当前位置:网站首页>二维数组实战项目--------《扫雷游戏》
二维数组实战项目--------《扫雷游戏》
2022-08-11 00:28:00 【许烦】
接上期介绍的三子棋游戏,今天给大家介绍与其相似的扫雷游戏!(源码在文章末尾)
一 . 游戏开发框架
- 建立游戏菜单
- 建立扫雷的棋盘
- 初始化棋盘
- 布置雷
- 排雷(判断是否踩雷)
- 游戏结束
二 . 游戏开发及细节详解
1.建立游戏菜单
首先,我们需要创建一个项目,添加一个头文件和两个源文件

![]()
test.c------------------------用于游戏的主体框架设计和扫雷游戏的逻辑测试
game.h----------------------用于相应函数的声明
game.c----------------------用于游戏函数的实现
游戏菜单的打印实现,上期分享的三子棋游戏已经声明过了,直接套用上次的代码就好了,代码块如下:
void menu() {
printf("-------------------------\n");
printf("---------1.paly----------\n");
printf("---------0.exit----------\n");
printf("-------------------------\n");
}
void game() {
printf("开始游戏\n");
}
int main() {
int input = 0;
do {
menu();
printf("请选择:");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
game();
break;
case 0:
printf("退出游戏:\n");
break;
default:
printf("选择错误,重新选择:\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
实现如下:
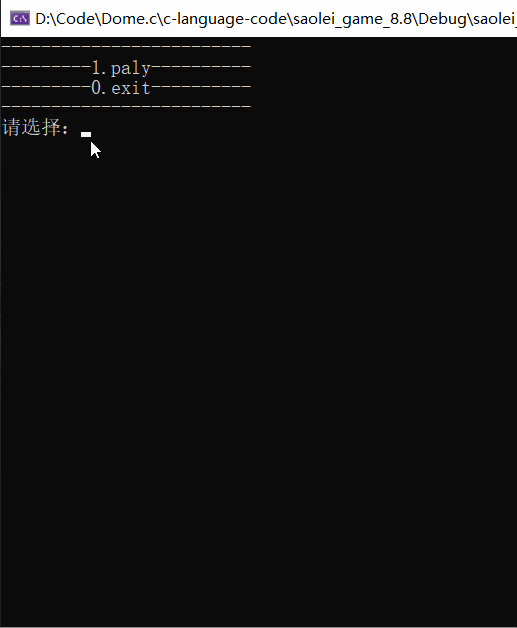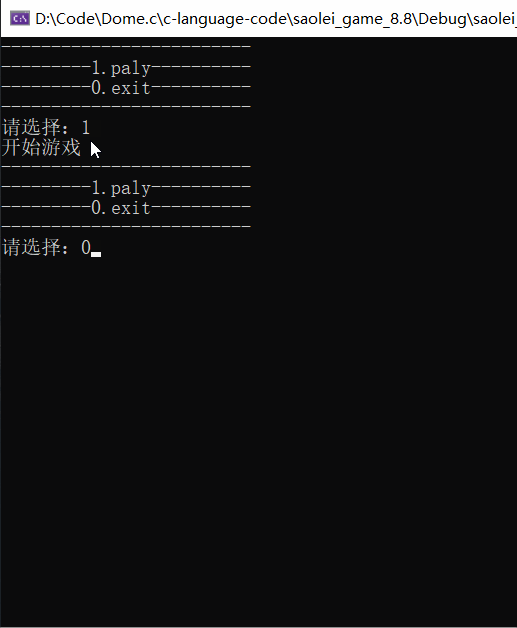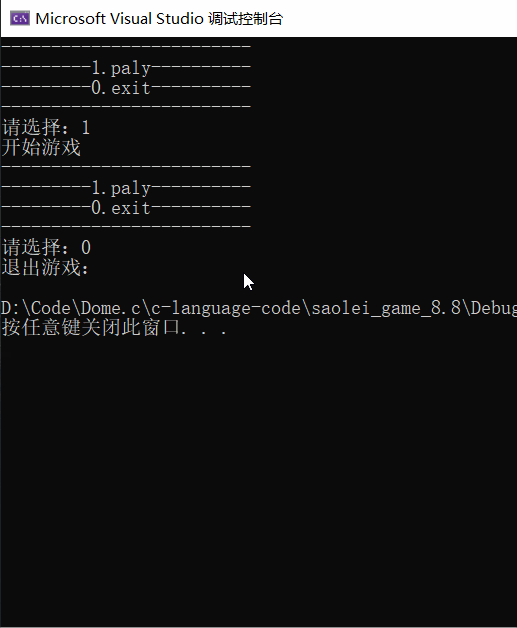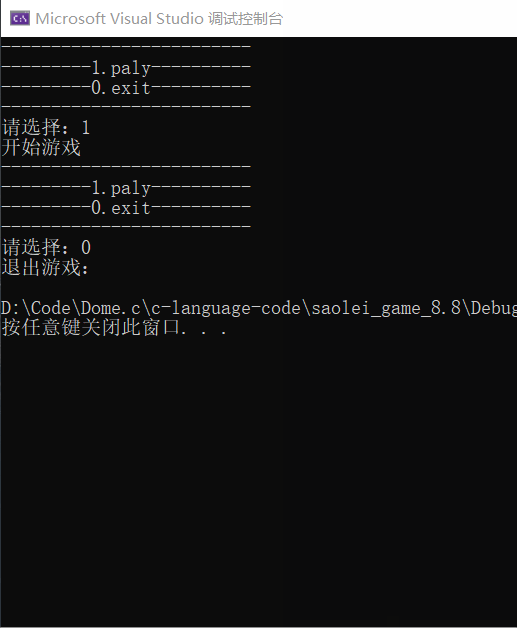
到这里,准备工作的游戏菜单打印部分就完成了。
2.建立扫雷的棋盘
关于游戏的规则这里就不多介绍了,参考下面的链接:https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/7f766daf9231e84101e1d03d.html

关于棋盘的打印,我们需要二维数组来定义,但是为了防止数组越界问题,我们适当扩大数组的大小,在定义棋盘的时候有雷的地方用 ‘ 1 ’表示,没有雷的地方用 ‘ 0 ’表示;
接下来要考虑扫雷的细节问题:

创建一个mine数组和一个show数组:
game.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#define ROW 9
#define COL 9
#define ROWS ROW+2
#define COLS COL+2
test.c
//设计2个数组存放信息
char mine[ROWS][COLS] = { 0 };
char show[ROWS][COLS] = { 0 };两个数组已经创建好了,接下来我们要初始化棋盘并打印棋盘
3.初始化棋盘
mine数组初始化用 ‘ 0 ’表示
show数组初始化用 ‘ * ’表示
test.c
void game() {
//设计2个数组存放信息
char mine[ROWS][COLS] = { 0 };
char show[ROWS][COLS] = { 0 };
//初始化棋盘
