当前位置:网站首页>信息学一本通-小球
信息学一本通-小球
2022-04-23 05:51:00 【Round moon】
小球
问题描述
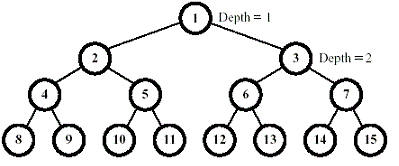
许多的小球一个一个的从一棵满二叉树上掉下来组成FBT(Full Binary Tree,满二叉树),每一时间,一个正在下降的球第一个访问的是非叶子节点。然后继续下降时,或者走右子树,或者走左子树,直到访问到叶子节点。决定球运动方向的是每个节点的布尔值。最初,所有的节点都是false,当访问到一个节点时,如果这个节点是false,则这个球把它变成true,然后从左子树走,继续它的旅程。如果节点是true,则球也会改变它为false,而接下来从右子树走。满二叉树的标记方法如下图:
因为所有的节点最初为false,所以第一个球将会访问节点1,节点2和节点4,转变节点的布尔值后在在节点8停止。第二个球将会访问节点1、3、6,在节点12停止。明显地,第三个球在它停止之前,会访问节点1、2、5,在节点10停止。
现在你的任务是,给定FBT的深度D,和I,表示第I个小球下落,你可以假定I不超过给定的FBT的叶子数,写一个程序求小球停止时的叶子序号。
输入
一行包含两个用空格隔开的整数D和I。其中2≤D≤20,1≤I≤524288。
输出
对应输出第I个小球下落停止时的叶子序号。
Sample Input
4 2
Sample Output
12
思路解析
稍微观察一下,整体上他是分成两份,左右分别放子,在第一层尤为明显。
我们可以想象一下,当最后一个球下落的时候。要么是构成左右平衡,要么是左右不平和,废话
但是我觉着这个才是关键,往往被人忽略。
我们还发现一个规律如果当前的小球是奇数个他会走左侧。当我们平衡掉两侧收如果有子那么走左侧,去掉一半,这个一半不包括多出来的那个球。所有要向上取整。对于除以二的向上取整只需要在原数上+1即可
如果是平衡的那么就是偶数个,那么他会走右侧。
规律大致如上,下面请看代码。
Accepted Code
//#include<unordered_map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<math.h>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<deque>
#include<map>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
const ll ll_inf = 9223372036854775807;
const int int_inf = 2147483647;
const short short_inf = 32767;
const ll less_inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const char char_inf = 127;
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#define accelerate cin.tie(NULL);cout.tie(NULL);ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define PI 3.141592653589793
#define EPS 1.0e-8
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
ll lcm(ll a, ll b) {
return a / gcd(a, b) * b;
}
inline ll read() {
ll c = getchar(), Nig = 1, x = 0;
while (!isdigit(c) && c != '-')c = getchar();
if (c == '-')Nig = -1, c = getchar();
while (isdigit(c))x = ((x << 1) + (x << 3)) + (c ^ '0'), c = getchar();
return Nig * x;
}
inline void out(ll a) {
if (a < 0)putchar('-'), a = -a;
if (a > 9)out(a / 10);
putchar(a % 10 + '0');
}
ll qpow(ll x, ll n, ll mod) {
ll res = 1;
while (n > 0) {
if (n & 1)res = (res * x) % mod;
x = (x * x) % mod;
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
