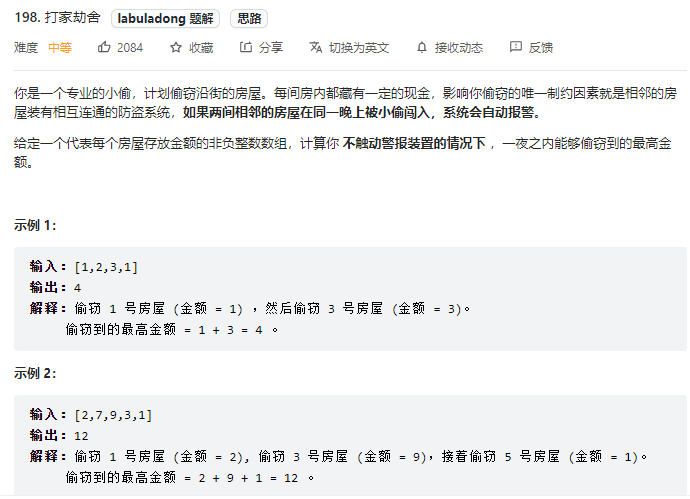
Force buckle - 198 raid homes and plunder houses
随机推荐
Download and install mongodb
451. 根据字符出现频率排序
Win11 / 10 home edition disables the edge's private browsing function
Intersection, union and difference sets of spark operators
ESP32编译环境的搭建
JIRA screenshot
Using JSON server to create server requests locally
How to quickly batch create text documents?
C语言自编字符串处理函数——字符串分割、字符串填充等
Day (10) of picking up matlab
Day 10 abnormal mechanism
What does cloud disaster tolerance mean? What is the difference between cloud disaster tolerance and traditional disaster tolerance?
C language self compiled string processing function - string segmentation, string filling, etc
下载并安装MongoDB
Website pressure measurement tools Apache AB, webbench, Apache jemeter
Oak-d raspberry pie cloud project [with detailed code]
Cloudy data flow? Disaster recovery on cloud? Last value content sharing years ago
Config learning notes component
基于GPU实例的Nanopore数据预处理
R语言中绘制ROC曲线方法二:pROC包