init_board(mine, ROWS, COLS,'0');
init_board(show, ROWS, COLS,'*');
//打印棋盘
display_board(mine, ROW, COL);
display_board(show, ROW, COL);
}game.c
void init_board(char board[ROWS][COLS], int rows, int cols, char set) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
board[i][j] = set;
}
}
}
void display_board(char board[ROWS][COLS], int row, int col) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= row; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= col; j++) {
printf("%c ", board[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}game.h
//初期化棋盘
void init_board(char board[ROWS][COLS], int rows, int cols,char set);
//打印棋盘
void display_board(char board[ROWS][COLS], int row, int col);棋盘的打印如下:

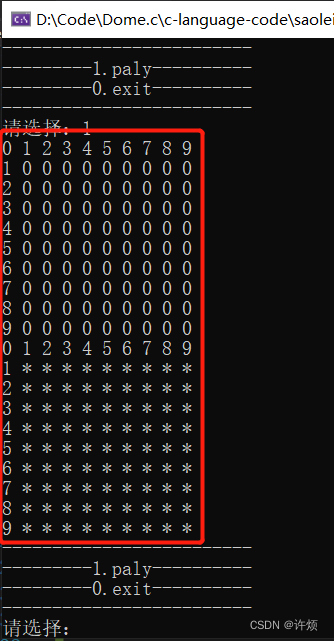
由上图可以看到,打印的棋盘对玩家不太友好,我们可以在棋盘上面加上行列标号,以便于玩家在进行游戏的时候输入坐标,只需改变game.c的代码即可:
void display_board(char board[ROWS][COLS], int row, int col) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j <= col; j++) {
printf("%d ", j);//打印列号
}
printf("\n");
for (i = 1; i <= row; i++) {
printf("%d ", i);//打印行号
for (j = 1; j <= col; j++) {
printf("%c ", board[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
实现如下:
4.布置雷
布置雷我们需要考虑两个问题:
1.坐标的合法性
2.坐标是否已经布置好雷,不可重复布置雷
这里我们使用rand函数来实现布置雷的随机性,关于rand函数的使用方法可以参考这个链接https://cplusplus.com/reference/cstdlib/rand/?kw=rand
int x = rand() % row + 1;
int y = rand() % col + 1;x代表横坐标,y代表纵坐标,rand()%row的值在0~8,加1就是1~9,正好符合玩家输入的坐标。
test.c
void game() {
//设计2个数组存放信息
char mine[ROWS][COLS] = { 0 };
char show[ROWS][COLS] = { 0 };
//初始化棋盘
init_board(mine, ROWS, COLS,'0');
init_board(show, ROWS, COLS,'*');
//打印棋盘
//display_board(mine, ROW, COL);
//display_board(show, ROW, COL);
//布置雷
set_mine(mine, ROW, COL);
