当前位置:网站首页>Fundamentals of in-depth learning -- a simple understanding of meta learning (from Li Hongyi's course notes)
Fundamentals of in-depth learning -- a simple understanding of meta learning (from Li Hongyi's course notes)
2022-04-23 05:59:00 【umbrellalalalala】
Know that the account with the same name is released synchronously
Catalog
One 、 A preliminary understanding
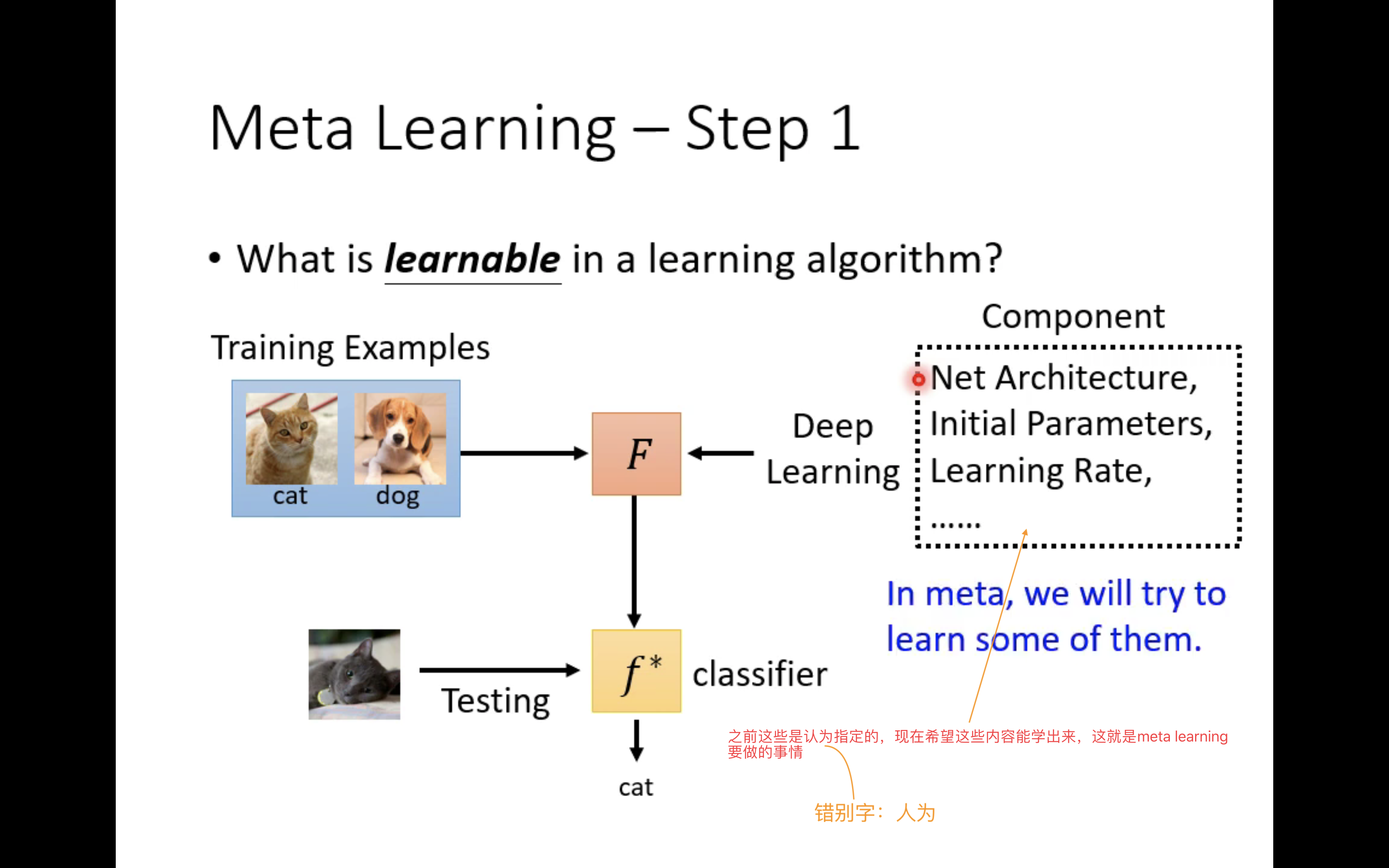
Let's take the classification problem as an example , before , The purpose of learning is to learn a binary classifier f ∗ f^* f∗; Now? , The purpose of learning is to learn a learning algorithm F, This learning algorithm F Be able to learn a binary classifier f ∗ f^* f∗.
Since you want to learn a learning algorithm directly F, Then we have to consider its parameters . Past learning , Is to learn a specific binary classifier f ∗ f^* f∗, Suppose that the learning algorithm specified artificially is a perceptron , So the process of parameter learning needs to be improved w w w and b b b. For now meta learning, The goal is to learn the algorithm directly F, Then the parameters that need attention ( In the picture above “component” Express ) Network architecture 、 Initialize parameters 、 Learning rate and so on , We use it Φ \Phi Φ To represent these parameters , Φ \Phi Φ Also known as learnable components.
meta learning Training process of , Is constantly adjusting Φ \Phi Φ, So as to obtain a good learning algorithm F, Then in the use phase , Users can use F To train a binary classifier on a given data set f ∗ f^* f∗, This two classifier should be a good two classifier .
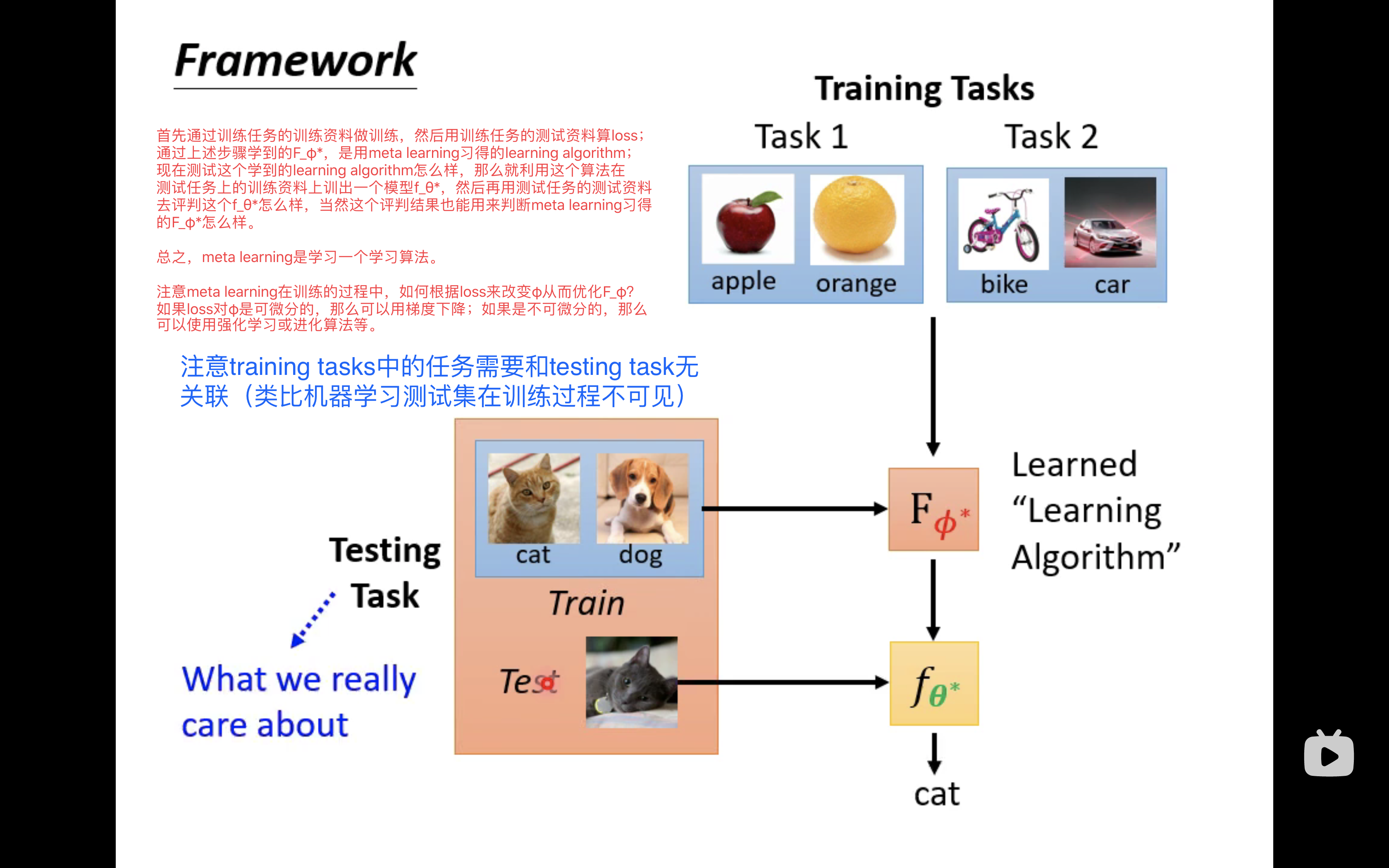
The picture above is meta learning An overall process architecture . To be specific , In previous studies , We have a training set , There is a test set , On the training set, we use the perceptron algorithm to train a loss Lower two classifiers , Then test whether the two classifiers are good or not on the test set ; And now there is meta learning, The situation has changed , We have a training task set ( There are a lot of training tasks in it ), There is a test task , There are training materials and test materials in each training task , There are training materials and test materials in each test task , We use this training task set or a pile of training tasks to train a good learning algorithm F Φ ∗ F_{\Phi^*} FΦ∗, Then in the test phase , Using this learning algorithm F Φ ∗ F_{\Phi^*} FΦ∗ A binary classifier is trained from the training data in the test task f θ ∗ f_{\theta^*} fθ∗, Then test the two classifiers on the test data in the test task f θ ∗ f_{\theta^*} fθ∗ Is it good or not .

