当前位置:网站首页>IO流和序列化与反序列化
IO流和序列化与反序列化
2022-08-11 05:30:00 【zhangkai__】
java中I/O流关键点总结
1.File类
1.1 文件封装File对象
//将文件封装为一个File类的对象(3种引入写法)
File f = new File("d:\\test001.txt");
File f2 = new File("d:/test001.txt");
File f3 = new File("d:"+File.separator+"test001.txt");
File f4 =new File("D:\\a");
File f5 =new File("D:\\a\\b\\c");
//创建目录
f4.mkdir();//创建单层目录
f5.mkdirs();//创建多层目录
//删除 只能是空目录,有内容则不删除
f4.delete();
2.I/O流
2.1 IO流理解
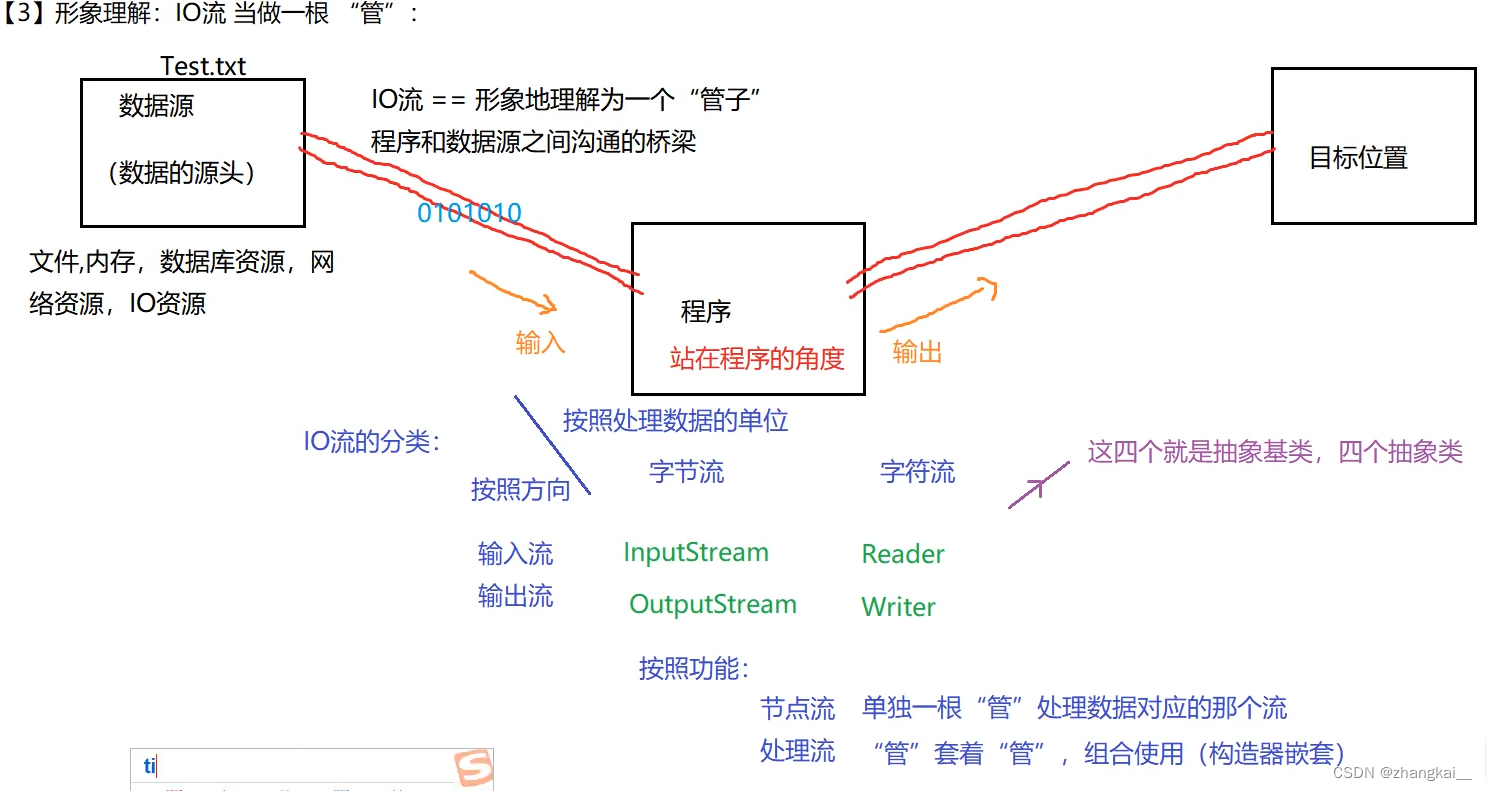
IO类可大致分为如下多种:其中黄色为常用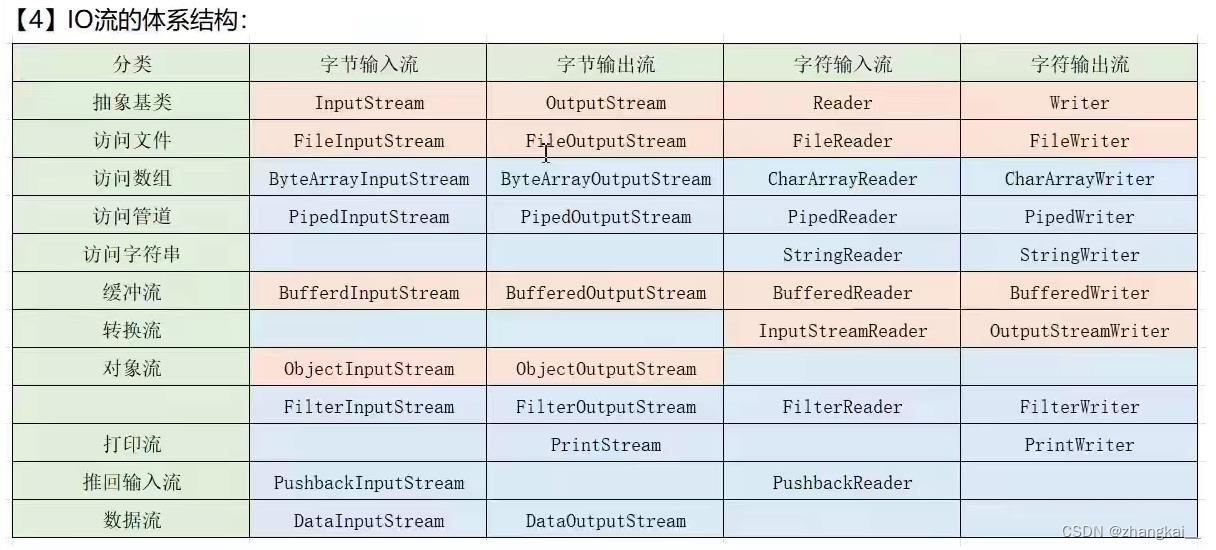
2.2 文件读入
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建一个File类的对象
File f =new File("d:/test001.txt");
//利用FileReader类 将程序和源文件进行管道连接-->创建FileReader流对象
FileReader fr = new FileReader(f);
//进行程序读取(单个字符)
fr.read();
int n;
n=fr.read();
System.out.println(n);
//引入多个字符
char [] ch =new char[5];
int len = fr.read(ch);
while (len!=-1){
//len 用来一次装填定量的元素
for (int i =0;i<len;i++){
System.out.println(ch[i]);
}
//len重新放入后面的字符
len=fr.read(ch);
}
//连接管道不用就关闭
fr.close();
}
2.3 文件写出
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//引入一个文件
File f=new File("d:/test002.txt");
//FileWriter连接源文件和程序管道
