当前位置:网站首页>Application of skiplist in leveldb
Application of skiplist in leveldb
2022-04-23 15:04:00 【Mrpre】
What is jump Watch
Specific reference http://zhangtielei.com/posts/blog-redis-skiplist.html
Leveldb Why use a skip watch
First skiplist As memtable Data structure of , If light is for storage kv, Then any data structure can be used , image Redis Of dict. however LevelDB There is a characteristic , Namely put 2 A the same key, that 2 Share the same key Will exist at the same time memtable in , Instead of using new... As people usually understand value Take the old value Replace . That means ,get It is necessary to ensure that what you get is new value Not the old . here , Simple tree There is no guarantee of order .
- Be careful : LevelDB Of delete It won't delete memtable in kv Of , But and put equally , Insert nodes , Mark as yes "delete".
How to ensure the order of jump table
First , Of course, a simple jump table can only handle key In the case of numbers , But users put Of key, Must be random binary , for example “mykey”."mykey" Can't be used as a jump watch key Did you? , Not really . Because you can set the skip table “ Comparison function ” A comparison used instead of numbers .
for example ,Level Specified in the :
mykey > mykeyb
mykey < myke
mykey == mykey
Second, consider how to ensure order .LevelDB in , For each user key All give a seq, It's globally increasing . Simply describe , Deposit in Jump table key, yes “key+seq”, With seq, that “ Comparison function ” In addition to comparing the above users key outside , We need to compare seq, User input at different times key Although the same , however seq Dissimilarity , Naturally, there are different sizes .
mykey$2 > mykey$1
int InternalKeyComparator::Compare(const Slice& akey, const Slice& bkey) const {
// Order by:
// increasing user key (according to user-supplied comparator)
// decreasing sequence number
// decreasing type (though sequence# should be enough to disambiguate)
int r = user_comparator_->Compare(ExtractUserKey(akey), ExtractUserKey(bkey));
if (r == 0) {
const uint64_t anum = DecodeFixed64(akey.data() + akey.size() - 8);
const uint64_t bnum = DecodeFixed64(bkey.data() + bkey.size() - 8);
if (anum > bnum) {
r = -1;
} else if (anum < bnum) {
r = +1;
}
}
return r;
}
Find out how to ensure the latest value
Suppose the user put 了 2 Time "key", however value Different , So the second time put Of "key", Because of his seq Than the first time put Of "key" Of seq Big , natural , In the jump table, the position is in the first "key" after . hypothesis seq Namely 1 and 2, So what's stored in the jump table key by “key$1” “key$2”.
here , user get With this key, It's operated by key Of seq Must be greater than or equal to 2, The assumption is 100( For example, in the middle put Other key, indicating contrast seq Added ).
LevelDB, At this time, you will query in the skip table "key$100". because Of the query key yes “key$100”, A normal jump table must be the result of missing , Because there is only... In the jump table "key$1" and “key$2”.
Let's see how the following query function handles .
iter.Seek(memkey.data()) Perform a search , Only when Skip one of the tables kv When none of them exist ,iter.Valid() It's just NULL, Other situations ,iter.Valid() All set up . iter.key() Saved the previous search "key$100" Small jump table node . And here it is comparator_.comparator.user_comparator()->Compare This scene .
bool MemTable::Get(const LookupKey& key, std::string* value, Status* s) {
Slice memkey = key.memtable_key();
Table::Iterator iter(&table_);
iter.Seek(memkey.data());
if (iter.Valid()) {
// entry format is:
// klength varint32
// userkey char[klength]
// tag uint64
// vlength varint32
// value char[vlength]
// Check that it belongs to same user key. We do not check the
// sequence number since the Seek() call above should have skipped
// all entries with overly large sequence numbers.
const char* entry = iter.key();
uint32_t key_length;
const char* key_ptr = GetVarint32Ptr(entry, entry+5, &key_length);
if (comparator_.comparator.user_comparator()->Compare(
Slice(key_ptr, key_length - 8),
key.user_key()) == 0) {
// Correct user key
const uint64_t tag = DecodeFixed64(key_ptr + key_length - 8);
switch (static_cast<ValueType>(tag & 0xff)) {
case kTypeValue: {
Slice v = GetLengthPrefixedSlice(key_ptr + key_length);
value->assign(v.data(), v.size());
return true;
}
case kTypeDeletion:
*s = Status::NotFound(Slice());
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
In fact, the overall logic is very simple , Is to find a greater than the current seq Of the same "key". It's a search "iter.key()", Or xx$zz Either or key$yy, The former , Explain what we are searching for key Not at all , Because it's better than us key The nearest one is actually others key; If the latter , explain key$yy This seq by yy Is the most recently inserted / Delete the key.
Is it possible The order in which the jump table appears is as follows
“key$1” > “ke$1” > “key$2” > “ke$2”, If so , We search "key$100" when , The previous value may be "ke$2", This causes the search to fail . Of course, reality is impossible ," Comparison function " This is guaranteed . same "key" It must be in accordance with seq Sort of .
summary
That's why we often say LevelDB The data is in order . Just imagine , If image Redis equally , hold kv Stored in the dictionary , Then naturally there is no order . That's why LevelDB Delete as a skip table Node, All operations are in sequence .
版权声明
本文为[Mrpre]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204231409587746.html
边栏推荐
- Programming philosophy - automatic loading, dependency injection and control inversion
- Detailed explanation of C language knowledge points -- data types and variables [1] - carry counting system
- 大文件如何快速上传?
- Have you really learned the operation of sequence table?
- Introduction to distributed transaction Seata
- select 同时接收普通数据 和 带外数据
- eolink 如何助力远程办公
- 【thymeleaf】处理空值和使用安全操作符
- 分享3个使用工具,在家剪辑5个作品挣了400多
- The win10 taskbar notification area icon is missing
猜你喜欢
nuxt项目:全局获取process.env信息

1 - first knowledge of go language
你还不知道责任链模式的使用场景吗?
8.3 language model and data set
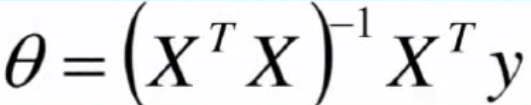
3、 Gradient descent solution θ

Swift - literal, literal protocol, conversion between basic data types and dictionary / array
![[NLP] HMM hidden Markov + Viterbi word segmentation](/img/9a/b39a166320c2f2001f10913f789c90.png)
[NLP] HMM hidden Markov + Viterbi word segmentation

Daily question - leetcode396 - rotation function - recursion
Detailed comparison between asemi three-phase rectifier bridge and single-phase rectifier bridge
Comment eolink facilite le télétravail
随机推荐
Select receives both normal data and out of band data
Mds55-16-asemi rectifier module mds55-16
Go basic reflection
3、 Gradient descent solution θ
大文件如何快速上传?
帧同步 实现
Five data types of redis
Llvm - generate addition
Swift protocol Association object resource name management multithreading GCD delay once
LeetCode 练习——396. 旋转函数
小红书 timestamp2 (2022/04/22)
Comment eolink facilite le télétravail
Bingbing learning notes: take you step by step to realize the sequence table
Ffmpeg installation error: NASM / yasm not found or too old Use --disable-x86asm for a clipped build
Detailed explanation of C language knowledge points -- data types and variables [1] - carry counting system
like和regexp差别
epoll 的 ET,LT工作模式———实例程序
Thinkphp5 + data large screen display effect
买卖股票的最佳时机系列问题
asp. Net method of sending mail using mailmessage