( Of course , The obvious thing is , As in previous studies , The test data cannot appear the same in the training process , stay meta learning in , Test tasks cannot be used during training .)
Seeing this, you may have questions ,meta learning To do so , Will it be a little superfluous ? Why do you have to learn algorithms first F, Then use the learning algorithm F To learn two classifiers f Well ? Learn two classifiers directly f Is it not good? ?
actually , In reality , We may face a problem , That is the lack of data . Take the above two classification problems as an example , If you want to classify cats and dogs , that labeled training data It's a lot , But if you're going to treat a strange looking beast —— For example, African pangolins and maned wolves are classified , And you have only a small amount of labeled training data, So what to do now ? Let's start with the answer : What you can do at this time is , Find a lot of training tasks , These tasks can include cat and dog classification tasks 、 Apple orange two classification task 、 Car and bicycle two classification tasks, etc , In short, these tasks are labeled data Very abundant , Then you take these two category tasks as meta learning The training task of , To train a binary learning algorithm F, Then take the dichotomous task of African pangolin and maned wolf as the test task , You may only collect a small amount of... For this test task labeled data, That is, there are few training materials and test materials for this training task , But because you already have a good F, Then you can use F On this small amount of training materials, a two classifier of African pangolin and maned wolf is trained ( Then test the two classifiers on the test data ).
Next , Let me further elaborate on the rationality of the above process , That is, we use easy data to train F, And then use F Train on data that is not easy to collect f, Why this f It can be effective ? We analyze this problem from the perspective of people's own growth , Just imagine , Before you can tell the difference between a computer and a mobile phone , You've probably only seen a few mobile phones 、 Several computers , But you can successfully distinguish between a computer and a mobile phone . Seems to be , You train yourself to “ Computer mobile phone II ” front , And I didn't get much training material , So why can you succeed ? actually , That's because you have accumulated a lot of experience in your previous life , Maybe when you were in primary school and middle school , You've seen the difference between whiteboard and blackboard , So you understand that objects can be distinguished by color ; Maybe you have eaten Tangyuan and xuetangyuan ( An ice cream ), Although they are very similar , But you see that objects can be distinguished by temperature ; Maybe you have encountered countless kinds of round and square objects in your life , So you see that shape is also an important reference for distinguishing objects … In short, before you come into contact with mobile phones and computers , You may have trained yourself on countless dichotomous problems , let me put it another way , You've been exposed to a huge amount of training materials for binary training tasks , Learning a learning algorithm for binary classification problem F. So now , When you first came into contact with computers and mobile phones , When thinking about the difference between them , You start using F In a small number of computers 、 Training computer on mobile training materials - The process of mobile phone two classifier , So I can easily get a good computer - Mobile phone II f.
That's all for the image , Next, let's go back to meta learning The technology itself .
Look again at the process architecture in the above picture , We said ,F It's trained by a bunch of training tasks , But I didn't talk about how to do it in the training process . We know that there are training materials and test materials in each training task , You may ask , Just mentioned how the training materials and test materials in the test task should be used , But we haven't talked about how to use the training materials and test materials in the training task , So how should I use it ? How to use the training materials in this pile of training tasks to train this learning algorithm F Φ ∗ F_{\Phi^*} FΦ∗ Well ? What is the purpose of the test data in this pile of training tasks ? How do we calculate this as usual loss Well ? Even with loss, How to optimize learnable components Φ \Phi Φ Well ?
Next, answer this question :
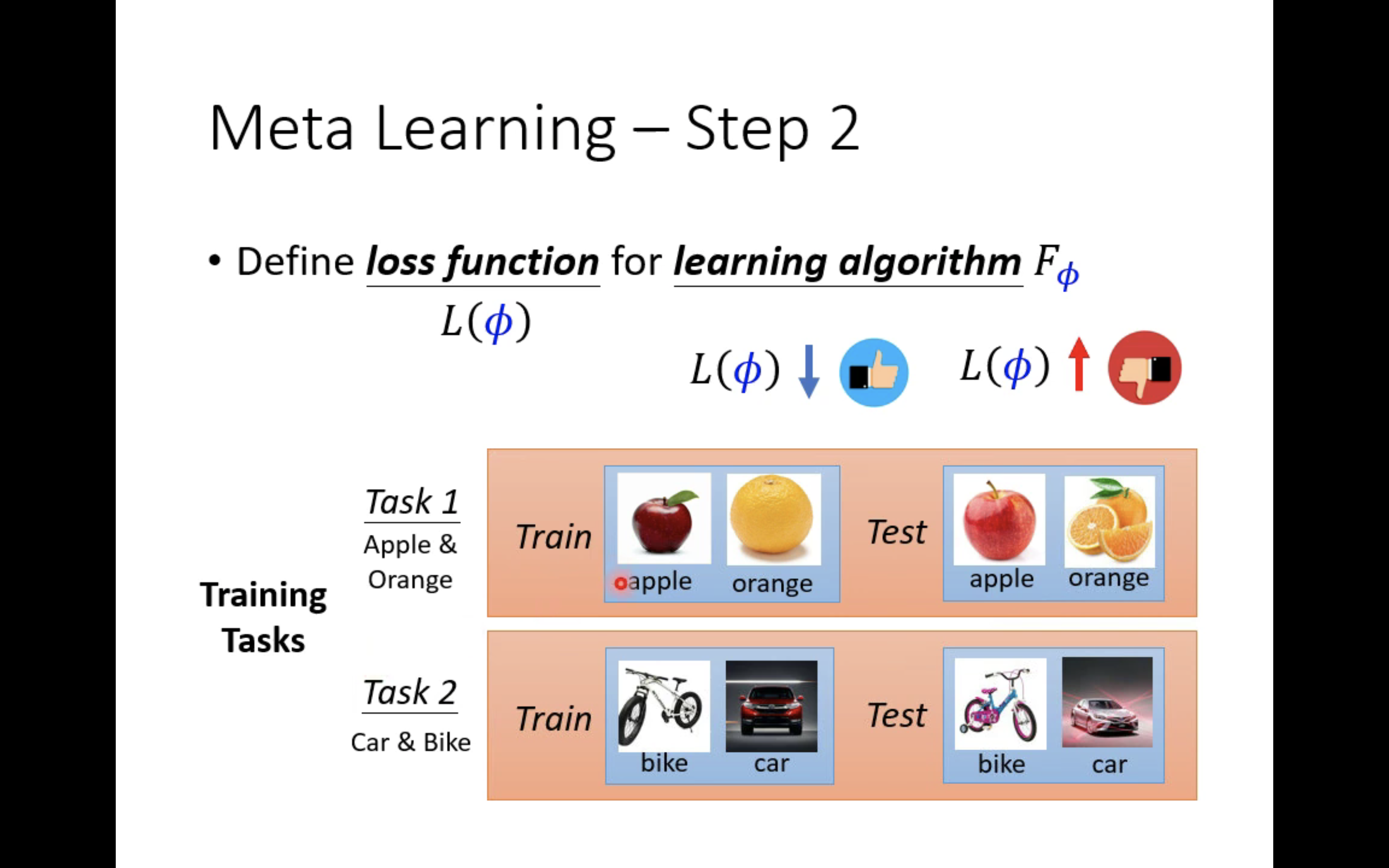
The figure above shows a training process . hypothesis , There are two tasks in the training task set , Task one is apple orange classification task , The second task is to classify bicycles and cars . Task 1 has some photos of apples and oranges as training materials , There are some photos of apples and oranges as test data ; Task 2 has some photos of bicycles and cars as training materials , There are some photos of bicycles and cars as test data .

