当前位置:网站首页>MySQL practical skills
MySQL practical skills
2022-04-23 19:14:00 【Li Siwei】
selected from :mysql note .pdf
help command
mysql Provided help command , For us, we only remember the keywords in the command , But forget the specific parameters of the command , Very useful .
for example :
help show;
help create;
help grant;
help drop;
We can go further : I want to create a new user , Just remember that the command is ’create user’ At the beginning , But I forgot some specific parameters later , You can use the following command :
mysql> help create user;
It is strongly recommended that all columns not null, Set the default value . because null A pit .
Shaping is simpler than character sets and proofreading rules , The operation speed of the corresponding column is also faster
Floating point unified selection decimal, because float and double There's a problem with accuracy , This is an inherent problem of the computer's representation of floating-point numbers
The date and time should preferably be stored in timestamp format , Convenient index .unix_timestamp(now()) / from_unixtime(123456) / from_unixtime(123456, ‘%Y’)
int(11)
11 Indicates the display width ;select When the query result is displayed , If the number does not 11 position , Can fill in with blanks 11 position ; It can also be used. 0 A filling , You need to define the column as int(11) unsigned zerofill, For 33, Will be displayed as 00000000033;
about int Column of type , If no display width is defined , The default is 11, because int The maximum value of type data is 11 Bit .
decimal If you do not set the precision and scale , The decimal places are rounded off , There are no decimal places finally stored in the database .
float and double If you do not set the precision and scale , It is directly expressed by accuracy and actual storage .
Clause and subquery
Clause :where / order by / limit And so on are clauses
clause: Clause , refer to where Query condition clause in clause :and Clause ,or Clause, etc .
Subquery : Other queries are nested in the query .
Subquery
The result set of sub query is divided into 4 Kind of :
- Scalar subquery , Line by line , Single result
- Column query , A column with many lines
- Line sub query , One row and many columns
- Table sub query , More columns, more lines
According to the occurrence position of sub query :
- select Only scalar subqueries are supported after
- from Support table sub query after
- where / having after , Support scalar 、 That's ok 、 Column
- exists after , Support table subquery
Such as : There is a purchase record sheet order, There are three columns user_id, price,year; The user id、 Price 、 year .
Find the record of the highest purchase price per user , Want to have user_id,price,year.
select * from order
where ( user_id,price ) in
(select user_id,max(price) from order
group by user_id)
When where When the subsequent subquery is multi column ( Row or table ), Must use () Enclose multiple column query criteria .
When where When the subsequent subquery is multi row ( Columns or tables ), Must use in, Or use = > < >= <= <> And any all some share
When where When the subquery after is one row ( Line or scalar ), It can be used = > < >= <= <> And .
And so on :
Department table departments, Listed dep_id,dep_name;
There's a staff watch employees, Listed emp_id,emp_name,dep_id,salary;
There is a salary scale job_grades, Listed grade_id,low,high
Query the number of employees in each department :
select dep_name,(select count(emp_id)
from employees e
where e.dep_id=d.dep_id)
from departments d;
The inquiry job number is ’11’ Department name of the employee :
select dep_name from departments
where dep_id=( select dep_id from employees e where e.emp_id='11');
or
select dep_name from departments d join employees e on e.dep_id=d.dep_id and e.emp_id='11';
or
select dep_name from departments d join employees e on e.dep_id=d.dep_id where e.emp_id='11';
Query the average salary grade of each department ;
select dep_id,grad_id
from (select dep_id, avg(salary) as s_avg
from employees
group by dep_id) a,
job_grades g
where s_avg>= g.low and s_avg<g.high
NULL The pit of
about null, Only use is null perhaps is not null To query , None of the other operators can .
Have a watch test1 The data are as follows :
| c1 | c2 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | NULL |
| NULL | NULL |
count(cname), No statistics cname==null The record of
select count(c1),count(c2),count(*) from test1; --- The result is : 2,1,3
select count(*) from test1 where c1 is null; --- The result is 1;
select count(c1) from test1 where c1 is null; --- The result is 0;
= <>, in, not in, exists, not exists None of these operations can act on NULL
select * from test1 where c1 = NULL; — The result set is empty;
select * from test1 where c1 != NULL; — The result set is empty;
select * from test1 where c1 in ( NULL ) ; — The result set is empty;
select * from test1 where c1 in ( NULL, 2 ) ; — The result set is empty;
select * from test1 where c1 not in ( NULL ); — The result set is empty;
select * from test1 where c1 not in ( NULL, 2 ); — The result set is empty;
Business
-
atomicity: Atomicity , A transaction must be an atomic operation . A batch of transactions SQL Statements either all work successfully on the database , Or it doesn't work on the database at all . You can refer to java Concurrent / Atomicity in multithreading operation ( stay java There are many AtomicXXX class , Take advantage of unsafe Of CAS Ensure atomicity and consistency of data )
-
consistency: Uniformity , Before the transaction is executed , The data in the database is in a consistent state in business ; After transaction execution , The data in the database is in a consistent state in business .
