当前位置:网站首页>Using MATLAB programming to realize the steepest descent method to solve unconstrained optimization problems
Using MATLAB programming to realize the steepest descent method to solve unconstrained optimization problems
2022-04-23 14:35:00 【I channel I】
This article contains the following
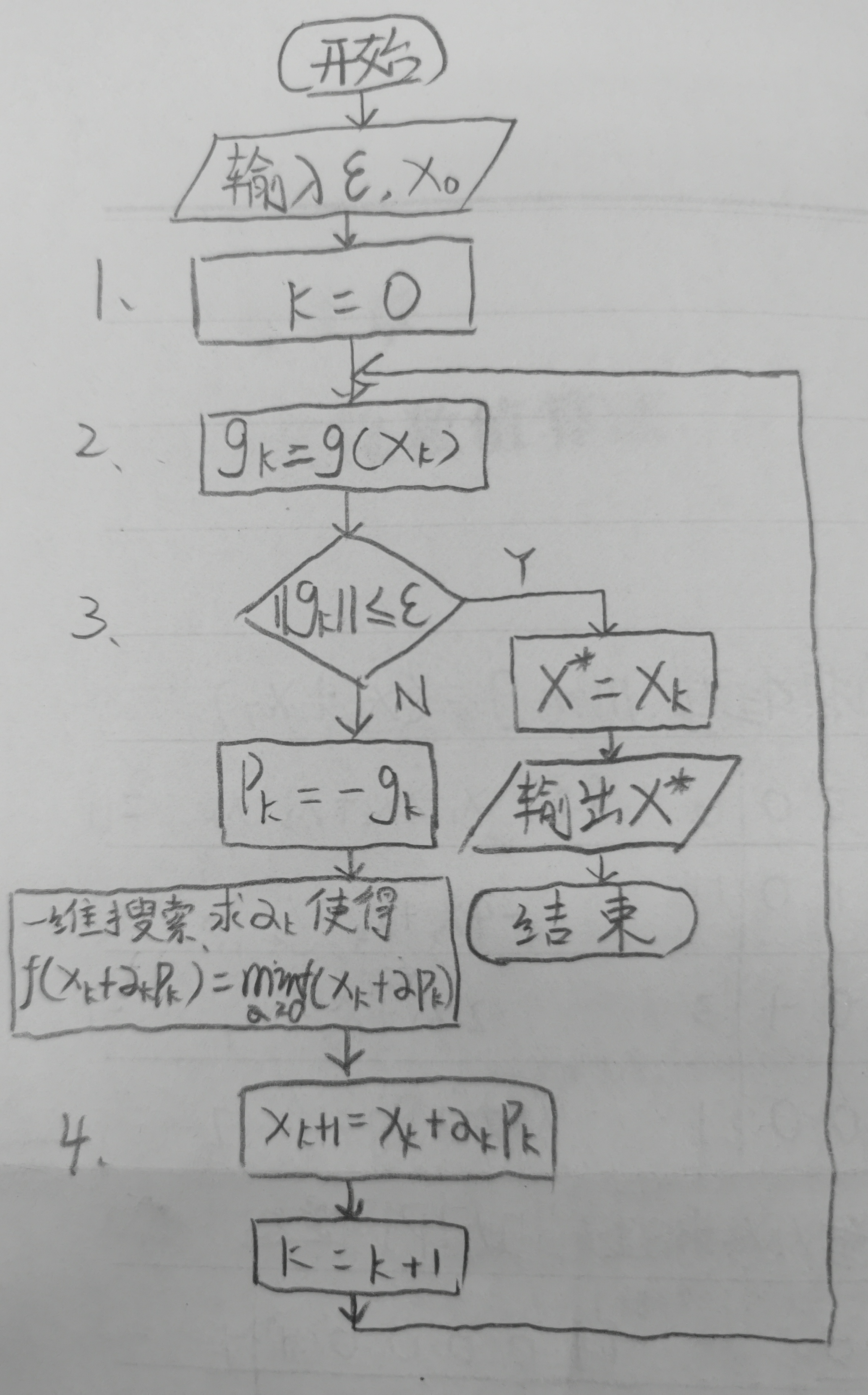
1、 Draw the algorithm flow chart of the steepest descent method ;
2、MATLAB Write gradient calculation function using numerical differentiation method ( Functional expression M file );
3、MATLAB Write the function of steepest descent method to solve unconstrained optimization problem , It is required to use the golden section method for accurate one-dimensional search , Calculate the gradient by numerical differentiation ( Functional expression M file , Precision set to epson Adjustable );
4、MATLAB Write the function of steepest descent method to solve unconstrained optimization problem , Required Wolfe-Powell Inexact one-dimensional search , Calculate the gradient by numerical differentiation ( Functional expression M file , Precision set to epson Adjustable );
5、MATLAB Programming ( imperative M file ), Using exact search and imprecise search respectively The steepest descent method , Solve the following problem :

Accuracy of 0.001, The initial point is (-1,1);
Change the initial point to (-1.2,1) Rerun , Run the observation .