FileWriter fw =new FileWriter(f);
//通过程序给源文件写入信息
String str="232哈哈";
for (int i=0;i<str.length();i++){
fw.write(str.charAt(i));
}
//追加信息
FileWriter w =new FileWriter(f);
String sr="zhongsg";
char [] da =sr.toCharArray();
fw.write(da);
//关闭流
fw.close();
}
注:文件不存在,那么自动创建文件
文件存在,FileWriter(f) 相当于源文件进行覆盖操作;
FileWriter(f,false) 相当于源文件进行覆盖操作,不是追加;
FileWriter(f,true) 对来原来的文件进行追加,而不是覆盖。
2.4 文件复制
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//一个源文件,一个目标
File f=new File("d:/test001.txt");
File f2=new File("d:/test003.txt");
//输入通道
FileReader fr=new FileReader(f);
//输出通道
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter(f2);
//进行复制
fw.write(fr.read());
char[] ch=new char[5];
int len =fr.read(ch);
while(len!=-1){
String s=new String(ch,0,len);
fw.write(s);
len=fr.read(ch);
}
//关闭通道
fw.close();
fr.close();
注:这里有可能出现复制中文出现异常,原因是在于创建文件时的类型默认ANSI类型,应该改成UTF-8类型。
打开文件另存为—>最下方有选择编码—>UTF-8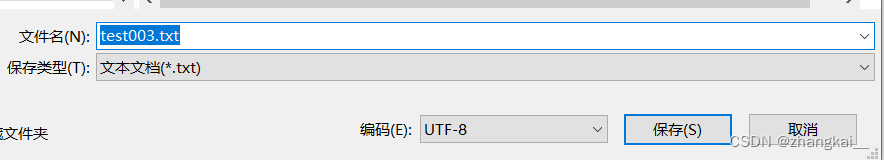
3.FileInputStream,FileOutputStream类
- 当文件是UTF-8进行存储时,其中英文字符占用1个字节;中文字符占用3个字节;
- 所以当文件是文本文件时,不建议使用字节流;因为会将字符拆开,失去意义;
- 字节流对象.read()方法读取字符返回int类型而不是byte类型,是因为底层做了处理,让返回数据都是“正数”,避免出现-1的情况,与结束条件(fr.read()!=-1)重合。