-
isolation: Isolation, , The execution of one transaction cannot be interfered by other transactions . The operations and data used within a transaction are isolated from other concurrent data , And the transactions executed cannot be
-
adopt commit and rollback, To achieve transaction atomicity .
-
Transaction isolation is achieved through transaction consistency view and lock
Read consistency 、 Read the snapshot 、 The current reading
Multi version concurrency control (MultiVersion Concurrecy Control), The database that supports this mechanism is called multi version database .
- mysql Consistent read operations in are divided into snapshot read and current read .
- Snapshot read is through MVCC Realization , The current read is realized by locking .
- Read the snapshot : What is read is not necessarily the latest data , But a snapshot of historical data .
- The current reading : For reading before writing , That is, the data will be updated immediately after reading the data . Naturally, the update must be updated on the latest data , If you update old data , It is very likely that there will be problems such as lost updates . The current reader will lock the read data , Then update . If the data has been locked by other transactions ( That is, other transactions are operating on these records ), Then the transaction must wait until the lock of the data is obtained , To read and update the data .
- ordinary select All operations are snapshot reads .
- Explicitly select …lock in share mode / for update It's the current reading .
- In a transaction update \ delete And other operations are also the current read .
How to realize snapshot reading
- Before each transaction starts , Must apply to a transaction id, Business id Reflected as a hidden field in the record tx_id.
- When each transaction starts , The system will create an array for it 、 This array stores all the currently active transactions at the moment when the transaction is started id, This is called the consistency view of this transaction
- When a transaction wants to read data , The system will be based on the of each row of data tx_id Value , Judge whether this line of data is visible to the current transaction . If not visible , Just through undo file file , Back to previous version , Then judge . Go back to... Based on the data tx_id Judge , The version of the data that is visible to the current transaction , This way of reading is snapshot reading .
- The data of all versions visible to the current transaction , Is a consistent data snapshot of the current transaction .
How to realize the current read
When doing update perhaps delete\insert when , The system locks the data to be updated , If the data is locked successfully , The data can be read and updated . If the data has been locked by another transaction , Then you have to wait for other transactions to release the lock of the data .
How to achieve different transaction isolation levels
- Read uncommitted : There is no control over reading and updating . Do not use MVCC function , No locks .
- Read submitted : Snapshot reading is adopted for reading , But every read in a transaction regenerates the consistency view 、 Read the latest snapshot data . Therefore, dirty reading can be avoided 、 But there will be non repeatable situations . Lock when updating , about lock in share mode \ update \ delete It will be locked later , Therefore, there will be no loss of the first type of updates .
- Repeatable : Snapshot reading is adopted for reading , During the transaction, only the consistency snapshot at the moment of transaction startup is read , Therefore, there will be no non repeatable . In addition, a clearance lock will be added , So there will be no unreal reading . Lock when updating , No lost updates . However, the second type of update will be lost .
myisam Pseudo transaction implementation of
myisam The engine itself does not provide the function of transaction management . But you can use lock tables t_name read | write, The pseudo transaction is realized by locking the table , Isolate transactions , Achieve safe concurrent operations .
lock
- Shared lock (S): After the transaction obtains the shared lock , Only read , Can't update . Other transactions can also continue to obtain the shared lock of the same record .
The user can go through lock in share mode, Add... To the data S lock .
The user did not explicitly declare lock in share mode Of select sentence , stay innodb Internally, the transaction isolation is realized by consistent reading , Not locked . - Exclusive lock (X-eXclusion): After the transaction gets the exclusive lock , Can be updated . Other transactions cannot obtain any locks of the same record .
Users can explicitly declare for update, Add... To the data X lock .
For those who have added X Lock data , Although no other locks can be added , But it can still be done select operation , Because ordinary select The query does not need to be locked .