//排雷
display_board(mine, ROW, COL);
}game.c
void set_mine(char mine[ROWS][COLS], int row, int col) {
//假设布置10个雷
int count = 10;
while (count) {
int x = rand() % row + 1;
int y = rand() % col + 1;
if (mine[x][y] == '0') {
mine[x][y] = '1';
count--;
}
}
}game.h
//布置雷
void set_mine(char board[ROWS][COLS], int row, int col);
运行如下:
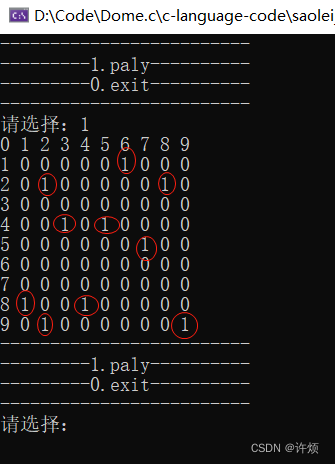
到这里10个雷就被我们布置好了
5.排雷
当排到一个坐标,我们需要判断改坐标周围的8个位置是否有雷,也就是字符‘ 1 ’,我们需要定义一个函数来相加8个位置的字符‘ 1 ’,将红线串起的相加,求出(x,y)周围雷的个数;

代码如下:
test.c
void game() {
//设计2个数组存放信息
char mine[ROWS][COLS] = { 0 };
char show[ROWS][COLS] = { 0 };
//初始化棋盘
init_board(mine, ROWS, COLS,'0');
init_board(show, ROWS, COLS,'*');
//打印棋盘
//display_board(mine, ROW, COL);
//display_board(show, ROW, COL);
//布置雷
set_mine(mine, ROW, COL);
//排雷
display_board(mine, ROW, COL);
find_mine(mine, show, ROW, COL);
}game.c
int get_mine_count(char mine[ROWS][COLS], int x, int y) {
return (mine[x - 1][y] +
mine[x - 1][y - 1] +
mine[x][y - 1] +
mine[x + 1][y - 1] +
mine[x + 1][y] +
mine[x + 1][y + 1] +
mine[x][y + 1] +
mine[x - 1][y + 1] - 8 * '0');
}
void find_mine(char mine[ROWS][COLS], char show[ROWS][COLS], int row, int col) {
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
printf("请输入要排查雷的坐标:");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
if (x >= 1 && x <= row && y >= 1 && y <= col) {
int count = get_mine_count(mine, x, y);
show[x][y] = count + '0';
display_board(show, ROW, COL);
}
else {
printf("坐标非法,重新输入:");
}
}
geme.h
//排查雷
void find_mine(char mine[ROWS][COLS], char show[ROWS][COLS] , int row, int col);
对上述一段代码的补充:

show[x][y] = count + '0';
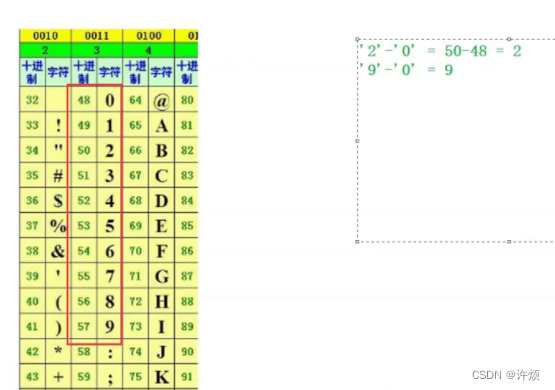
对此代码的补充,为什么统计周围雷的个数要+' 0 ' ? ? ?