4.处理流
4.1BufferedIuputStream,BufferedOutputStream类 字节流
4.1.1 原理
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-irMZjrym-1655126465738)(C:\Users\Administrator.DESKTOP-G8VK4LM\Desktop\markdown\图片资源\处理流BufferedReader.jpg)]](/img/e1/f733d18cba9c123362307c4db8562d.jpg)
4.1.2 注意点
- 相当于建立缓冲区进行存储,在FileInputStream, FileOutputStream外,再套一层流(多重管道)。
- 关闭流操作时,只需要关闭高级流,则内部流也会随之关闭。高级流在外部。
- 若存储数据量大于初始设定缓冲区8192时,底层自动将全部内部推送至目标文件,缓冲区清空
4.2 BufferedReader,BufferedWriter类 字符流
4.2.1 读取操作
方式1:一个字符一个字符读
方式2:利用缓冲数组
方式3:读取字符串String
利用readLine()方法一行一行读
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.源文件
File f=new File("test001.txt");
//2.目标文件
File f2=new File("Tesst004.txt");
//3.流管道
FileReader fr=new FileReader(f);
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter(f2);
//4.处理缓存流套管道
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(fr);
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(fw);
//5.读取写出
//5.1一个一个读
int n=br.read();
while (n!=-1){
bw.write(n);
n=br.read();
}
//5.2缓存数组
char[] ch=new char[30];
int len=br.read(ch);
while (len!=-1){
bw.write(ch,0,len);