-
Row lock : stay innodb in , When there is an index on the query criteria , Lock some indexes individually . When there is no index , You can only lock the watch , It can cause conflict . Note that the index is locked , Not to record . So if there are multiple records under an index , Even if two transactions need to lock different records of the same index , There will still be lock conflicts .
-
Clearance lock (gap-lock): Gap means , When we make a range query , If the result set has multiple rows , Then in the range 、 A non-existent record between two adjacent rows is called “ The gap ”.innodb This gap will also be locked , It's a clearance lock (next-key lock).
In addition, when performing equal current queries and , If the record to be queried does not exist , Gap locks will also be added .
for example : One session Perform the following query :begin; select id,name from t_user where user_id=101 for update.
If this is another session Execution insert :insert into t_user values(201,…). Will wait for -
next-key lock: The combination of row lock and gap lock .
-
Table locks : When there is no index on the query criteria , Lock the whole table . lock table t1 read;– Table share lock .lock table t1 write;– Table exclusive lock
If a gap has been locked by a transaction , It does not prevent other transactions from locking the same gap , It just excludes other transactions and inserts data into the gap .
Intent locks
Intent locks are table level , Its purpose is to make the coordination between transactions more efficient .
When a transaction needs to apply a table exclusive lock to a table , First, make sure that the table is not locked by other transactions 、 Table exclusive lock 、 No records in the table are shared or exclusive locked .
Table share lock 、 Table exclusive locks are marked on the table , It is easy to directly detect whether it has been locked by other transactions .
But the lock mark of the row in the table is marked on the row , If you go line by line to check whether any lines are locked , The efficiency is very low .
The solution is to add an intention lock before adding a shared lock or an exclusive lock to the records in the table , It's equivalent to marking the table , Mark that the records in this table will be locked .
If other transactions are locked at this time , You can see that the table level intent lock mark has been marked on the table , No more special locks .
- Intention sharing lock (IS,Intention-S); It means that the transaction intends to add a shared lock to the data in the table , The transaction must obtain the data of the table before adding a shared lock to the data IS lock . yes Innodb It's automatic , Users cannot actively intervene .
- Intention exclusive lock (IX): It means that the transaction intends to add an exclusive lock to the data in the table , The transaction is adding... To the data X Before the lock , You must get the of the table first IX lock . yes Innodb It's automatic , Users cannot actively intervene .
Explicitly in sql Use in statement lock in share mode when . The intention sharing lock will be added to the qualified records . If there are no records that meet the requirements , Then a gap lock will be added between the maximum keyword less than the condition and the minimum keyword greater than the condition ?
innodb The policy used for each isolation level
- Serial reading :innodb Will be responsible for all matters select Inquire about , Are implicitly converted to lock in share mode.
- Repeatable : For... In a transaction select Inquire about , Use consistent reading , For multiple executions of the same query , Read only the snapshot of the version that is read by the query for the first time , Therefore, there will be no non repeatable . about lock read\updae\delete, Lock strategy is adopted . If where There is a unique index on the query condition after , Then only the corresponding index record is locked . If there is no unique index on the query criteria , Then use gap-lock perhaps next-record lock, To lock the index range of the scan , So there will be no unreal reading .
- Read submitted ; For... In a transaction select Read operation , Use consistent reading . For multiple executions of the same query , Each time a query is executed, the latest version of the snapshot is read from the database , That is, semi consistent reading , Therefore, there will be non repeatable . And for lock read\upate\delete, Then only row level locks are added to the data , No clearance lock , Therefore, unreal reading may occur .
Transaction submission method : Implicit And Explicit
There are two ways to commit transactions : Automatic submission and Manual submission .
Implicit transaction submission : The default method of transaction submission ,show variable like ‘%autocommit%’, It's usually ON, That is, each statement will automatically commit;
Explicit transaction commit : If the implicit transaction submission mode state does not meet the business requirements , Can pass set autocommit ON/OFF; To set the transaction submission method of subsequent statements .
Partial fallback And Reservation point (savepoint xxx)
Sometimes it is necessary to according to the actual business situation , Yes SQL Partial fallback of statement .
such as :
start transaction;
sql1;
savepoint s1;
sql2;
savepoint s2;
sql3;
savepoint s3;
...
if(...) rollback to s1; -- In some cases , The business status needs to fall back to s1 It's about , follow-up commit When submitting , Only submit sql1. Subsequent statements will not be submitted to the database .
if(...) rollback to s2; -- In some cases , The business status needs to fall back to s2 It's about , follow-up commit When submitting , Only submit sql1 and sql2. Subsequent statements will not be submitted to the database .