Like traditional learning , At first we need to initialize learnable component Φ \Phi Φ, So we have an initial learning algorithm F Φ F_\Phi FΦ.
Let's do something about task one first , All you have to do is use F Φ F_\Phi FΦ The training materials in it ( Some photos of apples and oranges ) Come up and train a two classifier f θ 1 ∗ f_{\theta^{1*}} fθ1∗, This θ 1 ∗ \theta^{1*} θ1∗ It refers specifically to the use of F Φ F_\Phi FΦ Two classifiers learning on task one f θ 1 ∗ f_{\theta^{1*}} fθ1∗ Parameters of .
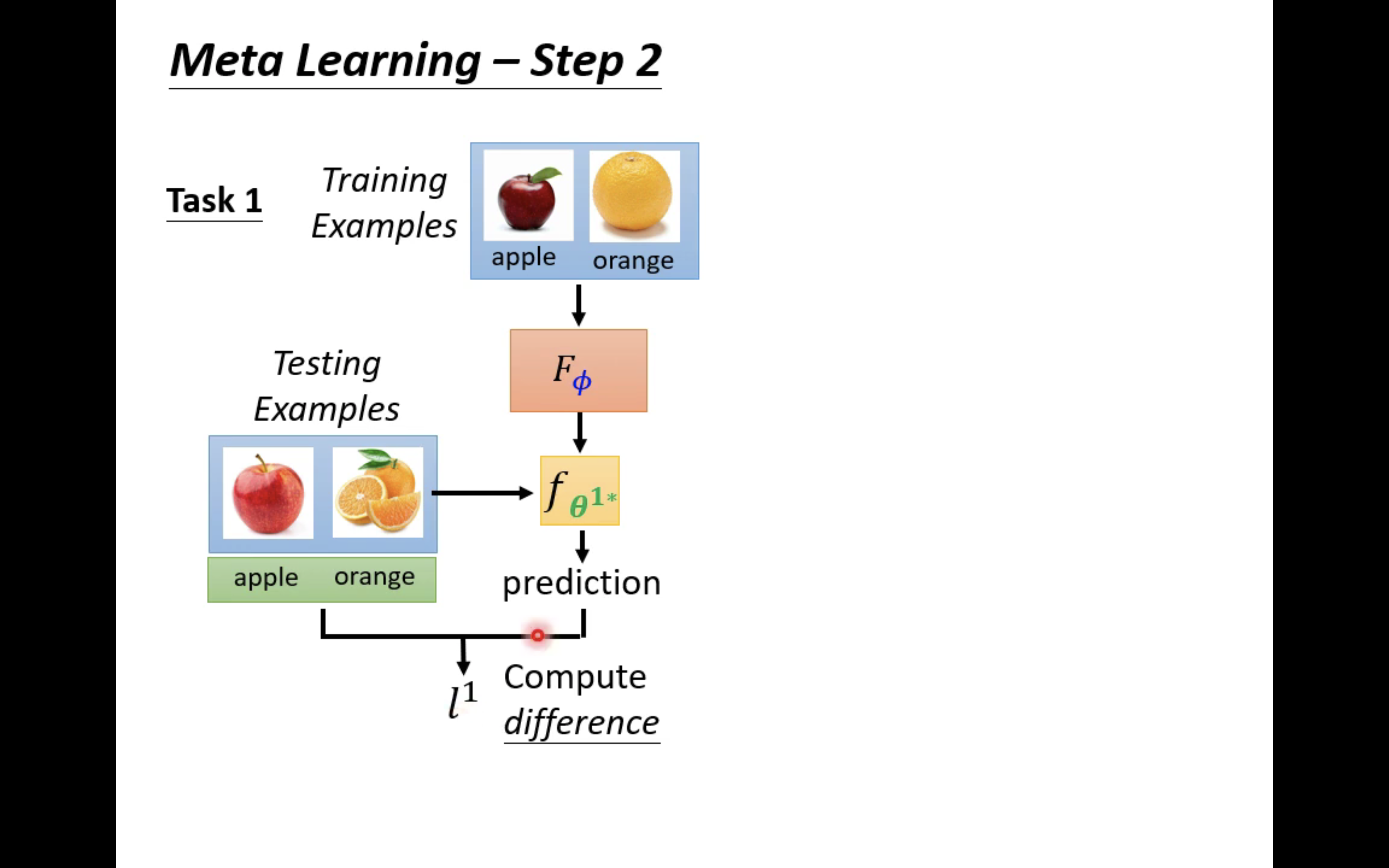
then , Use this two classifier to test the test data of task 1 , To calculate a loss l 1 l^1 l1;
similarly , We can also repeat the above process for task 2 , To get loss l 2 l^2 l2:
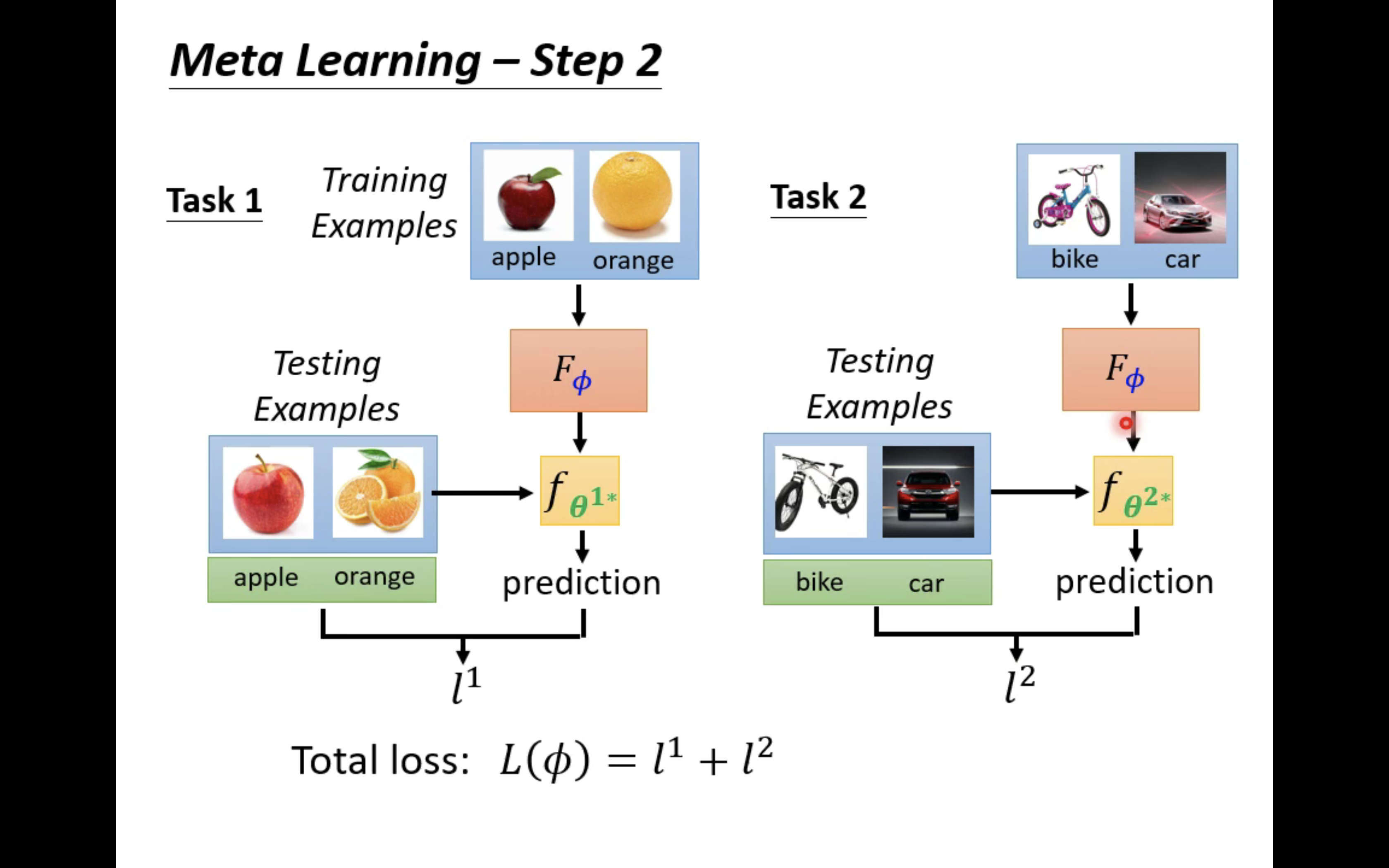
The final loss Nature is equal to l 1 + l 2 l^1+l^2 l1+l2
Of course , If the training task focus has N A mission , So the final loss As shown in the figure below :