len=br.read(ch);
}
//5.3 读取String:
String str=br.readLine();//每次读取一行数据
while(str!=null){
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();//补充换行
str=br.readLine();
}
//6.关闭流
bw.close();
br.close();
5.转换流
5.1 定义
InputStreamReader ,OutputStreamWriter
将字节流和字符流进行转换,属于字符流。
5.2 转换过程
将字节转换为字符时,需要指定一个编码格式,如:UTF-8,GBK这个编码要和文件本身的编码格式相同。
文件(字节)---->(字节流)---->(转换流)---->(字符)程序
程序(字符)---->(转换流)---->(字节流)---->(字节)文件
6.System类对IO流的支持

7.序列化与反序列化
实在写不动了,直接上笔记吧。。。

- 接上,static,transient修饰的属性不可以被序列化,但是其所在类不受影响,只是这些修饰属性反序列化不出来。
最后
Idea中的序列化标识码serialVersionUID的设置见:
添加链接描述
文章中图片引用赵珊珊老师讲课视频,仅作学习使用,感谢<^_^>
边栏推荐
- 星盟-pwn-babyheap
- Day 77
- ARM assembly instruction ADR and LDR
- Day 85
- Fourth Paradigm OpenMLDB optimization innovation paper was accepted by VLDB, the top international database association
- Goldbach's conjecture and the ring of integers
- Thesis unscramble TransFG: A Transformer Architecture for Fine - grained Recognition
- nepctf Nyan Cat 彩虹猫
- mysql basic summary
- 何凯明新作ViTDET:目标检测领域,颠覆分层backbone理念
猜你喜欢
实时特征计算平台架构方法论和基于 OpenMLDB 的实践
2021年vscode终端设置为bash模式
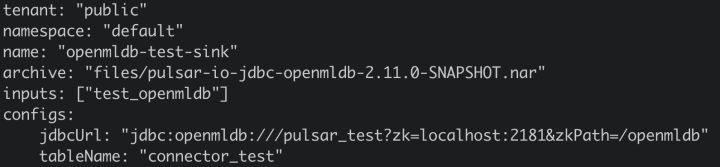