我们知道字符在数据存储是以ASCII存储的
由上图可知,字符-字符=一个数值,所以show[x][y](数字字符)=count(数值)+‘0’(数字字符);
到这里,排雷的工作就OK了,下面演示一下:

6.游戏结束(判断是否胜利或者踩雷)
在9x9的棋盘中,假设放置10个雷,只有2中情况,一种把剩下的71个坐标全部排完,游戏胜利,一种是踩雷,游戏结束;
此次我们只需在game.c文件中添加判断输赢的条件即可:
void find_mine(char mine[ROWS][COLS], char show[ROWS][COLS], int row, int col)
{
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int win = 0;
while (win < row * col - EASY_COUNT)
{
printf("请输入要排查雷的坐标:>");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
if (x >= 1 && x <= row && y >= 1 && y <= col)
{
//坐标被排查过
if (show[x][y] == '*')
{
if (mine[x][y] == '1')
{
printf("很遗憾,你被炸死了\n");
display_board(mine, ROW, COL);
break;
}
else
{
int count = get_mine_count(mine, x, y);
show[x][y] = count + '0';
display_board(show, ROW, COL);
win++;
}
}
else
{
printf("该坐标已经被排查过了\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("坐标非法,请重新输入\n");
}
}
if (win == row * col - EASY_COUNT)
{
printf("恭喜你,排雷成功\n");
display_board(mine, ROW, COL);
}
}在game.h中声明一个定义
#define EASY_COUNT 10好了,到这里游戏的设计就完成了,让我们看下效果吧:
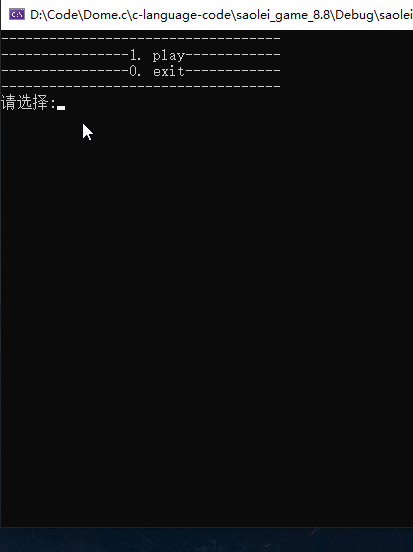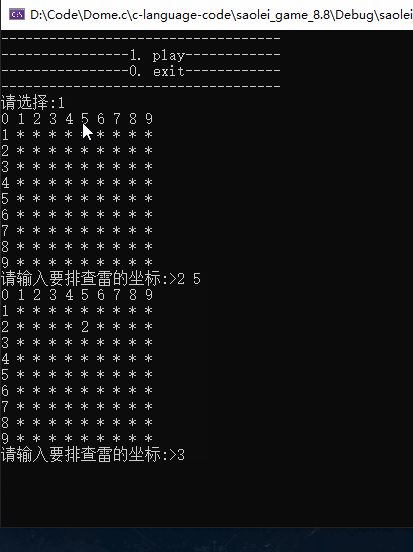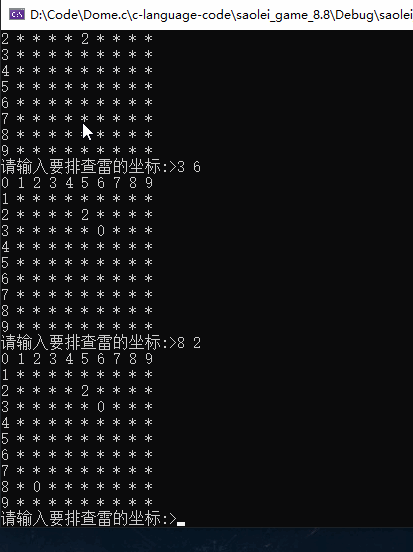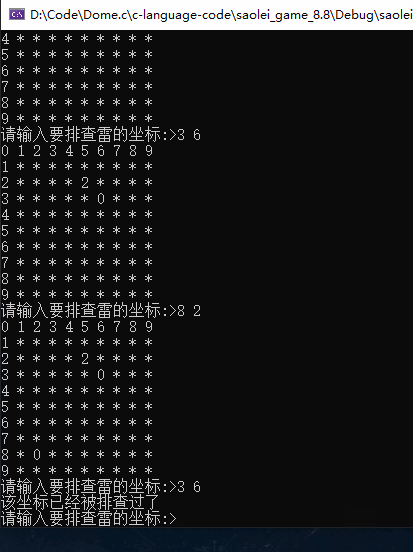
这里就不玩下去了,如果感兴趣可以自己尝试玩一下
源代码:
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "game.h"
void menu()
{
printf("-----------------------------------\n");
printf("----------------1. play------------\n");
printf("----------------0. exit------------\n");
printf("-----------------------------------\n");
}
void game()
{
//设计2个数组存放信息
char mine[ROWS][COLS] = { 0 };
char show[ROWS][COLS] = { 0 };
//初始化棋盘
//mine初始化为全‘0’
//show初始化为全‘*’
init_board(mine, ROWS, COLS, '0');
init_board(show, ROWS, COLS, '*');
//打印棋盘
//display_board(mine, ROW, COL);
//display_board(show, ROW, COL);
//布置雷
set_mine(mine, ROW, COL);
//排雷
//display_board(mine, ROW, COL);
display_board(show, ROW, COL);
find_mine(mine, show, ROW, COL);
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
do
{
menu();
printf("请选择:");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
game();
break;
case 0:
printf("退出游戏\n");
break;
default:
printf("选择错误,重新选择\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
game.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "game.h"
void init_board(char board[ROWS][COLS], int rows, int cols, char set)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
board[i][j] = set;
}
}
}
void display_board(char board[ROWS][COLS], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
//列号
for (j = 0; j <= col; j++)
{
printf("%d ", j);
}
printf("\n");
for (i = 1; i <= row; i++)
{
printf("%d ", i);
for (j = 1; j <= col; j++)
{