#define read read()
int main()
{
int n = read, m = read;
ll ans = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if (m & 1)
{
ans <<= 1;
m = (m + 1) >> 1;
}
else
{
ans = 1 + (ans << 1);
m >>= 1;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
By-Round Moon
版权声明
本文为[Round moon]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35339563/article/details/122383968
边栏推荐
- [UDS unified diagnosis service] i. diagnosis overview (1) - diagnosis overview
- Introduction to nonparametric camera distortion model
- 【UDS统一诊断服务】四、诊断典型服务(1)— 诊断和通信管理功能单元
- 基于VGG卷积神经网络的图像识别代码实现
- jenkspy包安装
- Programmers can also write novels
- 进程管理命令
- _findnext 报错
- 【UDS统一诊断服务】四、诊断典型服务(3)— 读故障信息功能单元(存储数据传输功能单元)
- [UDS unified diagnostic service] II. Network layer protocol (1) - overview and functions of network layer
猜你喜欢
基于VGG对五种类别图片的迁移学习
![[UDS unified diagnosis service] i. diagnosis overview (1) - diagnosis overview](/img/c5/4b3092daeabf0f4889d93fef327c88.png)
[UDS unified diagnosis service] i. diagnosis overview (1) - diagnosis overview
copy constructor
基于TensorFlow的线性回归实例
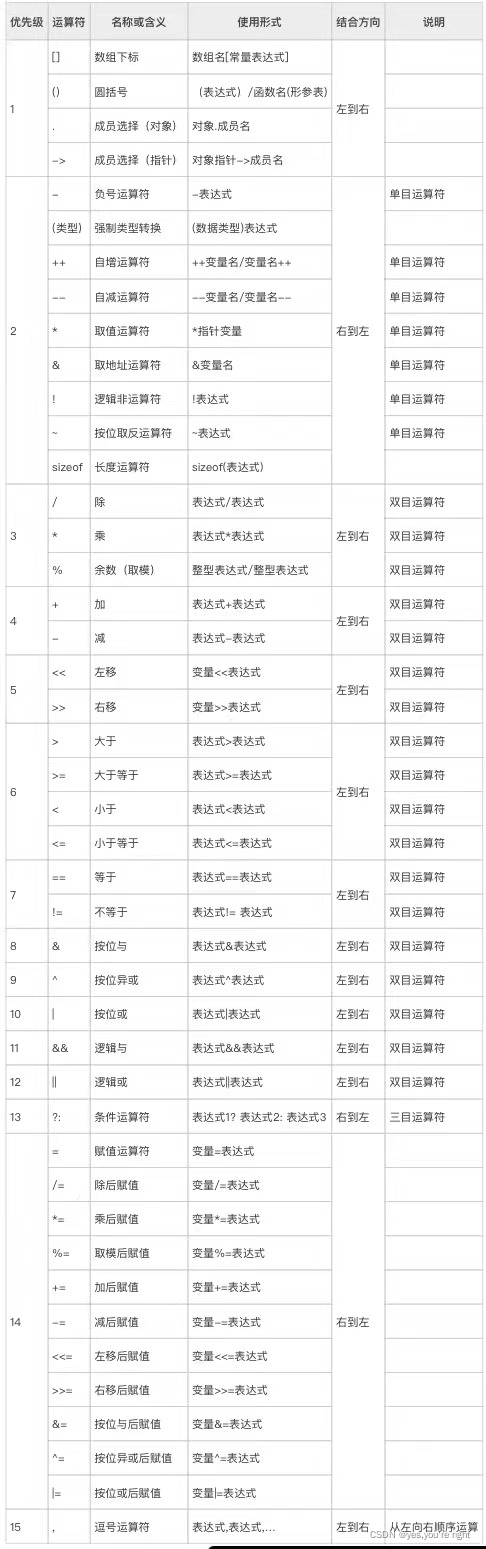
C语言的运算符

for()循环参数调用顺序
Programmers can also write novels
![[UDS unified diagnostic service] II. Network layer protocol (2) - data transmission rules (single frame and multi frame)](/img/4f/315a9b4cd85ebaad39cfa985dea45b.png)
[UDS unified diagnostic service] II. Network layer protocol (2) - data transmission rules (single frame and multi frame)

拷贝构造函数
逻辑回归原理及代码实现
随机推荐
声明为全局变量
【UDS统一诊断服务】(补充)五、ECU bootloader开发要点详解 (2)
函数的调用过程
逻辑回归原理及代码实现
类和对象的初始化(构造函数与析构函数)
基于VGG对五种类别图片的迁移学习
[UDS unified diagnostic service] III. application layer protocol (1)
[UDS] unified diagnostic service (UDS)
Detailed arrangement of knowledge points of University probability theory and mathematical statistics
LaTeX配置与使用
File viewing commands and user management commands
修改注册表的值
【UDS统一诊断服务】一、诊断概述(2)— 主要诊断协议(K线和CAN)
爬虫之requests基本用法
vs中的多字节与unicode
利用文件保存数据(c语言)
Notes on advanced points of C language 4
C#中?的这种形式
[learn] HF net training
文件查看命令和用户管理命令