In this experiment, the function is used separately function Calculation
function y=f(x)
if(length(x)==1)
global xk;
global pk;
x=xk+x*pk;
end
y=100*(x(2)-x(1)^2)^2+(1-x(1))^2;1. Algorithm flow chart of steepest descent method
2、MATLAB Write gradient calculation function using numerical differentiation method ( Functional expression M file );
function g=shuzhiweifenfa(x)
for i = 1:length(x)
m=zeros(1,length(x));
m(i)=(10^-3)/2;
g(i)=f(x+m)-f(x-m);
end
g=g/10^-3;3、 The steepest descent method is a function for solving unconstrained optimization problems , The golden section method is used to search one-dimensional accurately , Calculate the gradient by numerical differentiation ( Functional expression M file , Precision set to epson Adjustable );
function x=zuisuxiajiangfa_hjfg(e,x)
%step 1
% Not used k, Store only the value of the current iteration .
global xk;
global pk;
while 1
%step 2
g=shuzhiweifenfa(x);
%step 3
% The norm uses the square sum and the open root sign
if sqrt(sum(g.^2))<=e
return;
end
pk=-g;
xk=x;
% These two functions are shown in the previous code (matlab General algorithm of unconstrained optimization )
[a,b,c]=jintuifa(0,0.1);
a=huangjinfenge(a,c,10^-4);
%step 4
x=x+a*pk;
end
4、 The steepest descent method is a function for solving unconstrained optimization problems , Required Wolfe-Powell Inexact one-dimensional search , Calculate the gradient by numerical differentiation ( Functional expression M file , Precision set to epson Adjustable );
function a=Wolfe_Powell(x,pk)
%step 1
u=0.1;
b=0.5;
a=1;
n=0;
m=10^100;
%step 2
fx=f(x);
g=shuzhiweifenfa(x);
while 1
xk=x+a*pk;
fxk=f(xk);
gk=shuzhiweifenfa(xk);
if (fx-fxk)>=(-u*a*g*pk.')%(3-1)
if (gk*pk.')>=(b*g*pk.')%(3-2)
return;
else
%step 4
n=a;
a=min(2*a,(a+m)/2);
end
else
%step 3
m=a;
a=(a+n)/2;
end
end
function x=zuisuxiajiangfa_Wolfe(e,x)
%step 1
% Not used k, Store only the value of the current iteration .