...
commit;
Variable
Before the system variable, use @@, Before customizing global variables, use @, Don't use anything before customizing local variables
System variables
- See all system variables :show [ global|session ] variables;
- Fuzzy query a overall situation / Current session System variables :show [ global|session ] variables like ‘tx%’;
- Accurately query a global / Current session System variables :select @@[ global|session ].var_name;
- Set up overall situation / Current session System variables :set @@[ global|session ].var_name=‘var_value’;
Custom global variables ( The scope is the current session )
- Defining variables :set @var_name=‘var_value’;
- Query variables :select @var_name;
- Using variables :update t1 set [email protected]_name;
Custom local variables ( In a custom function or stored procedure )
- Statement :declare var_name;
- assignment :set var_name=‘var_value’;
- Use :select column1 into var_name from t1 where…
data type
enum
tinyint 1 byte
smallint 2
midiumint 3
int 4
bigint 8
float 4
double 8
decimal(m,d) M+2
date 3(1000-01-01~9999-12-31) 15 position (32768)-4 position -5 position
time 3(-838:59:59~838:59:59) Sign bit 2 position ?10 position :6 position :6 position
year 1(1901~2155) 254 It's worth ,8 Who can .
datetime 8
timestamp 4(1970-01-01 00:00:00~2038-01-19 11:14:07) 1 Sign bits ,2147483647 It's worth ,
char 1-255 Customize ; If the actual length is insufficient , Make up for it
varchar 1-255 Customize : If the actual length is insufficient , No complement , The length is for qualification purposes only .
tinyBlob(255 individual )blob(65535 individual )
profiling / profiles -- Displays the most recently executed sql Time consuming , as well as sql The time-consuming of each step in the execution process ;
select @@profilling;
set @@profiling=1;
show profiles;
HELP SHOW PROFILE;
show profile all ;
show profile for query n;
When the following steps appear , Explain the need to optimize
tmp table -- A temporary table
redo log
- redo log The meaning of :redo log Can recover mysql Transactions lost due to sudden power failure of the server . It can also be used for master-slave replication .
- mysql Why does the server lose transaction data when it suddenly loses power ? Because the transaction data submitted by the client will be mysql The server is cached in the memory of the server (buffer), No immediate write to disk , Therefore, some transaction data will be lost in case of sudden power failure .
- redo log Why can we recover the data lost due to power failure ? Because every time the data is updated ,mysql At the same time, the modified data will be written to redo log in . When mysql After the server is powered off and restored , Will compare the data tx_id And redo log Medium tx_id, If any inconsistency is found, it shall be based on redo log Resubmit transaction .
- mysql Why doesn't the updated data of the transaction be written to the disk file immediately ? Every time a transaction is committed , Do it all once redo log,io once , Isn't it time-consuming ? Reduced efficiency ?
because mysql Of the data file io It's random io, Random io Every time I have to find a way 、 Rotating head , More time-consuming .
and redo log Of io In sequence io, The order io Because every time I write io Just follow the last position and continue to write down , No need to seek 、 Rotating head , Very fast . - redo log There are also buffers , Will this lead to power failure and data loss ?
redo log Implementation principle of
redo log Just make sure that transactions that are not flushed back to disk are log that will do . The way to achieve this is :redo log Fixed file size , When the file is full , Write the transaction data in the cache to disk . It's a fixed size 、 Will be constantly truncate Space .
redo log There is also a cache in memory , Every second, the data in the buffer IO To disk . Whenever a transaction is committed , It will also brush out the data in the buffer to the disk .
redo log The log file size for mysql System impact :
When setting a larger value , The order IO The number of re seek and rotation of the head is reduced , Can greatly improve the order IO Performance of . But when recovering from a failure , Due to redo log Large files increase data recovery time , Prior to mysql In the version , It will be slow , But the current version doesn't have to think about these problems anymore , You can use it at ease ,
redo log Related parameters
innodb_log_file_size:redo log Log file size
binlog
binlog Log all operations ( except select and show This kind of ), Even if the number of operation target rows is 0. If update …set … where …, Even if there is no matching record according to the query criteria , No records were recorded update, It will also be recorded .