There is now a loss, Naturally, it can be optimized , Here's the picture :
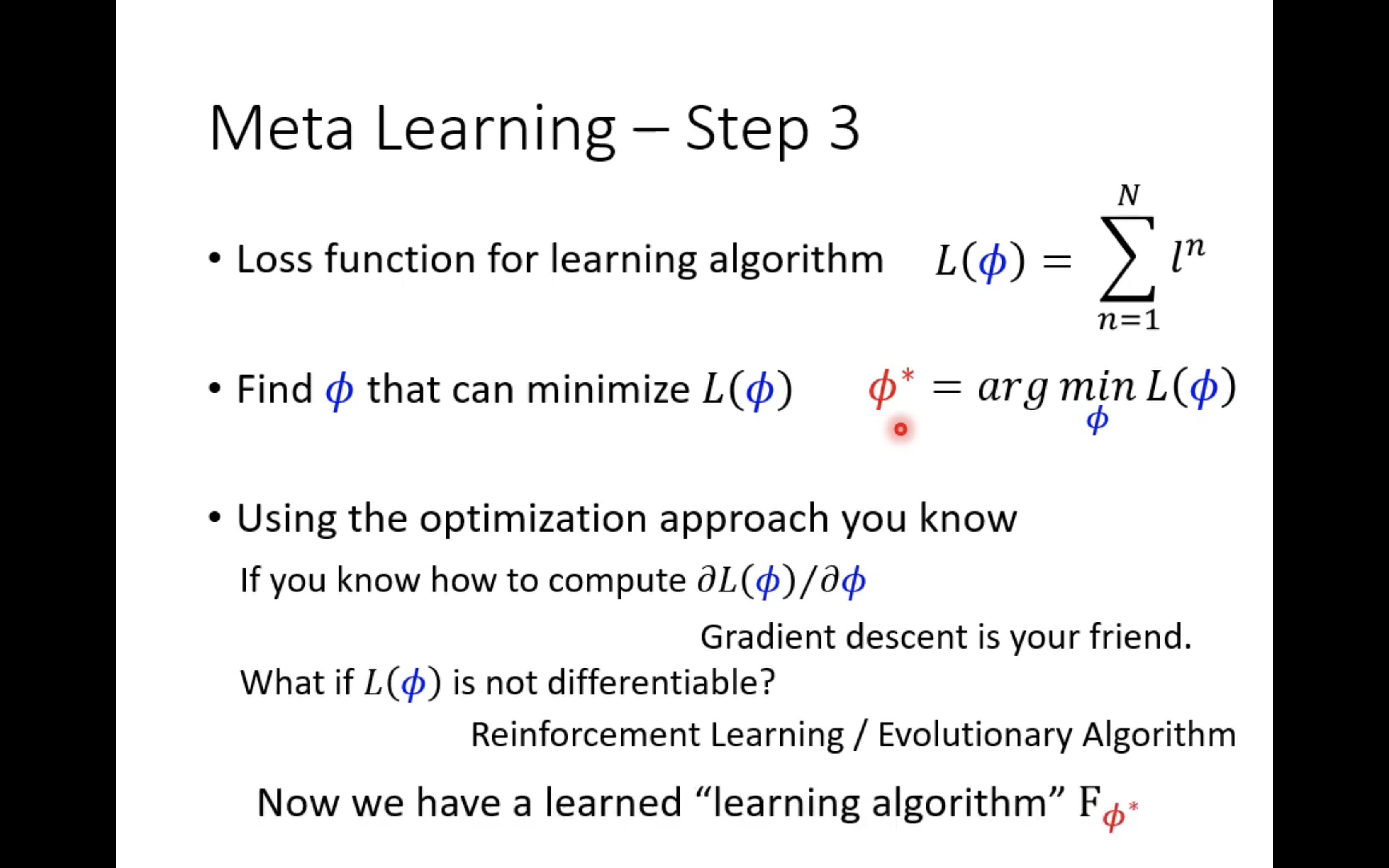
The process above is very similar to the traditional learning process . But there's a problem , We know that in the perceptron algorithm , You can just let loss Yes w w w and b b b Calculate the gradient , And then use gradient descent , But in meta learning Our parameter in is learnable component Φ \Phi Φ, It includes the architecture of the network and so on 、 stay loss Nondifferentiable elements in , How to optimize it ? Li Hongyi said , If you can calculate loss Yes Φ \Phi Φ Differential of , Then you can use gradient descent , If not , You can use Reinforcement Learning perhaps Evolutionary Algorithm.
Two 、 and ML The difference of
Come here ,meta learning The basic thought flow of is clear , Let's compare meta learning and machine learning Differences between :