while 1
%step 2
g=shuzhiweifenfa(x);
%step 3
% The norm uses the square sum and the open root sign
if sqrt(sum(g.^2))<=e
return;
end
pk=-g;
a=Wolfe_Powell(x,pk);
%step 4
x=x+a*pk;
end
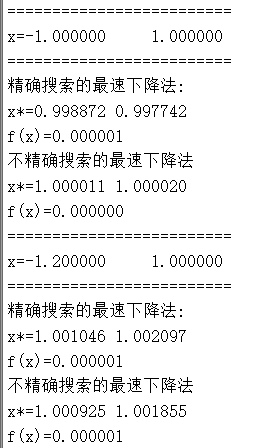
5、 Using exact search and imprecise search respectively The steepest descent method , problem :

clear
clc
for i=1:2
if(i==1)
x=[-1,1];
fprintf('=========================');
fprintf('\nx=%f\t\t%f\n',x(1),x(2));
fprintf('=========================\n');
else
x=[-1.2,1];
fprintf('=========================');
fprintf('\nx=%f\t\t%f\n',x(1),x(2));
fprintf('=========================\n');
end
fprintf(' The steepest descent method for accurate search :\n');
x_=zuisuxiajiangfa_hjfg(10^-3,x);
fprintf('x*=%f\t%f\n',x_(1),x_(2));
fprintf('f(x)=%f\n',f(x_));
fprintf(' The steepest descent method of imprecise search \n');
x_=zuisuxiajiangfa_Wolfe(10^-3,x);
fprintf('x*=%f\t%f\n',x_(1),x_(2));
fprintf('f(x)=%f\n',f(x_));
endresult :
版权声明
本文为[I channel I]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231433048632.html
边栏推荐
- 全连接层的作用是什么?
- Redis cluster 原理
- 科技的成就(二十一)
- Man man notes and @ reboot usage of crontab
- After entering the new company, the operation and maintenance engineer can understand the deployment of the system from the following items