binlog Is the function of the server layer .
binlog It's a logical log , yes sql sentence .redo log What is recorded is the physical log , Is the data .
binlog Only record one or more items after a transaction is committed sql sentence . and redo log It is written continuously during the transaction .
redo log Log writes are concurrent , Multiple transactions are in progress and are constantly writing redo log.
analize \ check \ optimize table
mysql> help ana%;
Name: ‘ANALYZE TABLE’
Description:
Syntax:
ANALYZE [NO_WRITE_TO_BINLOG | LOCAL] TABLE
tbl_name [, tbl_name] …
alter table tbx
rename as tbnewx;– Rename table name
add column cname … firset | after column_name; -- Add fields
add index idx_name(column1_name,…);– Add index
add primary key(column_name);– Add primary key
drop primary key;
drop index idx_name;
add unique idx_name(column1_name,…);– Add unique index
alter column column_name set default xx | drop default;– Set the default value , Cancel default
change column column_name column_name_new …;– Redefine a field , You can rename fields
modify column column_name …;– Redefine a field , But you can't rename
drop column column_name;– Delete a field
create table if not exists tbx_new like tbx;– Replicated table structure
create table tbx_new as select * from tbx;– Copy table contents
desc tbx
show columns from tbx;
show create table tbx;
System information function
select version(),connection_id(),database(),schema(),user(),system_user(),session_user(),current_user(),charset(str),last_insert_id();
Encryption function
password(‘pwd’),md5(‘xx’),encode(str,pswd_str)
Date time function
curdate(),curr_date(),curtime(),current_time(),now(),current_timestamp(),localtime(),sysdate(),localtimestamp();
版权声明
本文为[Li Siwei]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204210600381148.html
边栏推荐
- Xlslib use
- 12 examples to consolidate promise Foundation
- Zlib realizes streaming decompression
- The type initializer for ‘Gdip‘ threw an exception
- I just want to leave a note for myself
- Wechat video extraction and receiving file path
- Solve the problem of invalid listview Click
- SQL of contention for system time plus time in ocrale database
- FTP、ssh远程访问及控制
- Raspberry pie 18b20 temperature
猜你喜欢

【历史上的今天】4 月 23 日:YouTube 上传第一个视频;网易云音乐正式上线;数字音频播放器的发明者出生

An idea of rendering pipeline based on FBO
Esp01s with Arduino development environment
Oracle configuration st_ geometry
2022.04.23 (lc_763_divided into letter interval)
![[报告] Microsoft :Application of deep learning methods in speech enhancement](/img/29/2d2addd826359fdb0920e06ebedd29.png)
[报告] Microsoft :Application of deep learning methods in speech enhancement

Wechat applet part of the mobile phone Preview PDF did not respond
Network protocol: SCTP flow control transmission protocol
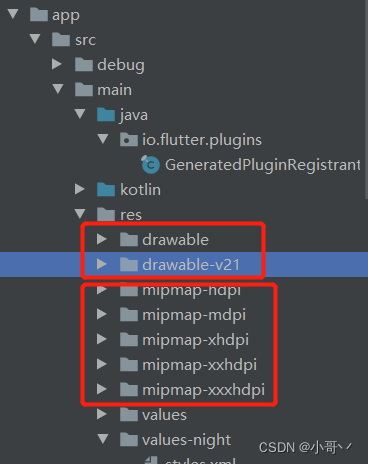
White screen processing method of fulter startup page

2022.04.23(LC_763_划分字母区间)
随机推荐
OpenHarmony开源开发者成长计划,寻找改变世界的开源新生力!
MySQL Téléchargement et installation de la version Linux
简化路径(力扣71)
SSDB foundation 3
Installation, use and problem summary of binlog2sql tool
Yyds dry goods inventory stringprep --- Internet string preparation
openlayers 5.0 离散聚合点
Openlayers 5.0 discrete aggregation points
Openlayers 5.0 two centering methods
c#:泛型反射
Simple use of viewbinding
ArcMap publishing slicing service
Simple use of navigation in jetpack
Why is PostgreSQL about to surpass SQL Server?
微搭低代码零基础入门课(第三课)
12个例子夯实promise基础
剑指 Offer II 116. 省份数量-空间复杂度O(n),时间复杂度O(n)
Wechat applet part of the mobile phone Preview PDF did not respond
Quick start to static class variables
JS controls the file type and size when uploading files