Wonderful linkage | OpenMLDB Pulsar Connector principle and practical operation
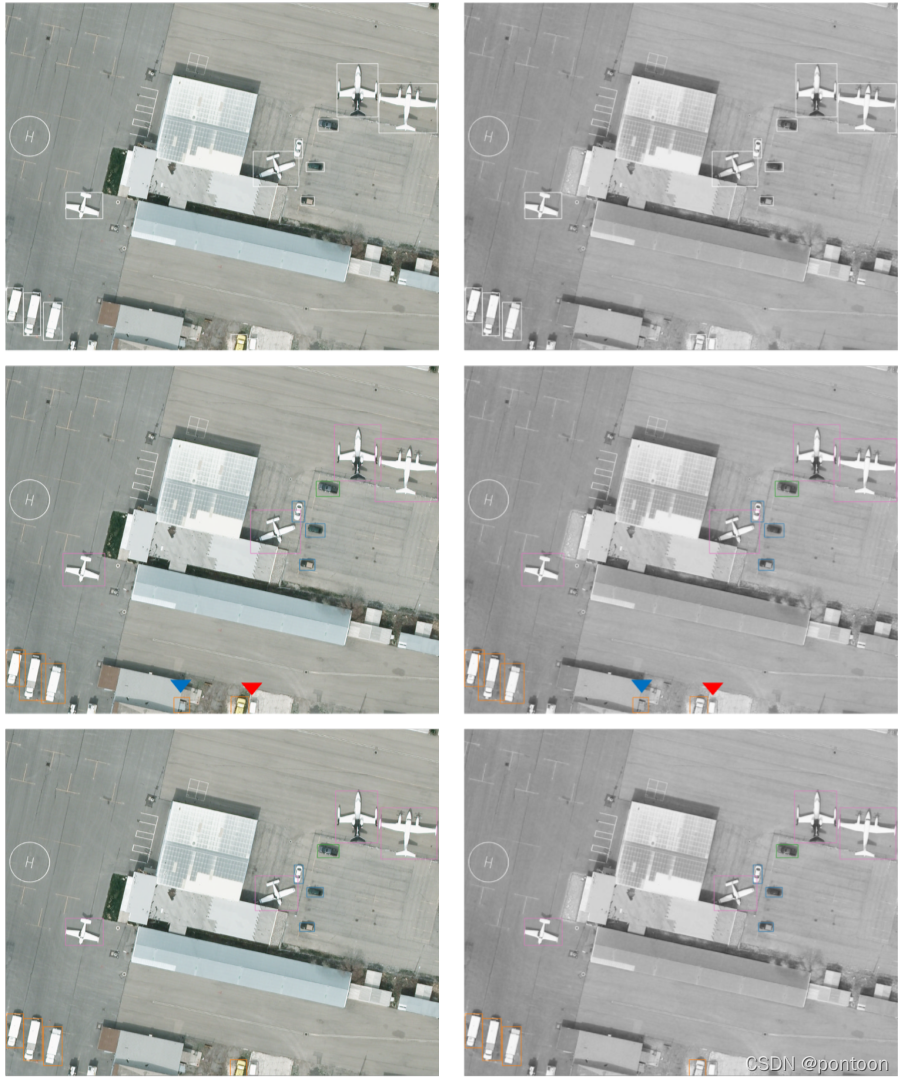
Interpretation of the paper: Cross-Modality Fusion Transformer for Multispectral Object Detection
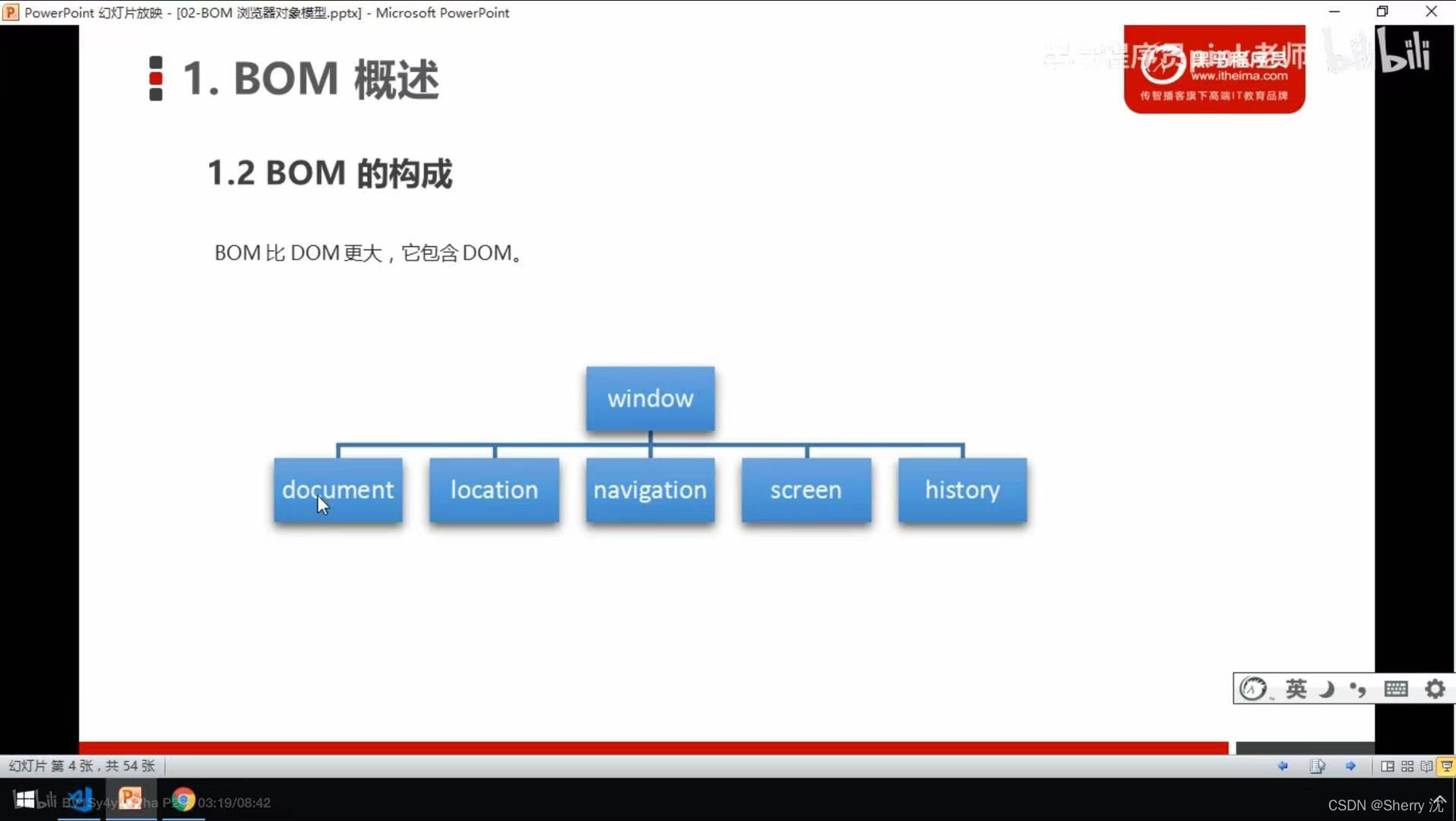
js learning advanced BOM part (pink teacher notes)

开源机器学习数据库OpenMLDB贡献者计划全面启动
何凯明新作ViTDET:目标检测领域,颠覆分层backbone理念
Visual studio2019 configuration uses pthread
mk文件介绍
Day 75
随机推荐
使用adb命令管理应用
第六届蓝帽杯 EscapeShellcode
Day 79
He Kaiming's new work ViTDET: target detection field, subverting the concept of layered backbone
Jetpack's dataBinding
Day 67
Day 81
JS事件循环机制
端口的作用
The whole process of Tinker access --- configuration
精彩联动 | OpenMLDB Pulsar Connector原理和实操
哥德巴赫猜想与整数环
Goldbach's conjecture and the ring of integers
The official website of OpenMLDB is upgraded, and the mysterious contributor map will take you to advance quickly
Day 82
品优购项目实战笔记
Scene-driven feature calculation method OpenMLDB, efficient implementation of "calculate first use"
C language implementation guess Numbers (with source code, can be directly run)
JVM tuning and finishing
Day 73