First , It's the picture above , One is looking for f, One is looking for F,F It's used to find f Of .

secondly ,ML Corresponding to a task ,meta learning Corresponding to multiple tasks . The training material in the attention task is also called Support set, The test data is also called Query set.meta learning The learning process is called Across-task Training.

The picture above shows Within-task and Across-task Comparison of , The meaning is self-evident .
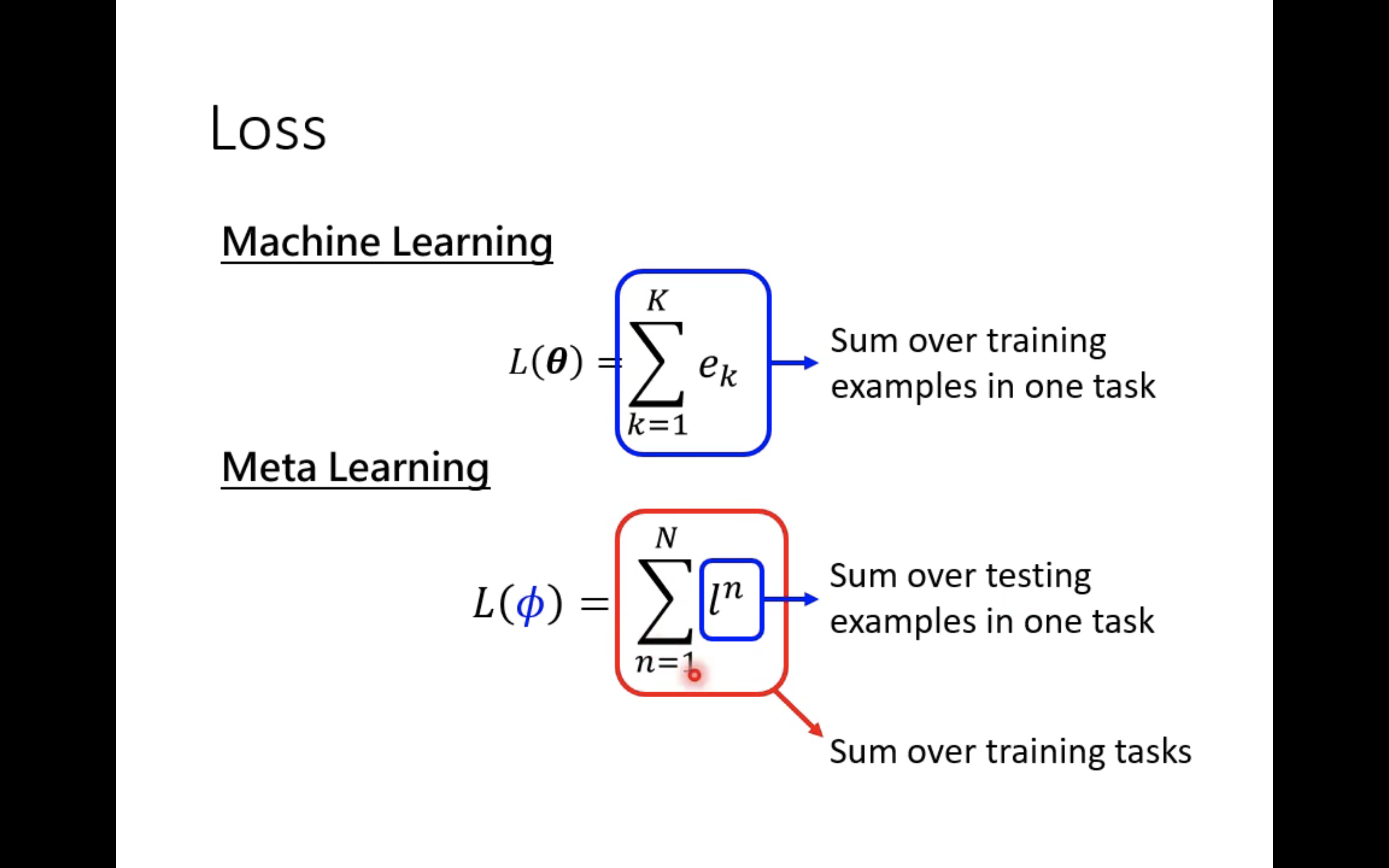
Of course, the difference between the two loss There is also a difference .

ML Technology or thing in , Can also be used or occur in meta learning On . With the above development task The corresponding is “ Verification task ”, It is between training task and testing task , Can be regarded as corresponding to ML Validation set in .
3、 ... and 、 Application understanding
Now let's talk about different kinds of meta learning.
meta learning How is it classified ? We first mentioned , Φ \Phi Φ It stands for meta learning Parameters in , It is called learnable components, It has a lot of component, May include network architecture 、 Parameter initialization 、 Learning rate and so on . Of course these component There may be 、 Or maybe not , So we will be different Φ \Phi Φ Corresponding to different kinds of meta learning On :

