当前位置:网站首页>A sharp tool to improve work efficiency
A sharp tool to improve work efficiency
2022-04-23 06:06:00 【New ape and horse】
Catalog
One Future Multithreading tasks
1.2 Future Practical application
3、 ... and Java8 stream Realize multi field sorting
4.2 Scroll API Process carding
This article is mainly to record some tools often used in work , And some common routines to solve common problems .
One Future Multithreading tasks
Have you ever encountered such a scene , There is a lot of data to process , Like millions 、 Tens of millions , Even hundreds of millions of data ?
If you use a one-way process to process a large amount of data , It will take a long time , Efficiency is too low . You might say , It's simple , Use multithreading . Yes , Multithreading is equivalent to multiple single threads processing at the same time , It's a lot faster .
So how to use multithreading to deal with ?
You would say using thread pool . ha-ha , Thread pools are really common , Using thread pool can really achieve the desired effect .
If you need to get the result of thread processing , How about ?
Runnable Interface , Its method does not return a value , Unqualified .
Callable Interface , and Runnable Interface than , There is one more return value , Meet the requirements .
1.1 Define thread pool
See this article for the principle of thread pool Deep understanding and application of thread pool
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Configuration
public class TaskThreadPoolConfig {
private int corePoolSize = 8;
private int maxPoolSize = 8;
private int queueCapacity = 1000;
@Bean(name = "taskExecutor")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);
executor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
return executor;
}
}1.2 Future Practical application
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class TaskExecutor {
@Resource(name = "taskExecutor")
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor;
public List<Integer> futureList() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// Initialize task array
List<Integer> initList = new ArrayList<>();
IntStream.range(0, 30).forEach(initList::add);
List<Future> futureList = new ArrayList<>();
// Multithreaded execution
initList.forEach(id -> {
Future<Integer> future = threadPoolTaskExecutor.submit(() -> getUserId(id));
// take future write in list
futureList.add(future);
});
// Get multithreaded execution results
List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Future<Integer> future : futureList) {
resultList.add(future.get());
}
return resultList;
}
public Integer getUserId(Integer i) {
return i;
}
}As you can see from the above example :
1 When we submit a Callable After the task , We'll get one at a time Future object ,
2 The main thread calls... At some point Future Object's get() Method , You can get the result of asynchronous execution .
3 Calling get() when , If the asynchronous task has been completed , We get the result directly ; If the asynchronous task is not completed , that get() It will block , Don't return results until the task is completed .
in summary : We can see , Use Future Object's get() Method , May block , The throughput of the system is difficult to improve .CompletableFuture yes Future Upgraded version , There is no in-depth study here .
Two paging
In practice , We often encounter such a scene , Need to show a list , For the sake of system performance , The list needs to be paged and rendered .
2.1 Paging code
import org.apache.commons.lang3.tuple.Pair;
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
Pair<Integer, List<Integer>> pair = page(list, 0, 2);
System.out.println(pair.getLeft());
System.out.println(pair.getRight());
}
public static Pair<Integer, List<Integer>> page(List<Integer> list, Integer offset, Integer limit) {
// offset Offset and total Compare
int total = CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(list) ? list.size() : 0;
if (offset > total) {
return Pair.of(total, Lists.newArrayList());
}
// Calculate the start offset and the final offset
int end = offset + limit;
// The final offset cannot be greater than total
end = Math.min(end, total);
// Paging subsets
List<Integer> result = list.subList(offset, end);
return Pair.of(total, result);
}2.2 Execution results