- OpenFaaS实战之四:模板操作(template)
- Detailed explanation of C language knowledge points -- first knowledge of C language [1]
- 8.4 循环神经网络从零实现
- QT actual combat: Yunxi chat room
- Tongxin UOS php7 2.3 upgrade to php7.0 two point two four
猜你喜欢
L'externalisation a duré quatre ans.

1N5408-ASEMI整流二极管1N5408

DS1302的电子万年历_51单片机,年月日、星期、时分秒、农历和温度,带闹钟,全套资料
顺序栈的基本操作
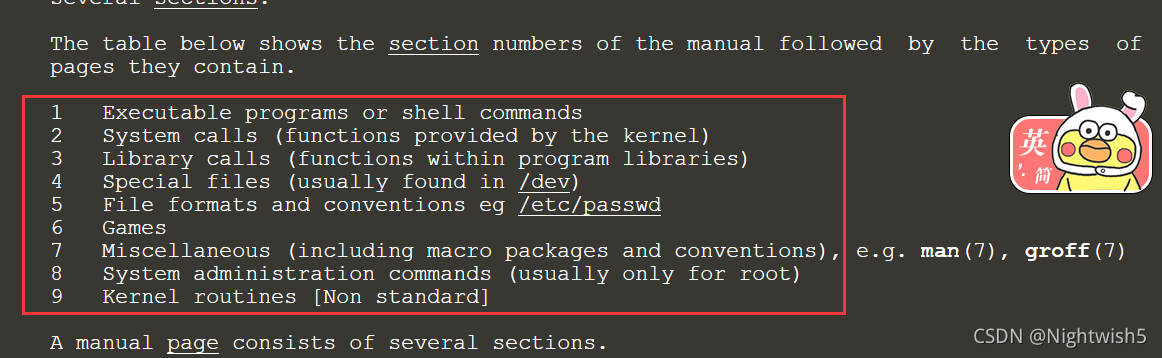
Man man notes and @ reboot usage of crontab
电容
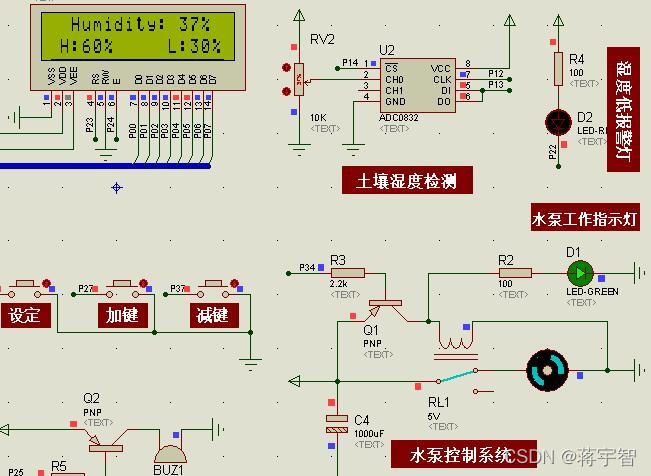
51单片机的花卉、农田自动浇水灌溉系统开发,Proteus仿真,原理图和C代码

I thought I could lie down and enter Huawei, but I was confused when I received JD / didi / iqiyi offers one after another
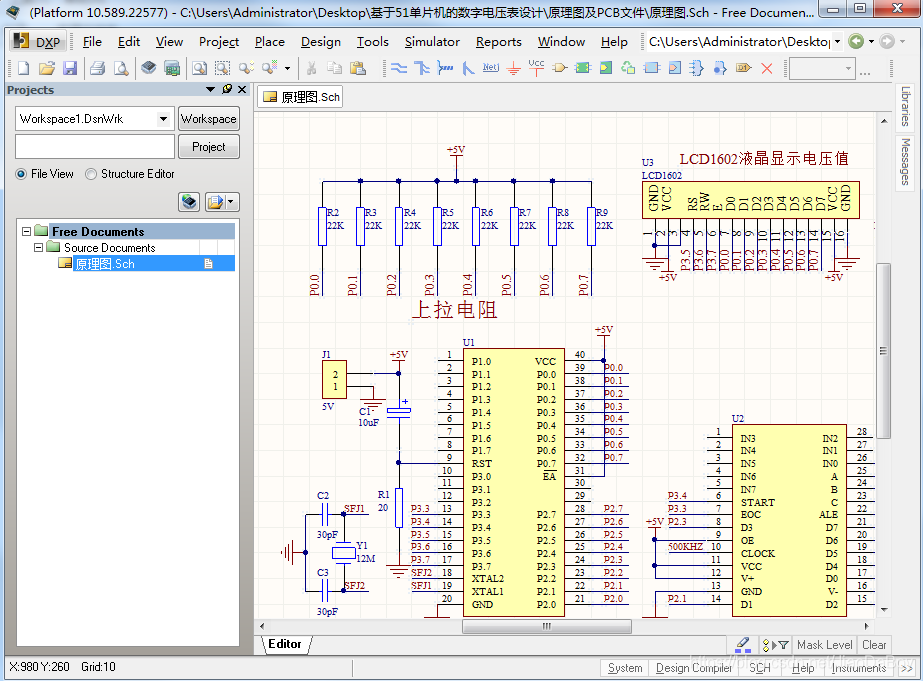
AT89C51单片机的数字电压表开发,量程0~5V,proteus仿真,原理图PCB和C程序等

如何5分钟上手使用OCR
随机推荐
A good tool: aardio
I thought I could lie down and enter Huawei, but I was confused when I received JD / didi / iqiyi offers one after another
JumpServer
asp.net使用MailMessage发送邮件的方法
pnpm安装使用
《JVM系列》 第七章 -- 字节码执行引擎
C语言知识点精细详解——数据类型和变量【1】——进位计数制
Use cases of the arrays class
查找水仙花数-for循环实践
MDS55-16-ASEMI整流模块MDS55-16
线程同步、生命周期
Qt界面优化:鼠标双击特效
【NLP】HMM隐马尔可夫+维特比分词
【无标题】
数组模拟队列进阶版本——环形队列(真正意义上的排队)
async void 导致程序崩溃
循环队列的基本操作,你学会了吗?
本以为能躺着进华为,结果陆续收到京东/滴滴/爱奇艺offer的我迷茫了
分分钟掌握---三目运算符(三元运算符)
flannel 原理 之 子网划分