for instance , If Φ \Phi Φ It refers to the network architecture , that meta learning It has become familiar to many people NAS:
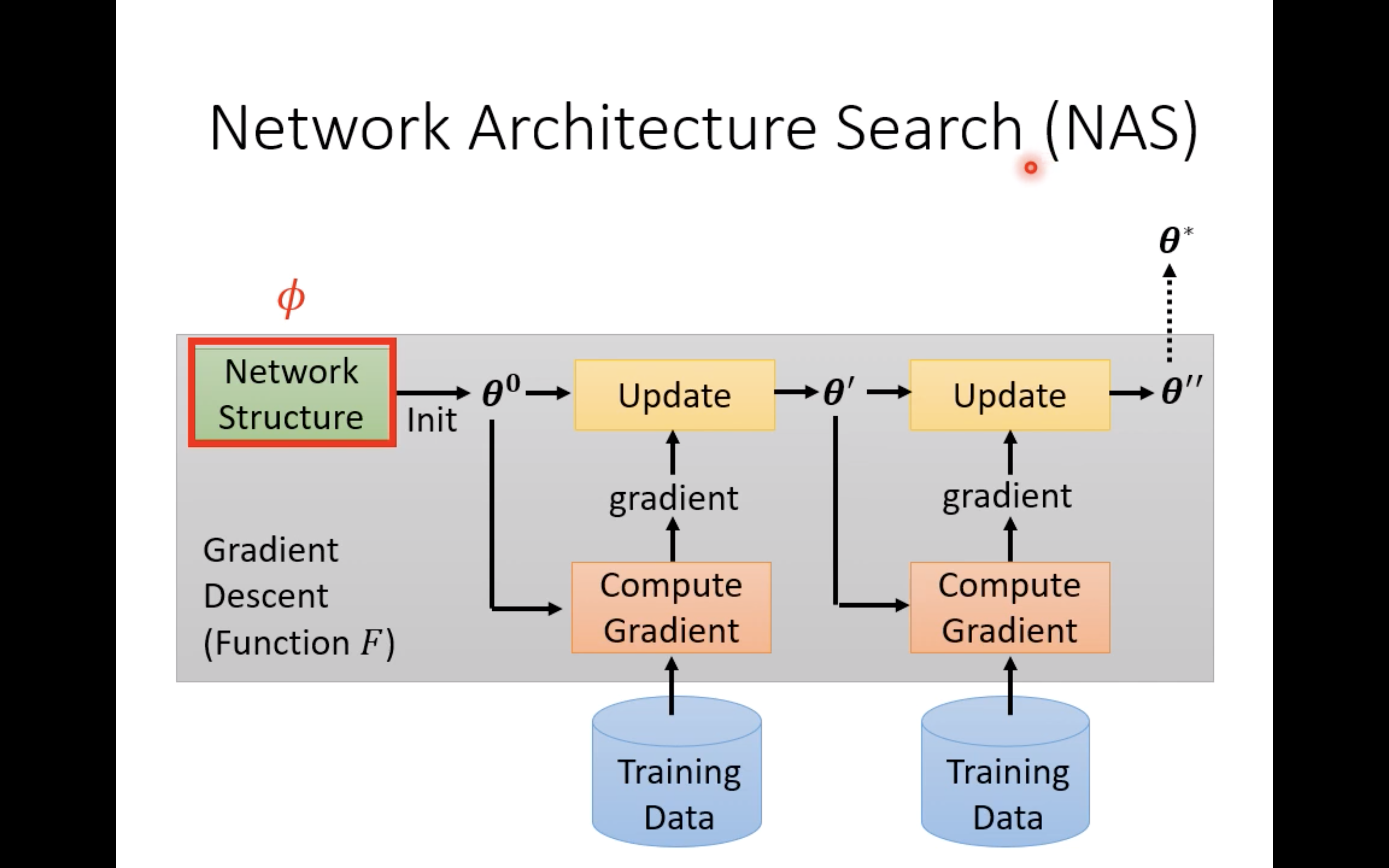