3、 ... and Java8 stream Realize multi field sorting
We often encounter the operation of sorting fields in our work , If you don't need to define sorting rules separately , have access to stream The sort provided API, Support multi field sorting , Simple and easy to use .
3.1 Code implementation
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(User.builder().id(10L).name("zs").age(11).build());
userList.add(User.builder().id(10L).name("zs").age(10).build());
userList.add(User.builder().id(5L).name("ls").age(9).build());
userList.add(User.builder().id(5L).name("mz").age(9).build());
userList.add(User.builder().id(19L).name("ww").age(10).build());
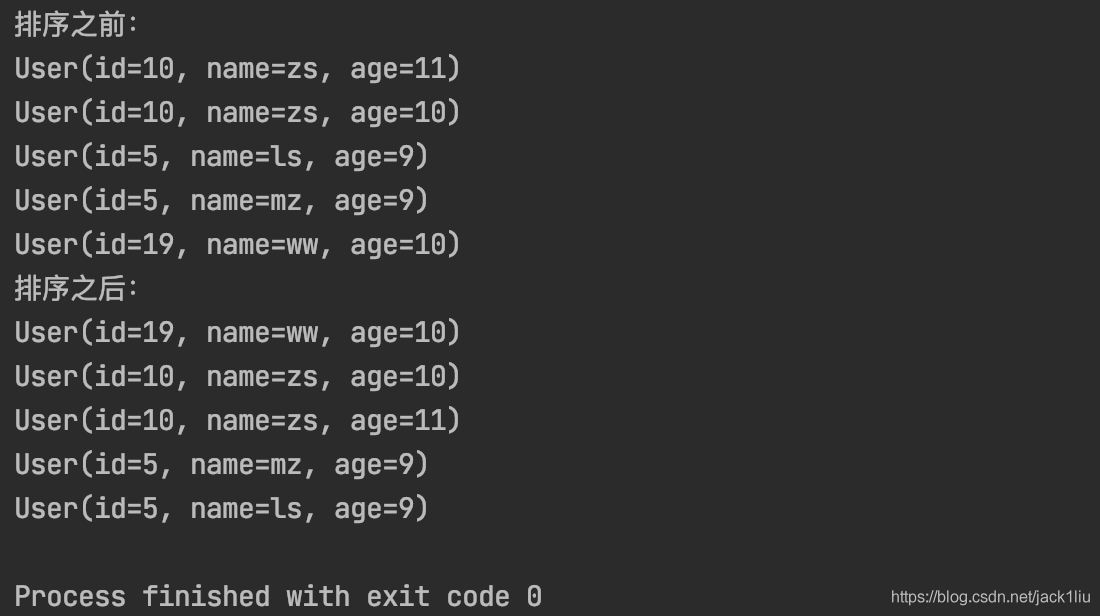
System.out.println(" Before sorting :");
for (User u:userList) {
System.out.println(u);
}
// Suppose we use id Descending 、name Descending 、age Sort the array in ascending order
List<User> sort = userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getId, Comparator.reverseOrder())
.thenComparing(User::getName, Comparator.reverseOrder())
.thenComparing(User::getAge, Comparator.naturalOrder())).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(" After the sorting :");
for (User u : sort) {
System.out.println(u);
}
}
}3.2 Running results
Four Search Scroll API
It mainly solves the scenario of fetching a large amount of data from the index ,Scroll API The way of fetching data in batches improves the query efficiency .
4.1 Scroll API Code
// catalog index
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("posts");
// Set up scroll Life cycle
final Scroll scroll = new Scroll(TimeValue.timeValueMinutes(1L));
searchRequest.scroll(scroll);
// Set search criteria
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
searchSourceBuilder.query(matchQuery("title", "Elasticsearch"));
// Set the number of single queries
searchSourceBuilder.size(size);
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
// The first query gets the result
SearchResponse searchResponse = client.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
String scrollId = searchResponse.getScrollId();
SearchHit[] searchHits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
while (searchHits != null && searchHits.length > 0) {
// structure scroll request , Check the next page
SearchScrollRequest scrollRequest = new SearchScrollRequest(scrollId);
scrollRequest.scroll(scroll);
searchResponse = client.scroll(scrollRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
scrollId = searchResponse.getScrollId();
searchHits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
}
// Clear data from context
ClearScrollRequest clearScrollRequest = new ClearScrollRequest();
clearScrollRequest.addScrollId(scrollId);
ClearScrollResponse clearScrollResponse = client.clearScroll(clearScrollRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
boolean succeeded = clearScrollResponse.isSucceeded();4.2 Scroll API Process carding
1. By sending the initial SearchRequest Initialize search context .
2. By calling in the loop Search Scroll api Retrieve all search hits , Until no documents are returned .
3. Process the returned search results .
4. Create a new SearchScrollRequest, It contains the last returned scroll identifier and scroll interval .
5. Clear the scrolling context when scrolling is complete .
Reference documents :Scroll API Official documents
版权声明
本文为[New ape and horse]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204220533487955.html
边栏推荐
- Pytorch学习记录(十):数据预处理+Batch Normalization批处理(BN)
- Custom exception class
- Dva中在effects中获取state的值
- Pytorch学习记录(十一):数据增强、torchvision.transforms各函数讲解
- Pytorch学习记录(十二):学习率衰减+正则化
- Create enterprise mailbox account command
- Pytorch学习记录(五):反向传播+基于梯度的优化器(SGD,Adagrad,RMSporp,Adam)
- The bottom implementation principle of thread - static agent mode
- Fundamentals of SQL: first knowledge of database and SQL - installation and basic introduction - Alibaba cloud Tianchi
- Rsync for file server backup
猜你喜欢

Pytoch learning record (x): data preprocessing + batch normalization (BN)

Fundamentals of in-depth learning -- a simple understanding of meta learning (from Li Hongyi's course notes)

PyTorch笔记——实现线性回归完整代码&手动或自动计算梯度代码对比

Pyemd installation and simple use

Paper on LDCT image reconstruction: edge enhancement based transformer for medical image denoising

PyEMD安装及简单使用

Latex快速入门
开发环境 EAS登录 license 许可修改

线性代数第三章-矩阵的初等变换与线性方程组

Multithreading and high concurrency (1) -- basic knowledge of threads (implementation, common methods, state)
随机推荐
Pytorch learning record (V): back propagation + gradient based optimizer (SGD, adagrad, rmsporp, Adam)
umi官网yarn create @umijs/umi-app 报错:文件名、目录名或卷标语法不正确
JDBC operation transaction
JSP语法及JSTL标签
Pyqt5 learning (I): Layout Management + signal and slot association + menu bar and toolbar + packaging resource package
对比学习论文——[MoCo,CVPR2020]Momentum Contrast for Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning
Pytorch学习记录(十二):学习率衰减+正则化
Complete example demonstration of creating table to page - joint table query
MySQL basic madness theory
去噪论文阅读——[RIDNet, ICCV19]Real Image Denoising with Feature Attention
A general U-shaped transformer for image restoration
Custom exception class
线性代数第二章-矩阵及其运算
Linear algebra Chapter 2 - matrices and their operations
实操—Nacos安装与配置
Kingdee EAS "general ledger" system calls "de posting" button
container
Pytorch学习记录(十三):循环神经网络((Recurrent Neural Network)
Pytorch learning record (IV): parameter initialization
去噪论文——[Noise2Void,CVPR19]Noise2Void-Learning Denoising from Single Noisy Images