printf("%c ", board[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void set_mine(char mine[ROWS][COLS], int row, int col)
{
//布置10个雷
int count = EASY_COUNT;
while (count)
{
int x = rand() % row + 1;
int y = rand() % col + 1;
if (mine[x][y] == '0')
{
mine[x][y] = '1';
count--;
}
}
}
int get_mine_count(char mine[ROWS][COLS], int x, int y)
{
return (mine[x - 1][y] +
mine[x - 1][y - 1] +
mine[x][y - 1] +
mine[x + 1][y - 1] +
mine[x + 1][y] +
mine[x + 1][y + 1] +
mine[x][y + 1] +
mine[x - 1][y + 1] - 8 * '0');
}
void find_mine(char mine[ROWS][COLS], char show[ROWS][COLS], int row, int col)
{
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int win = 0;
while (win < row * col - EASY_COUNT)
{
printf("请输入要排查雷的坐标:>");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
if (x >= 1 && x <= row && y >= 1 && y <= col)
{
//坐标被排查过
if (show[x][y] == '*')
{
if (mine[x][y] == '1')
{
printf("很遗憾,你被炸死了\n");
display_board(mine, ROW, COL);
break;
}
else
{
int count = get_mine_count(mine, x, y);
show[x][y] = count + '0';
display_board(show, ROW, COL);
win++;
}
}
else
{
printf("该坐标已经被排查过了\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("坐标非法,请重新输入\n");
}
}
if (win == row * col - EASY_COUNT)
{
printf("恭喜你,排雷成功\n");
display_board(mine, ROW, COL);
}
}game.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define EASY_COUNT 10
#define ROW 9
#define COL 9
#define ROWS ROW+2
#define COLS COL+2
//初期化棋盘
void init_board(char board[ROWS][COLS], int rows, int cols,char set);
//打印棋盘
void display_board(char board[ROWS][COLS], int row, int col);
//布置雷
void set_mine(char board[ROWS][COLS], int row, int col);
//排查雷
void find_mine(char mine[ROWS][COLS], char show[ROWS][COLS] , int row, int col);
三. 总结
对于这个小游戏,小编学起来也很吃力,也是花了不少时间去研究,揣摩里面的细节问题,最重要的是理解,学习如何设计一个游戏的思路,编程这东西不是一天两天就能搞会的,慢慢积累,温故而知新,才会得到我们想要的结果,小编是一名刚接触编程不久的在校学生,如果对上文有意见或者有错误,还请大佬们斧正,觉得有帮助的童鞋们,蟹蟹三连!
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Design and implementation of flower online sales management system
使用mysql语句操作数据表(table)
HW-蓝队工作流程(1)
Difference Between Image Recognition and Semantic Segmentation
7. yaml
PMP每日一练 | 考试不迷路-8.10(包含敏捷+多选)
How engineers treat open source
微信小程序自定义navigationBar
云原生-FRP内网穿透(详解)使用云服务器将内网集群服务暴露至公网(二)
使用 BeanUtils 做属性拷贝,性能有点拉胯!
Analysis of LENS CRA and SENSOR CRA Matching Problems
J9数字论:DAO治理更像一种生态过程:治理原生于网络,不断演变
复制带随机指针的链表——LeetCode
Jvm. Profiling tools (jconsole, jvisualvm, arthas, jprofiler, mat)
【C语言】探索数据的存储(整形篇)
"NIO Cup" 2022 Nioke Summer Multi-School Training Camp 3 DF Problem Solving
16. File upload
【mysql】mysql分别按年/月/日/周分组统计数据
12. Handling JSON
李彦宏拆墙交朋友,大厂“塑料友情”能否帮百度啃下硬骨头?