So at this time loss Yes Φ \Phi Φ It must be non differentiable , You can use techniques such as reinforcement learning :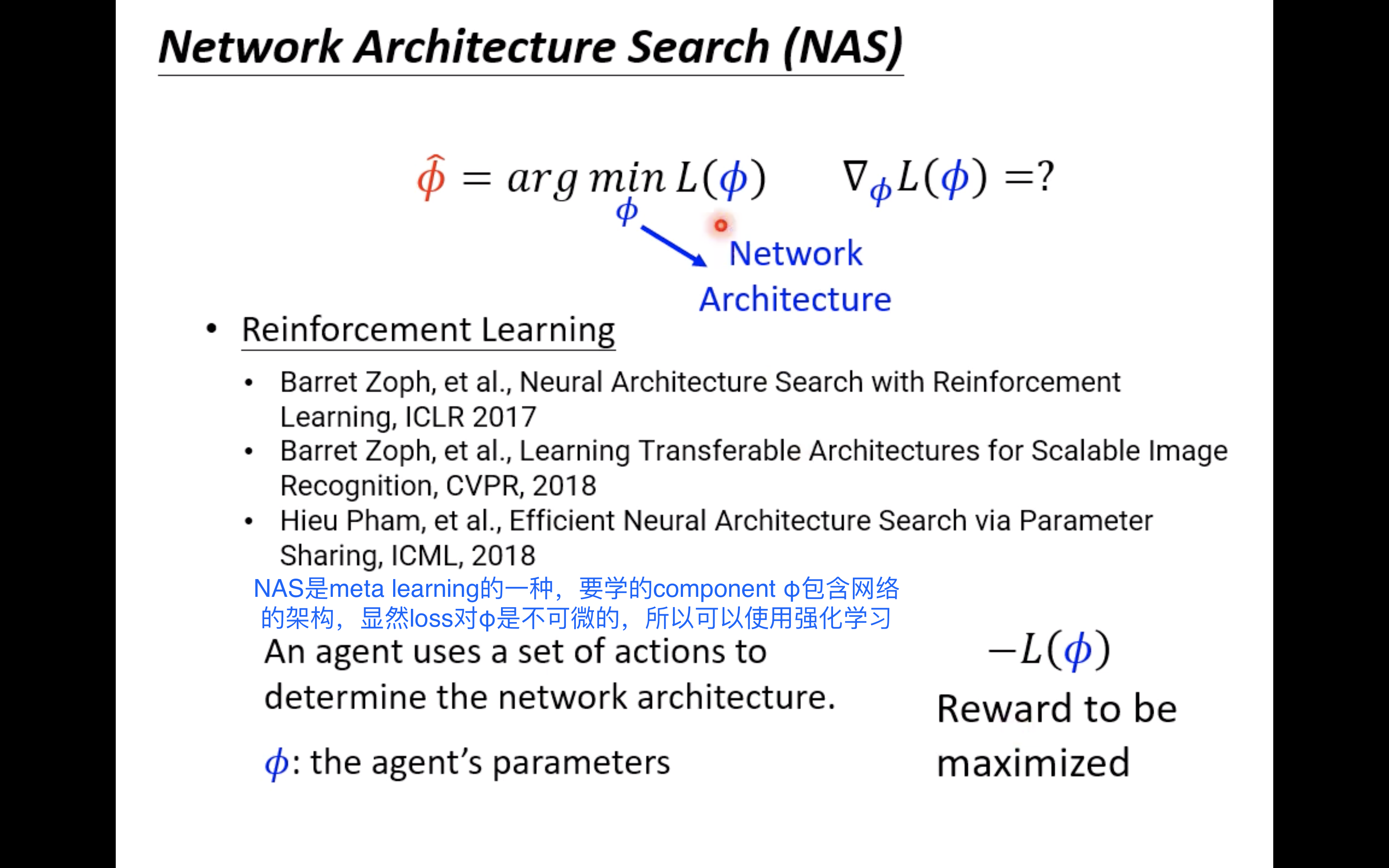
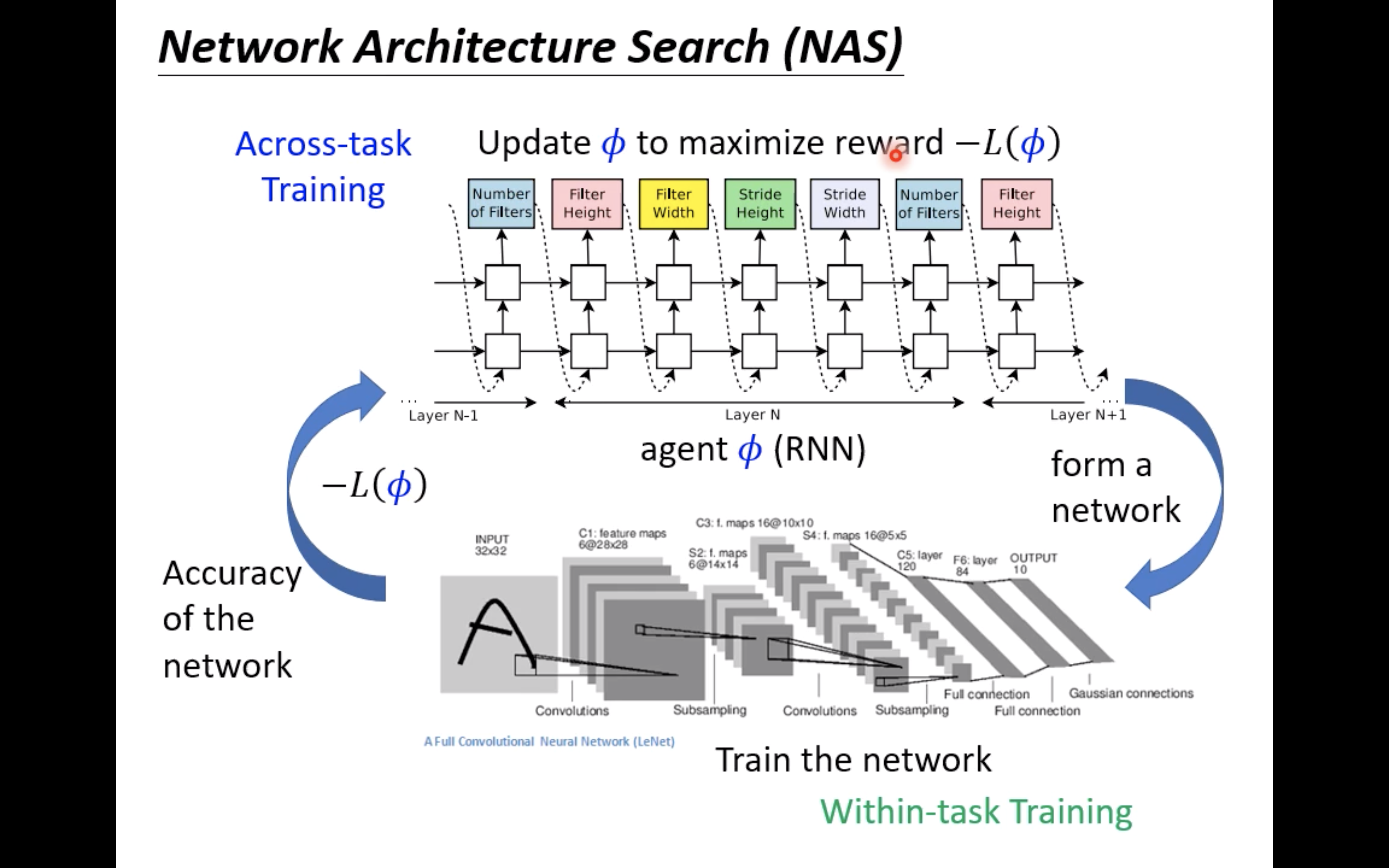

Of course, in addition to intensive learning , Evolutionary algorithms can also be used , The figure above shows some related paper.
meta learning There are also some applications , such as Few-shot Image Classification:

Remember so much first , Li Hongyi has another class , That class is about more specific algorithm details , Today, let's learn about meta learning The basic idea , See it when you need it .
版权声明
本文为[umbrellalalalala]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230543474233.html
边栏推荐
- 治療TensorFlow後遺症——簡單例子記錄torch.utils.data.dataset.Dataset重寫時的圖片維度問題
- Pyqy5 learning (4): qabstractbutton + qradiobutton + qcheckbox
- PyTorch笔记——实现线性回归完整代码&手动或自动计算梯度代码对比
- Pytorch learning record (IX): convolutional neural network in pytorch
- 在Jupyter notebook中用matplotlib.pyplot出现服务器挂掉、崩溃的问题
- 手动删除eureka上已经注册的服务
- JVM series (3) -- memory allocation and recycling strategy
- Ptorch learning record (XIII): recurrent neural network
- Pytorch——数据加载和处理
- What is JSON? First acquaintance with JSON
猜你喜欢

Pytorch學習記錄(十三):循環神經網絡((Recurrent Neural Network)

深入源码分析Servlet第一个程序

The user name and password of users in the domain accessing the samba server outside the domain are wrong

Solve the error: importerror: iprogress not found Please update jupyter and ipywidgets

Pytorch Learning record (XIII): Recurrent Neural Network
![无监督去噪——[TMI2022]ISCL: Interdependent Self-Cooperative Learning for Unpaired Image Denoising](/img/cd/10793445e6867eeee613b6ba4b85cf.png)
无监督去噪——[TMI2022]ISCL: Interdependent Self-Cooperative Learning for Unpaired Image Denoising
线性代数第二章-矩阵及其运算

Font shape `OMX/cmex/m/n‘ in size <10.53937> not available (Font) size <10.95> substituted.

Pytorch学习记录(七):处理数据和训练模型的技巧

多线程与高并发(2)——synchronized用法详解
随机推荐
Pytorch学习记录(十一):数据增强、torchvision.transforms各函数讲解
Fundamentals of digital image processing (Gonzalez) I
Shansi Valley P290 polymorphism exercise
Font shape `OMX/cmex/m/n‘ in size <10.53937> not available (Font) size <10.95> substituted.
Opensips (1) -- detailed process of installing opensips
深入理解去噪论文——FFDNet和CBDNet中noise level与噪声方差之间的关系探索
去噪论文阅读——[RIDNet, ICCV19]Real Image Denoising with Feature Attention
线性代数第三章-矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组
Anaconda安装PyQt5 和 pyqt5-tools后没有出现designer.exe的问题解决
Illustrate the significance of hashcode
如何利用对比学习做无监督——[CVPR22]Deraining&[ECCV20]Image Translation
Pytorch学习记录(十):数据预处理+Batch Normalization批处理(BN)
去噪论文——[Noise2Void,CVPR19]Noise2Void-Learning Denoising from Single Noisy Images
ValueError: loaded state dict contains a parameter group that doesn‘t match the size of optimizer‘s
Postfix变成垃圾邮件中转站后的补救
Gaussian processes of sklearn
Filebrowser realizes private network disk
EditorConfig
RedHat realizes keyword search in specific text types under the directory and keyword search under VIM mode
Ptorch learning record (XIII): recurrent neural network